Electric field lines are imaginary, conceptual drawings to understand the vector nature of an electric field and its strength or magnitude in physics. They do not have any physicality or real-life visibility, but only help us visualise what’s inside the electric field, based on how electric charges are arranged.
Among the world’s greatest experimental physicists, Michael Faraday, introduced the concept of field lines in an electric field in the 19th century. It was for an intuitive understanding of how they would exist without any actual mathematical analysis. The formal mathematical representation of the direction and strength of Electric Field Lines (or EFLs) was built on Faraday’s idea by James Clerk Maxwell.
Below, we will define electric field lines comprehensively. Have a look at the key learning objectives here.
- What electric field lines are and their purpose in Physics, when they are not actual physical entities.
- The rules for electric field lines, from where they begin and end, and the most important characteristics.
- Representation of different charge configurations, from single point charges to opposite charges.
- What are Electric Field Lines?
- Why Do We Draw Electric Field Lines?
- Properties of Electric Field Lines
- Understanding Electric Field Lines Diagrams
- What Type of Questions to Expect on Electric Field Lines in Exams?
- Complete Class 12 Study Material
What are Electric Field Lines?
Electric field lines are imaginary curves. They keep changing in direction and magnitude when positive or negative charges are present.
If you go look into the maths, one electric field line can be an imaginary integral curve. This gives rise to two reasons why these are not abstract but backed by maths.
- Drawing Tangents Along the EF Line: The direction of the vector is at whichever point you draw.
- The Electric Field Line has to be the Locus: It's a locus to help us trace the path of the field. From this, we get to know how correct this curve is. Instead of just randomly charting it out.
Why Do We Draw Electric Field Lines?
EFLs are imaginary curves, but does not mean they are random. The tangent at any given point on one of the lines in the field gives us the direction of where electric field goes from that point.
By simply asking ourselves where the electric field line would be at any XYZ point, we look at the sign of the source charge.
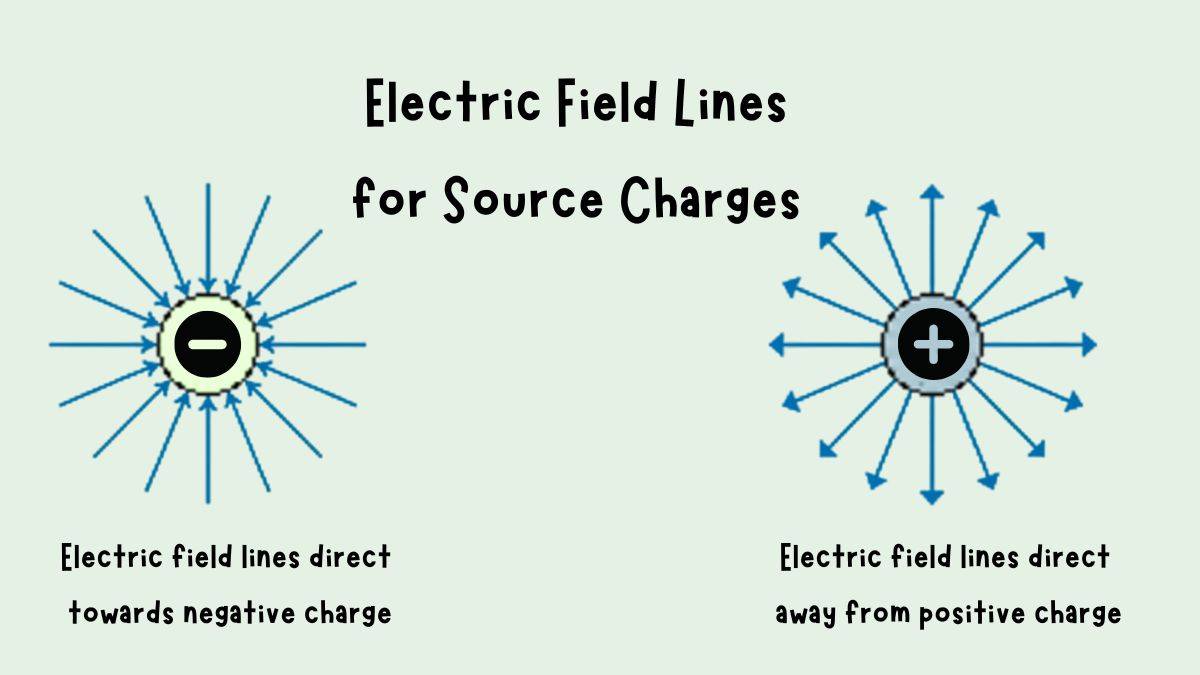
We have to know some rules of polarity telling us that these lines flow from positive to negative charge.
Then, we have the magnitude to understand as well. If we draw, we can see where these lines could be closer. Now that could tell us why there is a strong electric field with the presence of more charges at that same point where the charge points towards. With far-apart lines, we would have a weaker electric field.
After learning that the electric field lines show us direction and give us a sense of the density with less or more distance between the lines, we move to one more reason why we need to draw them.
Field lines in the electric field never cut through. It isn’t possible, as it would be wrongly implying that there are two directions from the same point. So this property is the reason why we get to understand how these lines exist uniquely, at any point.
Properties of Electric Field Lines
For CBSE boards, just remember the four properties of electric field lines, which are highlighted on page 21 of Class 12 Physics chapter 1 book.
“(i) Field lines start from positive charges and end at negative charges. If there is a single charge, they may start or end at infinity.
(ii) In a charge-free region, electric field lines can be taken to be continuous curves without any breaks.
(iii) Two field lines can never cross each other. (If they did, the field at the point of intersection will not have a unique direction, which is absurd.)
(iv) Electrostatic field lines do not form any closed loops. This follows from the conservative nature of electric field.”
The explanations of these properties below will be helpful to learn and develop a more conceptual base when you know that these electric field lines are in a three-dimensional space - always.
1. Direction and Continuity of Electric Field Lines
From above, we got to know that an electric field line is drawn in a way that the tangent to it at each point tells us which direction the total electric field is.
These lines are curves, yes, but they are also continuous and do not break when the 3d region of the electric field is free of charges.
2. Origin, Termination, and Closed Loops
We also discussed that electric field lines cannot originate from a negative charge. A line or curve we draw in the electric field must always start from a positive charge to end in a negative one.
If it’s a single point charge, the line will start or stop at infinity. As you move to later chapters to revise with Class 12 Physics notes, you’ll learn that electric field lines can never form closed loops. It’s because we cannot move a charge around a closed loop, ever, and even return to that starting point as that would mean there is loss or gain in total energy. That’s impossible as per the conservation principle in electrostatics.
3. EFLs follow Non-Intersection
They cannot intersect with each other at any point. The electric field intensity at a single point can never have two directions. So we cannot draw two tangents originating from the same point.
But field lines can be perpendicular to the direction of charge when the electric is field is non-uniform. In a uniform one, the lines are parallel to each other.
4. Proportionality to Magnitude of Charge and Field Strength
The strength of charge in the field is directly proportional to the number of electric field lines that are present in the field. These field lines, again, should originate from a positive charge or terminate in a negative charge.
As we denote electric charge as q, a charge of 2q will have two times more lines when you compare a charge of 1q.
Understanding Electric Field Lines Diagrams
See these important diagrams in how electric field lines are represented under different conditions of polarity and space.
How Electric Field Lines Look When Discrete Sources are Together
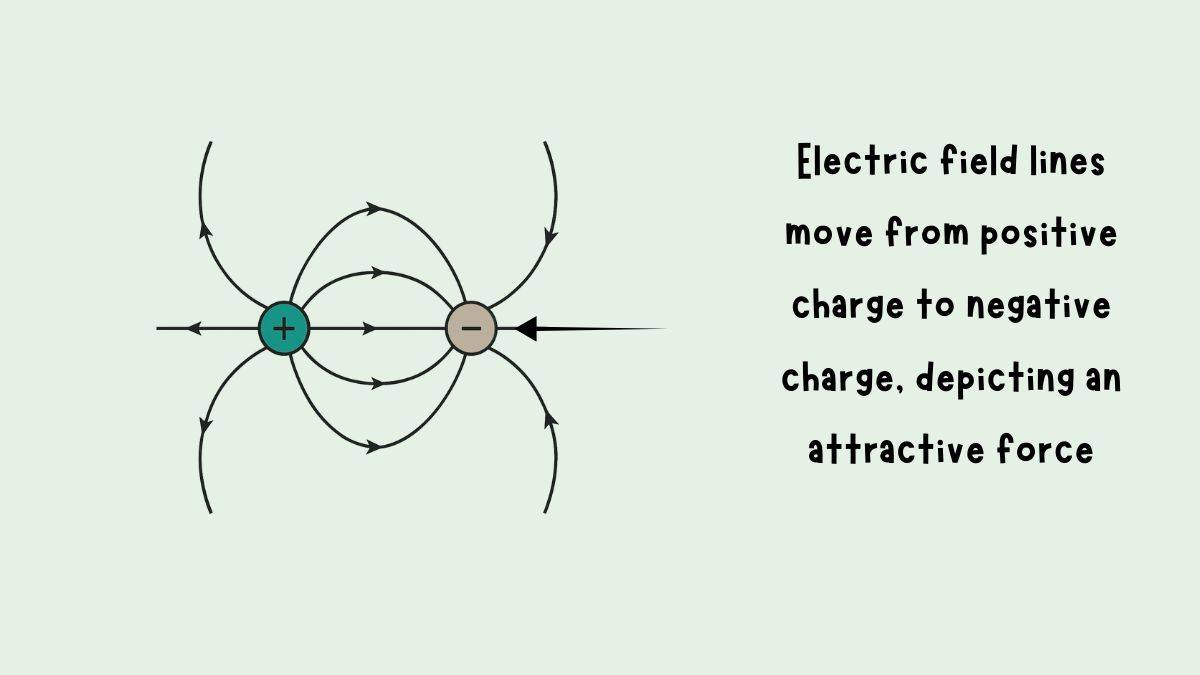
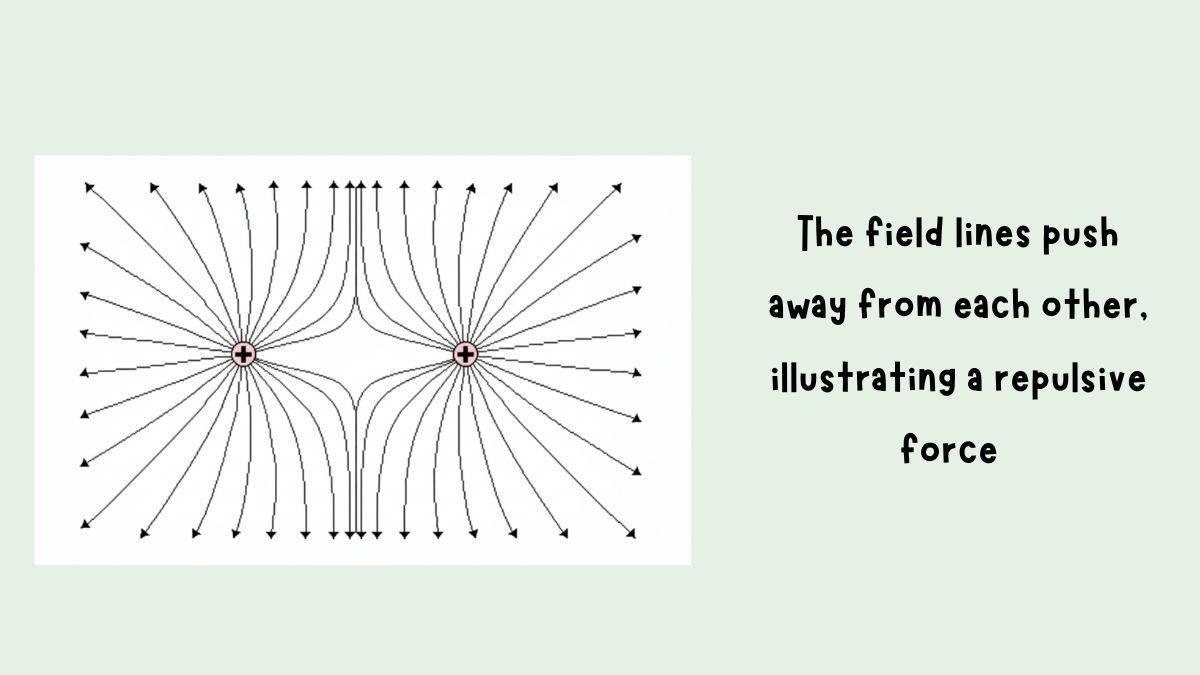
If you remember Coulomb's Law Class 12, like charges repel while when charges are opposite they attract. The same idea applies in the diagrams below.
For charges when they are opposite, or when it is a dipole.
When charges are alike, see what happens to like charges.
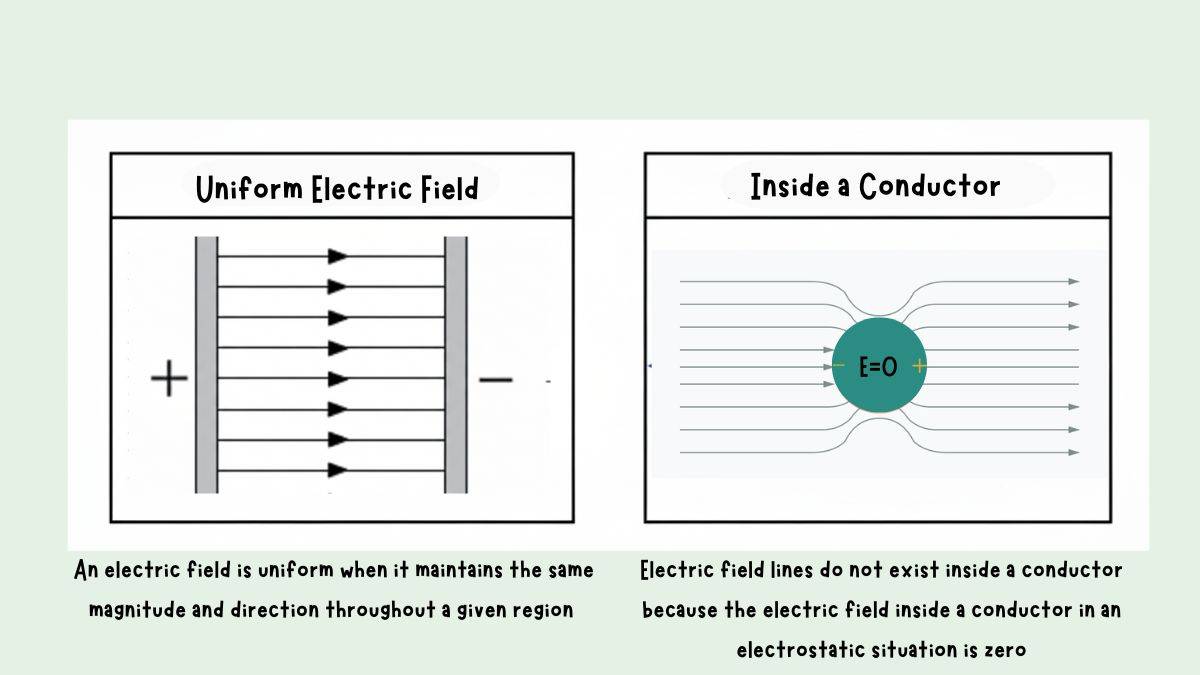
What Happens to Field Lines When They're in Specific Environments
Field lines in different environments act differently. See how right below.
What Type of Questions to Expect on Electric Field Lines in Exams?
Prepare for three kinds of questions, where you are mostly going to be tested on how you see, explain, or draw electric field lines. Practice these along with NCERT Exemplar Solutions for this chapter.
- Here you look at field line diagrams and figure out what they show. You might have to:
-
- See which charges are positive or negative by looking at the line direction
- Compare charge strength from how many lines come out or go in.
- Find where the field is zero by seeing where lines spread or sometimes disappear.
- You must learn to explain why electric field lines work due to the properties you just learned from above here. You could be asked:
-
- Why lines never cross.
- Why lines are smooth and why they do not break.
- Why they never make loops.
- From the above diagrams you just saw, in exams you will have to pick the correct diagram for a setup.
For example, how will you explain the field lines near conductors or around two like charges.
Complete Class 12 Study Material
We have prepared some notes for Class 12 CBSE exams based on NCERT Textbooks.Go have a look.
| Complete CBSE Class 12 Study Material |
||
|---|---|---|
Commonly asked questions
Why do the electric field lines not form closed loops?
Electric field lines never form closed loops as we should know the electrostatic field is conservative. In a conservative field, the work done in moving a charge around any closed path is zero. If lines formed loops, a charge would keep gaining energy along the path, which breaks this rule of zero net work.
Why do the electric field lines never cross each other?
Electric field lines never cross as the field no matter what point you take will have only one direction. If two lines met, there would be two tangents at that point, meaning two directions for the same field. That would make the field undefined there, which is physically impossible.
What do electric field lines provide information about?
Electric field lines show how electric fields look and act but they are imaginary and have physics backing for their presence. They point the way a positive charge would move and their closeness shows field strength. Lines start on positive charges and end on negative ones. Crowded lines mean strong fields, spaced lines mean weak ones, and straight parallel lines mean uniform fields.
Physics Electric Charge and Field Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter