As we read about Electric Flux Class 12, we slowly begin to move into the territory of electromagnetism. It’s the primer to learning Gauss’ Law.
Electric flux is why we can remember for CBSE boards that the denser field lines pass through an area, the greater will be the flux at the area’s surface.
What you’ll learn today in this article on electric flux at the Class 12 level:
- Learn the electric flux definition with maths formation and what combining area vector and electric field concepts results in.
- Draw the connection between total electric flux and Gauss' Law with units. That’s how you get better at practising Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions.
- How electric flux can be characterised in physics for applying to real-life calculations.
- Flux Meaning in Physics: How to Understand Electric Flux Class 12
- What is Electric Flux Class 12?
- How Many Types of Electric Flux Are There?
- Electric Flux Formulas Class 12
- Electric Flux Units in Class 12
- Electric Flux and Gauss Law: How They’re Related
- Properties of Electric Flux Class 12 Level
- What Type of Electric Flux Questions Should You Prepare For?
- Complete Class 12 Study Material: PCM
Flux Meaning in Physics: How to Understand Electric Flux Class 12
The flux meaning in physics tells us about how much of any physical quantity passes through a surface. And this is how we understand electric flux too. It tells us how many electric field lines pass through a surface wherever there is an electric field.
Now comes the bigger question of how do we even measure something which we cannot see?
It’s like saying that wind is blowing everywhere and you have a flat sheet, and you need to measure how much of the sheet’s surface is catching the air.
And most importantly, what should we even measure? The strength, yes, that tells us the electric field magnitude. We use E, sometimes with a vector sign on top. But what if we change the direction or orientation of the sheet?
Now think this sheet is directly against the direction of the wind blowing and compare that position to when you turn the sheet parallel to the direction. In the first instance, the flow will be too much. In the second example, the wind will just flow through it and not against it.
This is the same way we should approach the calculation of those imaginary field lines crossing through a surface.
We not only look at strength or how strong the electric field is, much like the wind hitting the sheet. There is another factor, ie., how the surface is positioned, just as how the sheet and wind interact.
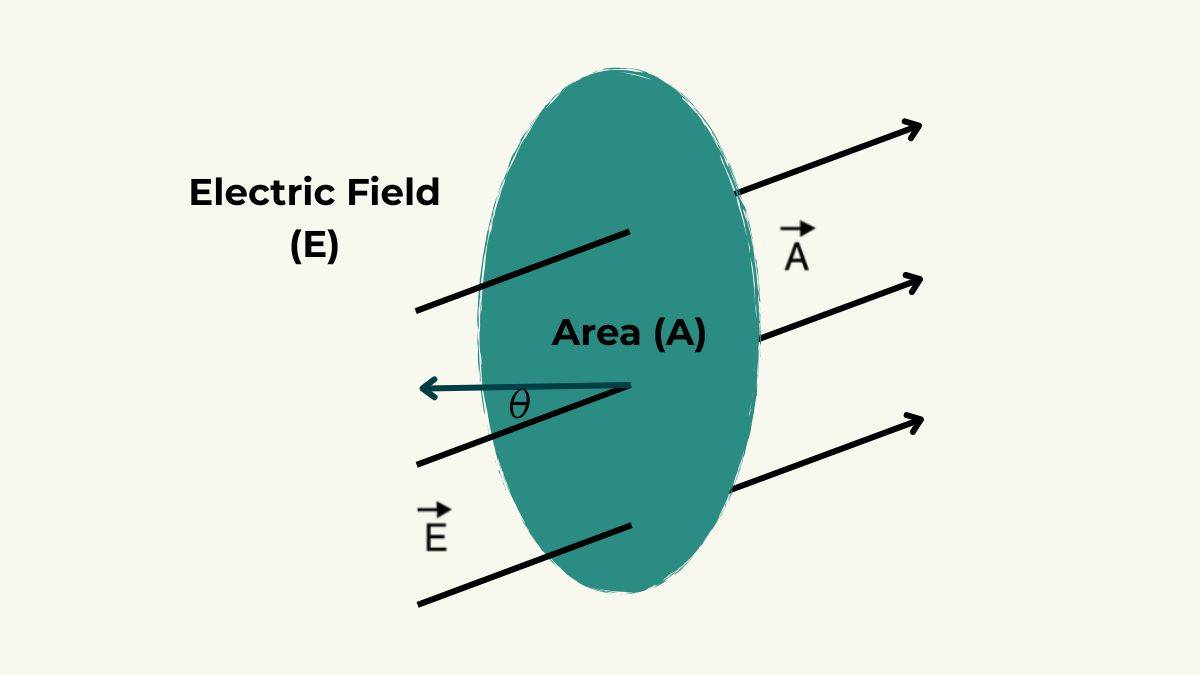
The terms in physics and maths become a little more nuanced as you know. We define the surface direction as something that a vector quantity would be defined as. That’s where we would introduce the concept of an area vector, which has the A symbol.
The area vector needs to have a magnitude like the size or area of the surface. Now for direction, we just choose the direction of the line that exists perpendicular to the surface plane, which is called normal (n). The direction of the area vector is the direction along the normal to the surface.
More precisely we can come to a correct understanding of how much electric flux there is. The amount of flux will totally depend on the angle that’s between the electric field lines (E) and this normal line lying perpendicular.
This means the amount of flux depends on the angle (θ) between the electric field lines (E) and this perpendicular normal line (A).
As you understand these aspects, it gets easier to define electric flux.
What is Electric Flux Class 12?
Electric flux measures how many electric field lines are passing through a surface. Its formula uses the strength of the field through the electric field vector (E). Then it takes the area vector (A) to account for how the surface orientation could be like.
Electric flux is shown as phi or Φ_E, which we form by using the dot product of two vectors, namely the electric field and area. This summarises both magnitude and directional effects. The result is then a scalar quantity.
The formula for electric flux would be
Φ_E = E. A = EAcosΘ
Why are we including the theta symbol at all here, and why cos instead of sin?
In the electric flux formula we need to add the theta symbol to signify the angle that tells us what the orientation of the surface is and how that is relative to the direction of the electric field.
For those of you who may get blind-sided with the usage of cos and sin, just remember we are considering the lines flowing through the area and not along the area.
CosΘ shows us only one part of the electric field that remains perpendicular to the surface. SinΘ picks the other part of the field that runs along the surface. Not through it. So if field lines are going along the surface, they won’t really add to the flux which would not make the calculation correct.
Take a quick look at these scenarios to see why sin doesn’t work and cosine does.
- If the electric field remains exactly parallel to the surface we would have θ = 90 degrees and then using cos 90 degrees would be zero. That means there will be no electric flux.
- Let’s take sin 90 degrees, which equals one. This situation tells us the amount of line passing along the field’s surface, but not through it. That does not contribute to the flux.
- But when the field line is exactly perpendicular to the surface, ie., θ = 0 degree. So cos 0 degree equals one, and that’s the maximum amount of field passing through. Here electric flux is at the maximum.
- Now if the angle again is 0 degree and we take sin 0 degree, that equals zero. What this means, there is no field present on the surface.
How Many Types of Electric Flux Are There?
This is a broad question in general, as we can consider physics as a subject that makes us think and use many relative perspectives in the real world. So based on the nature of the surface, we can stick to saying electric flux is of two types:
- Electric Flux through a Closed Surface: It’s the total electric flux that passes through a fully covered surface, usually enclosed. This type is usually necessary to understanding Gauss Law.
- Electric Flux through an Open Surface: Just the opposite, where the surface is not forming a closed boundary and is uneven, leading to the change in orientation and surface area with the field direction. This is where we will have to use calculus.
