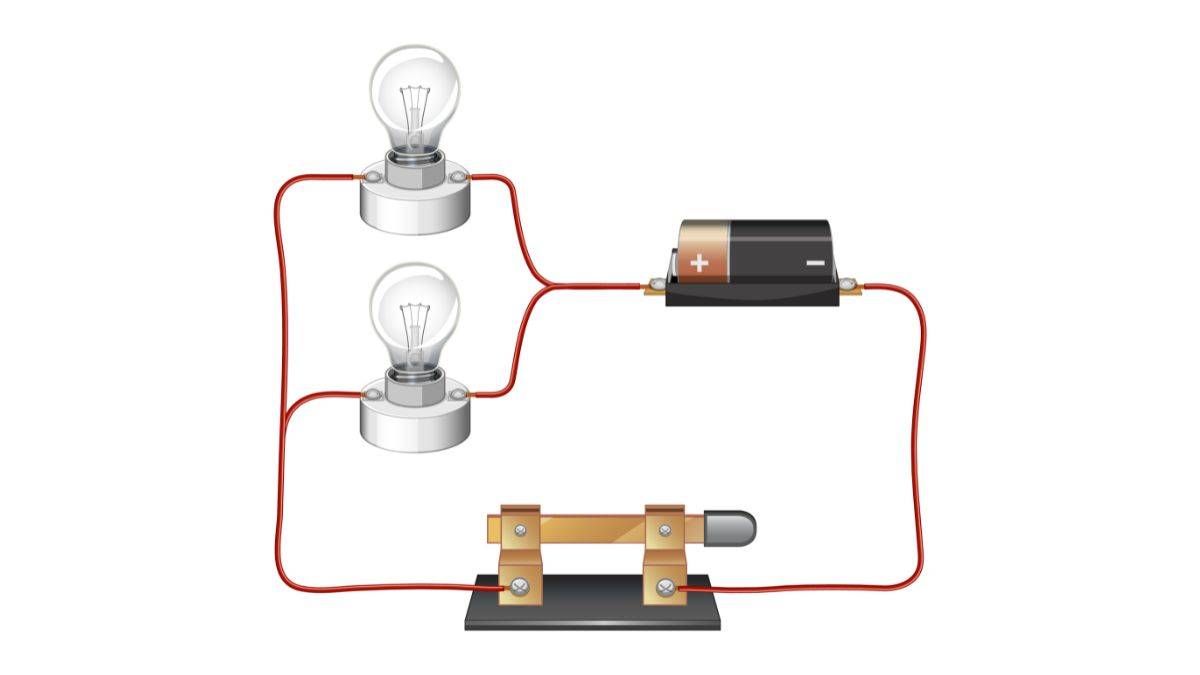
Understanding electric current is not only important for engineers and scientists but also for those who want to learn how the world around us operates. This lesson explains electric current, the requirements for the flow of current, and the various effects it produces.
Those who are currently in class 12th and starting out with the chapter Current electricity, will first understand what exactly is electric current. CBSE board also ask questions related to electric current, which makes it an important topic for students.
- What are the Conditions To Ensure Current Flow in Conductors?
- What is Electromotive Force (EMF)?
- What are the Properties of Electric Current?
What are the Conditions To Ensure Current Flow in Conductors?
JEE Main exam and NEET entrance exam aspirants must be well aware of the conditions that ensure current flow. For electric current to flow within a conductor, the following conditions must be fulfilled:
- Free Charge Carriers: Conductors must have free charge carriers, like electrons, that can freely move within the material.
- Closed Circuit: The conductor must be part of a closed circuit, providing a complete path for the current to flow.
- Potential Difference: A potential difference (voltage) must be there across the conductor. This voltage pushes the charge carriers through the conductor.
What is Electromotive Force (EMF)?
For IIT JAM exam and GATE exam students, many questions based on the EMF are important. Therefore, understanding what it means as well as its mathematical expression is important. EMF is energy per unit charge that is converted from non-electrical form (like chemical/mechanical energy) into electrical energy within a circuit. It is the force that causes current to flow. EMF is measured in volts. It is provided by sources such as batteries and generators. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
Here,
- is the electromotive force in volts
- dW is the infinitesimal amount of work done (energy) in joules (J)
- dq is the infinitesimal amount of charge flowing
What are the Properties of Electric Current?
Electric current has the following properties that IISER exam aspirants must be well aware of:
- Electric current flows from positive to negative direction in conventional current flow.
- The magnitude of electric current can fluctuate and it is measured in amperes.
- As per Ohm's Law, the electric current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied and it is inversely proportional to the resistance of a conductor.
Physics Current Electricity Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Cells in Series and Parallel
- Kirchhoffs Law
- Ohms Law
- Wheatstone Bridge
- Overview
- Electric Current in Conductors
- Resistivity of a Material
- Limitations of Ohm's Law
- Electric Current
- Temperature Dependence of Resistivity
- Cells, EMF, Internal Resistance
- Electrical Energy and Power
- Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter