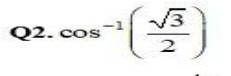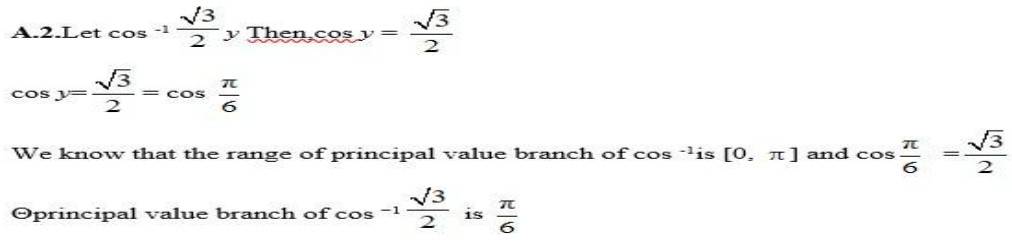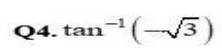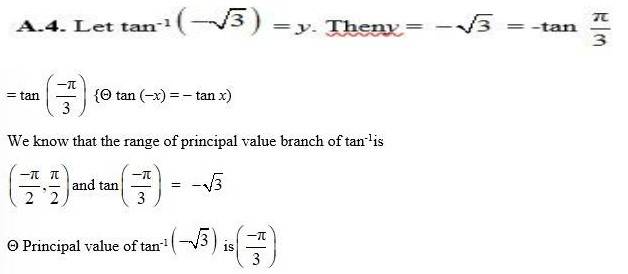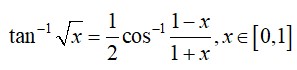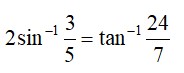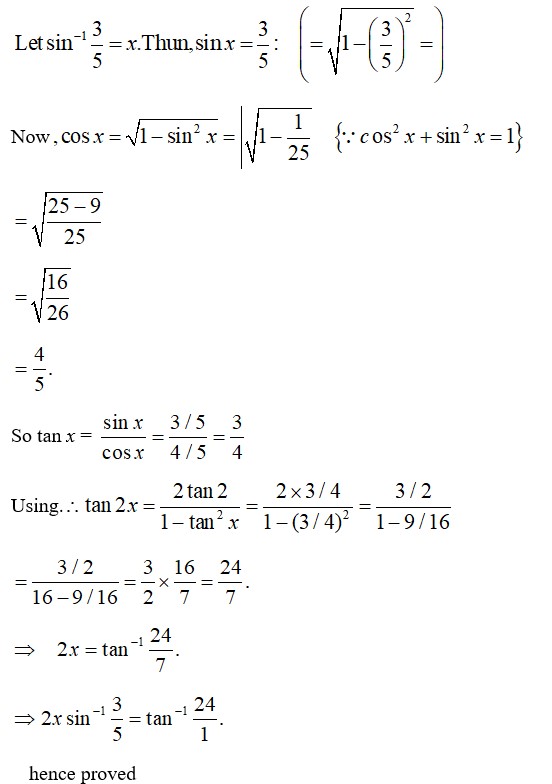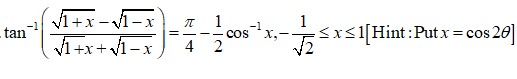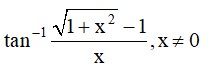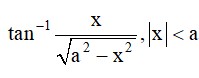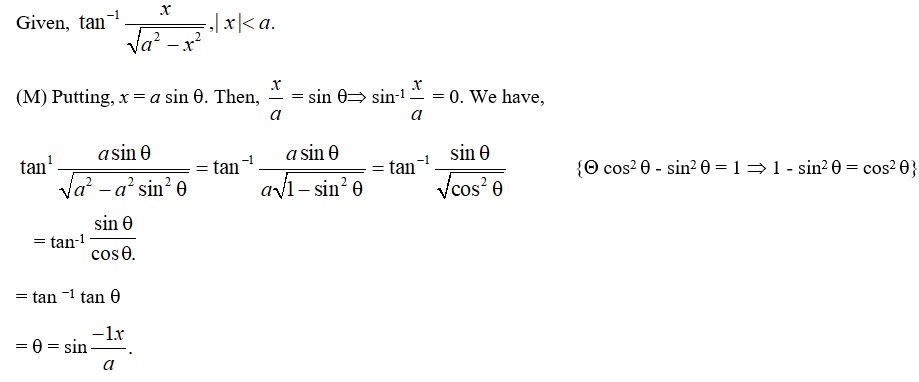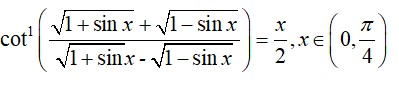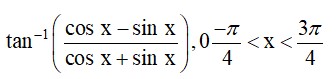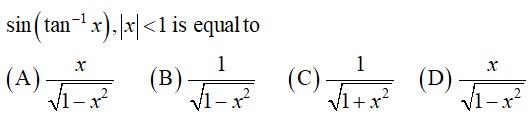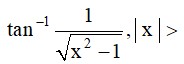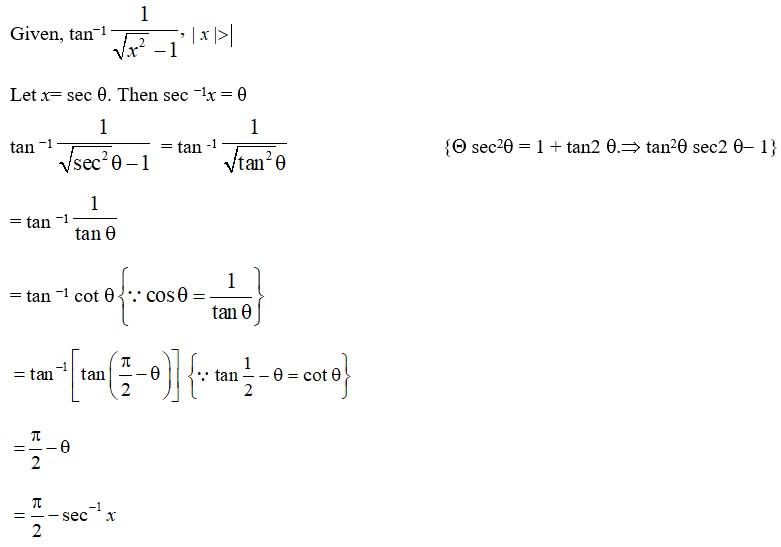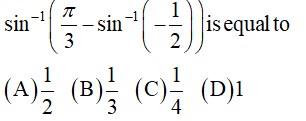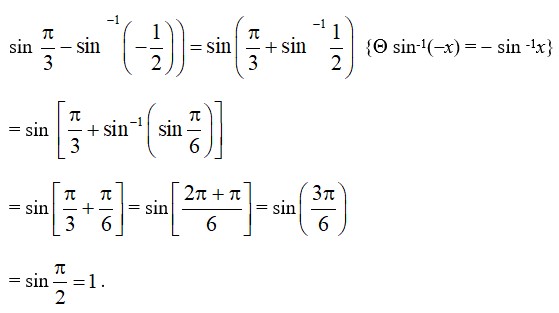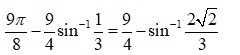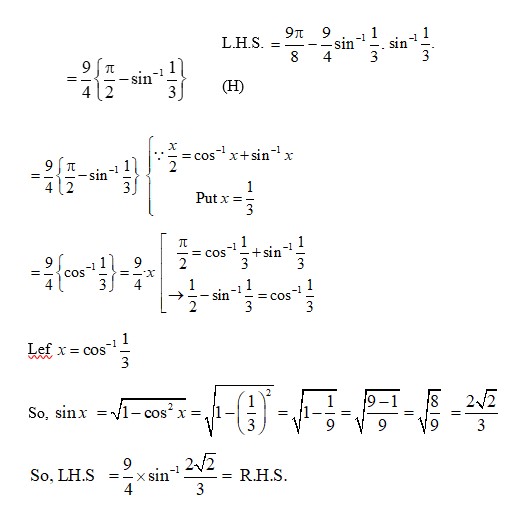Inverse Trigonometric Functions in Class 12 is important for students preparing for the CBSE Board exams and other entrance tests, such as JEE Mains. The concepts covered in the Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 chapter are also used in science and engineering. The inverse trigonometric functions are also important in calculus.
Inverse Trigonometry Class 12 covers the basic concepts and the properties of the inverse trigonometric functions. Students must thoroughly study the NCERT solutions to understand the concepts, improve their problem-solving skills, and be confident to appear in their examinations. The solution will help students in solving even the most complex problems of the chapter.
Explore here the comprehensive NCERT solutions of the Class 11 and Class 12 for all three subjects - Maths, Physics, and Chemistry. The solutions are given in a step-by-step format.
- Key Concepts of Trigonometric Functions – Class 12 at a Glance
- Class 12 Maths Ch 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions – NCERT Solutions PDF
- Inverse Trigonometric Function Exercise-wise NCERT Solutions
- Class 12 Math Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Function Exercise 2.1 Solutions
- NCERT Class 12 Math Chapter 2: Key Topics, Weightage
- Important Formulas of Inverse Trigonometry Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Inverse Trigonometric Functions- FAQs
Key Concepts of Trigonometric Functions – Class 12 at a Glance
Find below an overview of the Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12:
Here is a table showing the domains and ranges of inverse trigonometric functions:
| Functions | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
| [–1, 1] | ||
| [–1, 1] | [0, π] | |
| R – (–1,1) | ||
| R – (–1, 1) | ||
| R | ||
| R | (0, π) |
Get the Class 12 Maths NCERT Solutions here. It will provide all the important topics for concept clarity, chapter-wise weightage information and free PDFs.
Class 12 Maths Ch 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions – NCERT Solutions PDF
Shiksha provides the free Inverse Trigonometry Class 12 PDF link below. Students must download it and practice from it to score well in the CBSE Board exams and other competitive exams.
Class 12 Math Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Function Solution: Free PDF Download
Related Links
| NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 | NCERT Class 12 Notes | Class 12 Maths Notes PDF for CBSE Exams |
Inverse Trigonometric Function Exercise-wise NCERT Solutions
Inverse Trigonometric Function is an essential topic for building foundational trigonometric concepts. Chapter 2 Class 12 Math Inverse Trigonometric Function deals with the properties, domains, and ranges of inverse trigonometric functions. The ITF concepts also play a vital role in calculus, Matrices, Determinants, and other important physics and Math concepts and real-world applications. Students can check the exercise-wise Chapter 2 ITF math solutions below;
Class 12 Math Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Function Exercise 2.1 Solutions
Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Function Exercise 2.1 focuses on problems finding principal values, range, domain, and co-domain. Chapter 2 ITF Exercise 2.1 includes 14 Questions (12 Short Answers, 2 MCQs) primarily based on finding the values of inverse trigonometric functions. Students can check the complete the exercise 2.1 solutions below;
Inverse Trigonometric Function Exercise 2.1 Solutions
Find the principal values of the following:
| Q1. |
| A.1. Let sin−1 =y. Then, sin y=- We know that the range of principal value branch of sin−1 is and sin−1
=
Principal value of sin−1
|
Commonly asked questions
33.
Cos-1 cos
(M) As
cos-1
= cos-1
=
So, option B is correct
15.
We know that.
sin 3θ =3 sin θ 4sin3θ (identity).
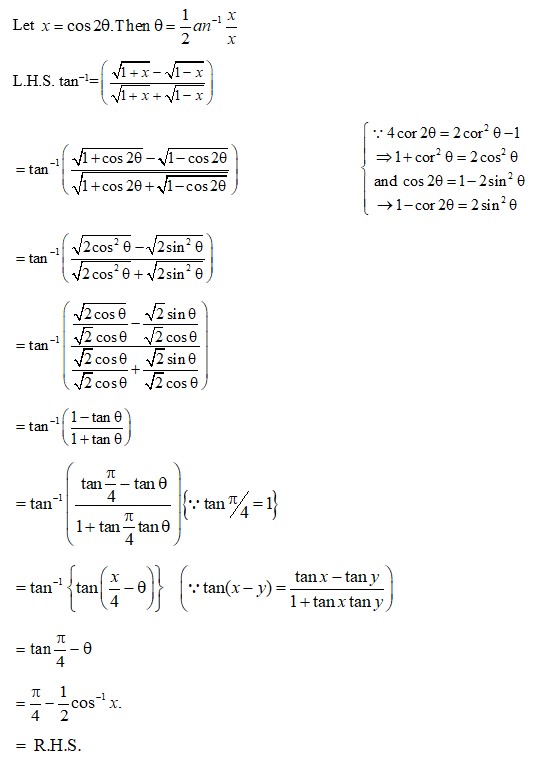
(E) Let x = sinθ. Then, sin −1x=θ . We have,
Sin3 (sin −1x) = 3x−4x3
3sin −1x =sin-1 (3x−4x3)
Hence proved.
42.
Let
Then,
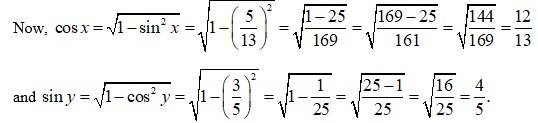
So,
Using
tan
Hence proved.
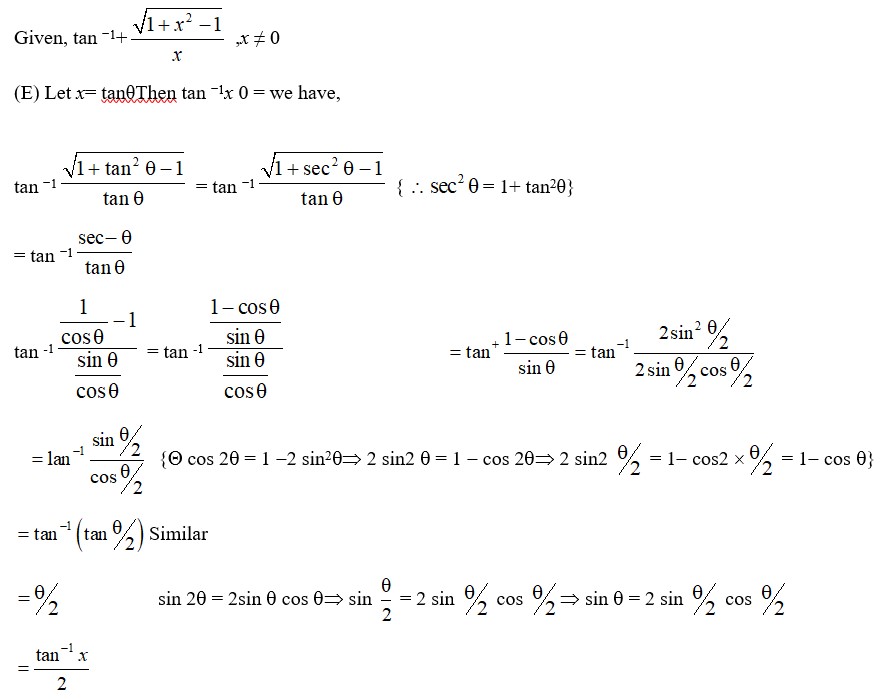
44. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
31.
(M). As
=
38. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
Solve the following equations:
48.
Given,
11.
tan−1 (1) + cos−1
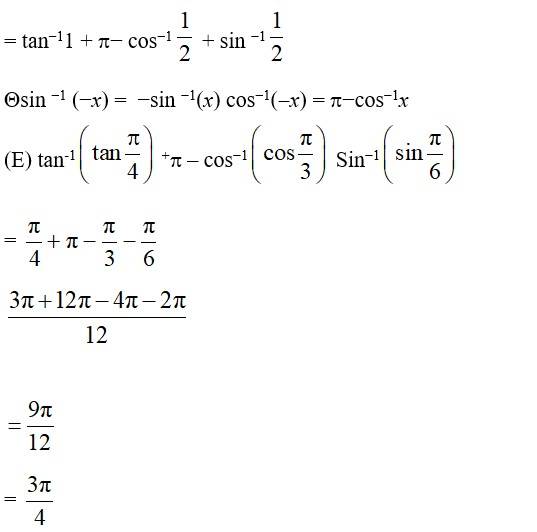
39.
Let
(N. then,
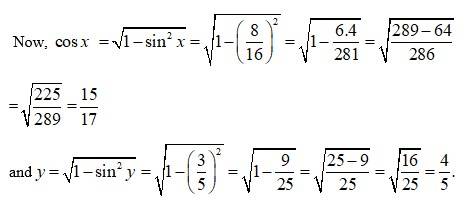
So,
Using.
tan
sin-1
Hence proved.
46. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
17.
L.H.S = tan -1
Using tan -1x+ tan -1y= tan -1
L.H.S =tan -1
tan -1
20. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
52.
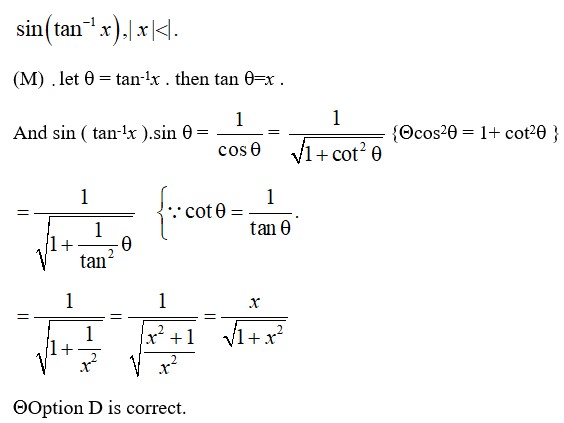
Option C is correct.
28.
(E)
= x =
Find the values of each of the following:
25.
(E)
36.
Cos-1
=
=
24. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
45. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
27.
(M) Let x = tanØ . then tan-1x= 0 and y = tan ω then tan-1y = ω. we have,
tan
=
49.
Given, (M)
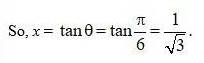
23. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
50. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
1.
Let sin−1
We know that the range of principal value branch of sin−1 is
and sin−1
=
Principal value of sin−1
12.
cos−1
=
=
=
13.
Given, Sin−1x=y.
(E) We know that the principal value branch of Sin−1 is
Option B is correct.
5.
Let cos -1
= cos
= cos
branch of cos−1 is [0,
Principal value of cos−1
26.
cot
(E)
29.
(E)Using
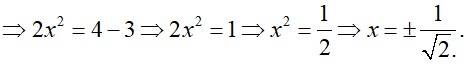
Find the values of each of the expressions in Exercises 16 to 18.
30.
(M) As
16.
We know that,
cos3θ= 4cos3θ - 3cosθ
Letx = cosθ Then θ = cos-1x. We have,
Cos3 (cos-1x) = 4x3-3x
3cos-1x = cos-1 (4x3- 3x)
Hence Proved
18.
L.H.S= 2 tan -1
(E) Using2 tan -1x= tan -1
L.H.S = tan -1
= tan -1
= tan -1
= tan -1
= tan -1
= tan -1
34.
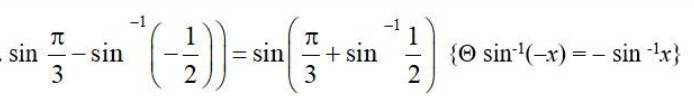
= sin
= sin
= sin
14.
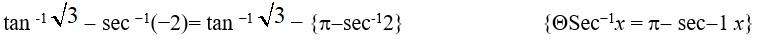
=tan−1
=
=
=
Option B is correct.
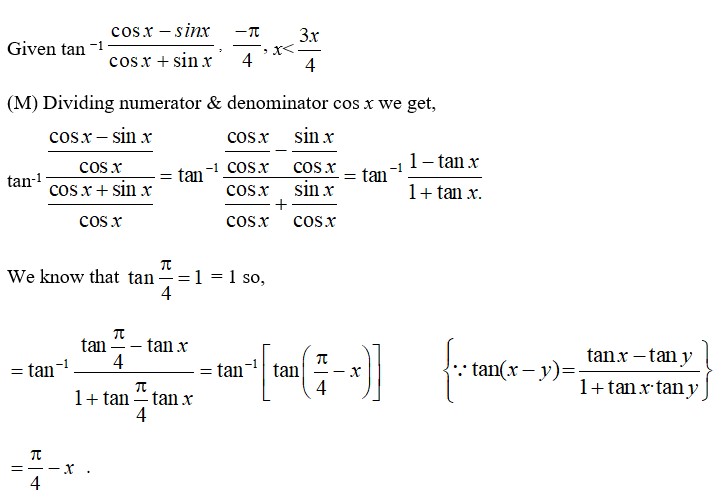
22.
Given tan -1
(M) Dividing numerator & denominator cos x we get,
tan -1
We know that
32.
(M) Let
Then
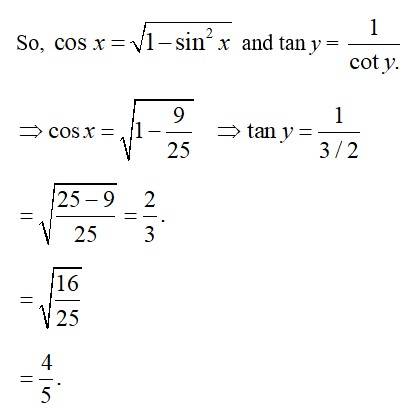
Hence, tan x =
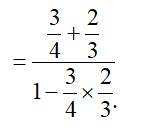
37.
40.
Let cos-1
Then,
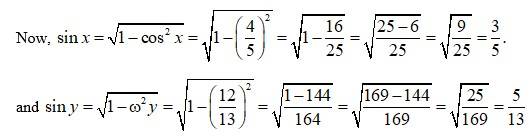
Using
41.
Let
Thin,
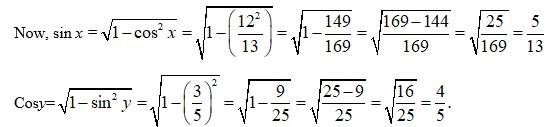
Using
43.
LH.S
=
51.
(M) Let
Putting this in
Putting
L.H.S
So,
Option (c) is correct.
21. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
35. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
47. Kindly Consider the following
Kindly go through the solution
NCERT Class 12 Math Chapter 2: Key Topics, Weightage
In the Inverse Trigonometry Class 12, students should practice the graphs, properties, and domain/range of inverse trigonometric functions. See below the topics covered in this chapter:
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 2.1 | Introduction |
| 2.2 | Basic Concepts |
| 2.3 | Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions |
Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 Weightage in JEE Mains
| Exam | Weightage |
|---|---|
| JEE Main | 2% to 3% |
Important Formulas of Inverse Trigonometry Class 12
Inverse Trigonometric Function Important Formulae for CBSE and Competitive Exams
Basic Properties
-
sin − 1 ( − x ) = − sin − 1 ( x ) , x ∈ [ − 1 , 1 ] \sin^{-1}(-x) = -\sin^{-1}(x), \quad x \in [-1, 1] -
cos − 1 ( − x ) = π − cos − 1 ( x ) , x ∈ [ − 1 , 1 ] \cos^{-1}(-x) = \pi - \cos^{-1}(x), \quad x \in [-1, 1] -
tan − 1 ( − x ) = − tan − 1 ( x ) , x ∈ R \tan^{-1}(-x) = -\tan^{-1}(x), \quad x \in \mathbb{R} -
cot − 1 ( − x ) = π − cot − 1 ( x ) , x ∈ R \cot^{-1}(-x) = \pi - \cot^{-1}(x), \quad x \in \mathbb{R} -
sec − 1 ( − x ) = π − sec − 1 ( x ) , ∣ x ∣ ≥ 1 \sec^{-1}(-x) = \pi - \sec^{-1}(x), \quad |x| \geq 1 -
csc − 1 ( − x ) = − csc − 1 ( x ) , ∣ x ∣ ≥ 1 \csc^{-1}(-x) = -\csc^{-1}(x), \quad |x| \geq 1
Domain and Range of ITF
| Function | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sum and Difference Formulas
-
sin − 1 x + cos − 1 x = π 2 , x ∈ [ − 1 , 1 ] \sin^{-1}x + \cos^{-1}x = \frac{\pi}{2}, \quad x \in [-1, 1] -
tan − 1 x + cot − 1 x = π 2 , x ∈ R \tan^{-1}x + \cot^{-1}x = \frac{\pi}{2}, \quad x \in \mathbb{R} -
sec − 1 x + csc − 1 x = π , ∣ x ∣ ≥ 1 \sec^{-1}x + \csc^{-1}x = \pi, \quad |x| \geq 1
NCERT Solutions for Inverse Trigonometric Functions- FAQs
Students can access few of the frequently asked questions below;
Maths Ncert Solutions class 12th Exam