Electric Flux Formulas Class 12
The generalised formula for electric flux is Φ_E = EAcosΘ. Beyond this, we must look into some relevant physical situations, where the field could be either uniform or irregular.
Electric Flux Formula when Field is Uniform
When the electric field is uniform with lines passing through a surface that’s perfectly curved or flat, we use the general formula, Φ_E = EAcosΘ. We can exactly figure out the maximum or minimum orientation of the flux.
We primarily look at three conditions.
| Orientation Described Here |
Angle (θ) |
cosθ |
Resulting Flux (ΦE) |
| The surface is perpendicular to E when the flow of lines is maxed out |
0 degree |
1 |
Φ_E=EA, when Flux is to its Maximum |
| The surface becomes parallel to E when there's zero or no flow |
90 degree |
0 |
Φ_E=0, when there is very little or the least flux |
| Field lines entering the closed surface create an inward flow |
>90 degree |
Negative |
Φ_E is Negative |
Electric Flux Formula when Field is Non-Uniform
For irregular electric field surfaces, the formula for electric flux remains the same but we need to introduce calculus here.
The reason is the electric field vector does not remain constant across all parts of the surface. So the orientation gets different all the time.
We need to use the integral method where use approximation on patches considering them to be flat at smaller regions. So the area element is too tiny and we can use that as dA. Naturally, that will become dΦ_E.
We can then use the formula of electric flux in an irregular electric field surface at a very small region as
dΦ_E = E.dA
But what would be the total electric flux? Of course, we need integration here to sum up for all the tiny parts of the surface as one complete whole.
So, the total electric flux formula for an entire irregular surface in two dimensions would be
Φ_E = ∬_s E. dA
If the surface were a one-dimensional one, we would use a single integral symbol. For three-dimensional surface, three symbols.
Electric Flux Units in Class 12
There are two units of electric flux to learn in Class 12 Physics.
- Volt Metre: The most common SI unit of electric flux is Volt-metre that tells us the electric field vector (E) and the area in metre (m). Or, in short form, we can write that as V m.
- Newton Metre Squared Per Coulomb: The other known unit of electric flux that assigns the angle is Newton metre squared per Coulomb. Just simplify that to N m^2 /C.
Find the reason why these two exist, when learning the dimension of electric flux, important for tricky calculations in your exams.
Electric Flux and Gauss Law: How They’re Related
We begin to move to bigger concepts after reading electric flux, namely distribution of charges on closed surfaces using the Gauss’ Law. Besides drawing connection to this law, we also get to understand the connection of flux in the electric field with electric charges in Class 12.
So what this law does is give us the best shortcut to understand that the total electric flux (Φ_E) passing through any closed surface is in direct proportion to the net electric charge inside it.
We speak mathematically about the Gauss Law in relation to electric flux and charge as
Φ_E = q _enclosed / ϵ _ 0
This equation becomes a universal understanding of what the total flow of the field is determined by in a closed surface, ie., the charge that’s inside it. The surface's size, shape, or the presence of charges outside this enclosed surface do not even matter.
Properties of Electric Flux Class 12 Level
Electric flux has these four important properties that should be helpful when you are approaching preparation for engineering exams.
- Electric Flux is Proportional to Electric Field Strength - It's true for every case, where a stronger electric field will create more flux and we can use the mathematical equivalent as Φ ∝ E.
- Surface Area and Electric Flux are in Direct Proportion - A larger surface area will have more flux, so we can use this relationship Φ ∝ A.
- Cosine of Orientation and Flux are Proportional - The angle between the field always must remain proportional to the surface normal and we can show it like this Φ ∝ cosθ.
- Φ_E = q _enclosed / ϵ _ 0 says that the total electric flux is proportional directly with the total charge in an enclosed surface.
What Type of Electric Flux Questions Should You Prepare For?
Complete Class 12 Study Material: PCM
Physics Electric Charge and Field Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter