Elements are the basic units of all types of matter. Currently, there are more than 100 elements, and the efforts to synthesise new elements are in progress. In 1800, only 31 elements were known. By 1865, the number of known elements had more than doubled to 63.
With a larger number of identified elements, it becomes confusing and difficult to remember all of them. So, the elements were arranged in groups and patterns based on their similarities and differences. This process is known as the classification of elements.
The elements classification helps to understand their properties, predict their behaviour, and study them in an organised way. It's just like arranging books in a library, which helps to find them quickly; similarly, the classification of elements helps chemists to study the elements systematically.
- Historical Context and Need for Classification
- Key Reasons for Classification of Elements
- Early Attempts at Classification
- Prout's Hypothesis
- Döbereiners Triads
- Newlands Law of Octaves
- Lothar Meyers Volume Curves
- Mendeleevs Periodic Table
- Modern Periodic Table and Moseleys Contribution
- Illustration
Historical Context and Need for Classification
When a few elements were identified then it was easy to study them individually. After the increase in the known elements, it became difficult to remember their properties. To tackle this issue, scientists started looking for similarities among the elements.
Reason for Classifying Elements
- The number of known elements was more than 100, and it was difficult to study them separately.
- Many elements have similar properties, so grouping them made learning easier.
- Element classification helped in predicting the properties of newly discovered elements.
- It helped to arrange the elements in systematic order, which made the study of chemistry more logical and simple.
Important link:
| NCERT Class 12 notes | |
| Maths Class 12 NCERT Notes |
Key Reasons for Classification of Elements
The reason to classify the elements was to arrange them in order and simplify the study of their properties. Also, it helps in predicting the properties of newly discovered elements. Here we have provided the detailed reason for the elements' classification.
Managing a Large Number of Elements
When few elements were known, it was easy to study them. But after the number of known elements increased, it became difficult to study their properties separately.
After classifying the elements in groups, it is easy to study them.
Grouping elements with similar properties
Many elements share similar behaviour, such as sodium, lithium, and potassium, all of which react strongly with water.
Grouping such elements makes it easy to study them in a systematic and logical way.
To predict the properties of new or unknown elements
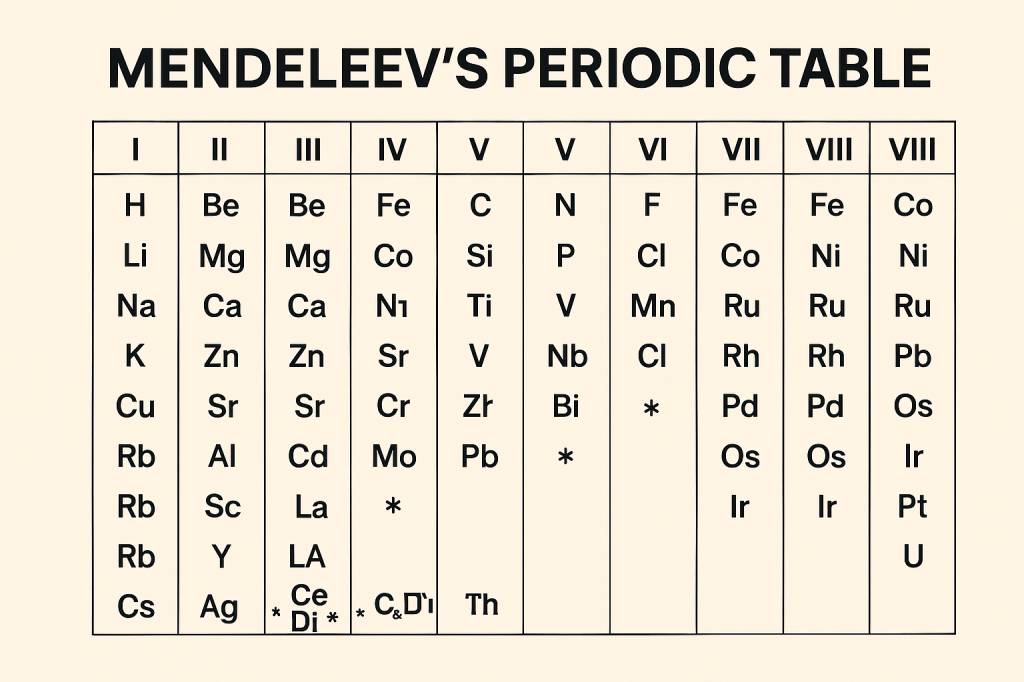
In Mendeleev's periodic table, gaps were left for undiscovered elements.
This helped scientists to predict the properties of new elements based on their position in the periodic table.
To understand trends and relationships among elements
Elements classification shows that the properties of elements change with atomic number.
This will help to understand the behaviour of elements in detail, rather than memorizing each separately.
Early Attempts at Classification
Earlier, several attempts were made by the scientists to classify elements, each contributing to the development of the modern periodic table. These efforts highlight the evolving need for a robust classification system.
Important Links:
| NCERT Class 11 Notes | |
| CBSE Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Notes |
Prout's Hypothesis
William Prout, an English chemist and physician, proposed Prout's Hypothesis in 1815. According to him, atoms are made of hydrogen atoms.
Significance of Prout's Hypothesis
- It was the first theory to propose a unifying concept of matter composition.
- Furthermore, more research was conducted into atomic structure and the atomic mass of elements.
- More accurate techniques for measuring atomic weights were developed.
Limitations of Prout's Hypothesis
- Accurate measurement of atomic masses showed that not all atomic weights are whole-number multiples of that of hydrogen.
- Isotopes helped to explain these inconsistencies.
- Finally, the proton-neutron model replaced the hypothesis.
Döbereiners Triads
In 1817, Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner introduced the concept of Dobereiner's triads by categorizing elements. This classification was based on the chemical properties and atomic masses of the elements. That was the starting point for the modern periodic table.
Also Read: NCERT Solution for Class 11 & 12 | NCERT Solution for Class 12 Chemistry
Key Features of Dobereiner's Triads
- Triads: Dobereiner grouped three elements, known as triads. These had similar chemical properties.
- Atomic Mass Pattern: The arrangement of elements was done in such a way that the atomic mass of the middle element was approximately the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements.
- Chemical Similarity: Elements in the triads have similar chemical behaviour.
Limitations of Dobereiner Triads:
- Grouping of elements in triads was not possible with all the elements available at that time.
After the discovery of more elements, it was noticed that the pattern was incomplete and inconsistent.
Newlands Law of Octaves
The Newlands' Law of Octaves was introduced by John Newlands, an English chemist, in 1865. According to this law, the properties of every eight elements are similar to the first when they are arranged in order of increasing atomic mass.
Significance of Newland's Law
- The eighth element showed similar properties to the first.
- Newland compared the repetition of properties to the musical notes (Do, Re, Mi).
Limitations of Newland's Law
- Worked with lighter elements only.
- Space for undiscovered elements was not left.
- Dissimilar elements were placed in the same group ( like Co and Ni with halogens)
- Initially rejected by the scientific community.
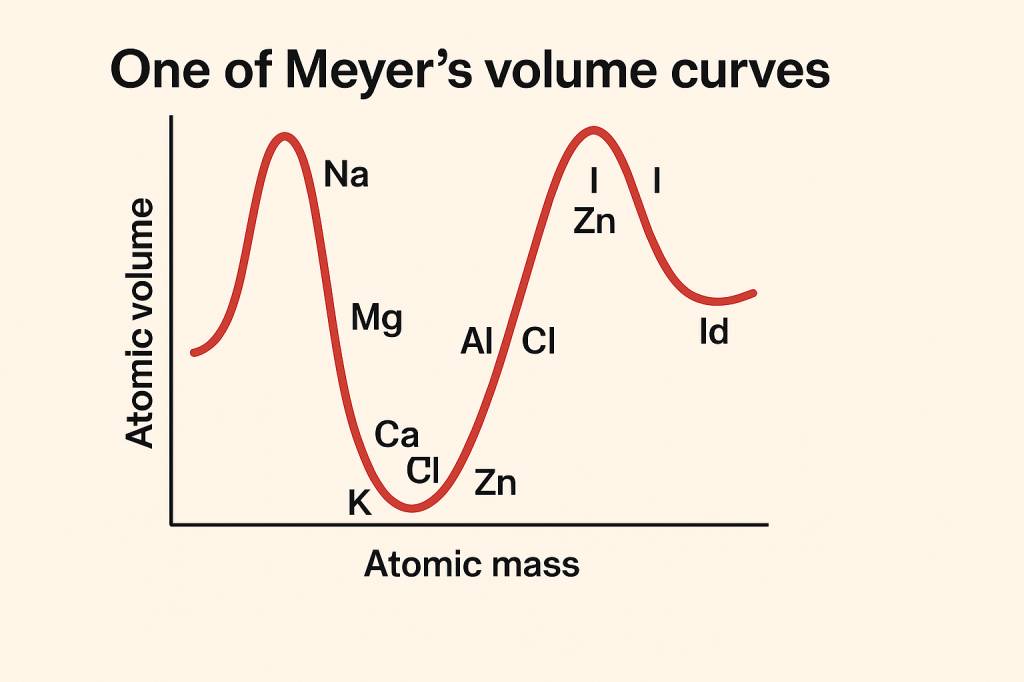
Lothar Meyers Volume Curves
Lothar Meyer created a graph of atomic volume curves against atomic mass for various elements.
Key Observations
- The wave-like pattern showed repeating peaks, where the elements with similar properties appeared at similar positions.
- Alkaline metals (Li, Na, and K) appeared at the peak of the curve.
- The representation of the graph curve gave the idea of periodicity in elemental properties.
Significance of Lothar Meyer's Volume Curves
- The curve demonstrated the periodic nature of elements.
- While Mendeleev received recognition for the modern periodic table, Meyer's work is equally important.
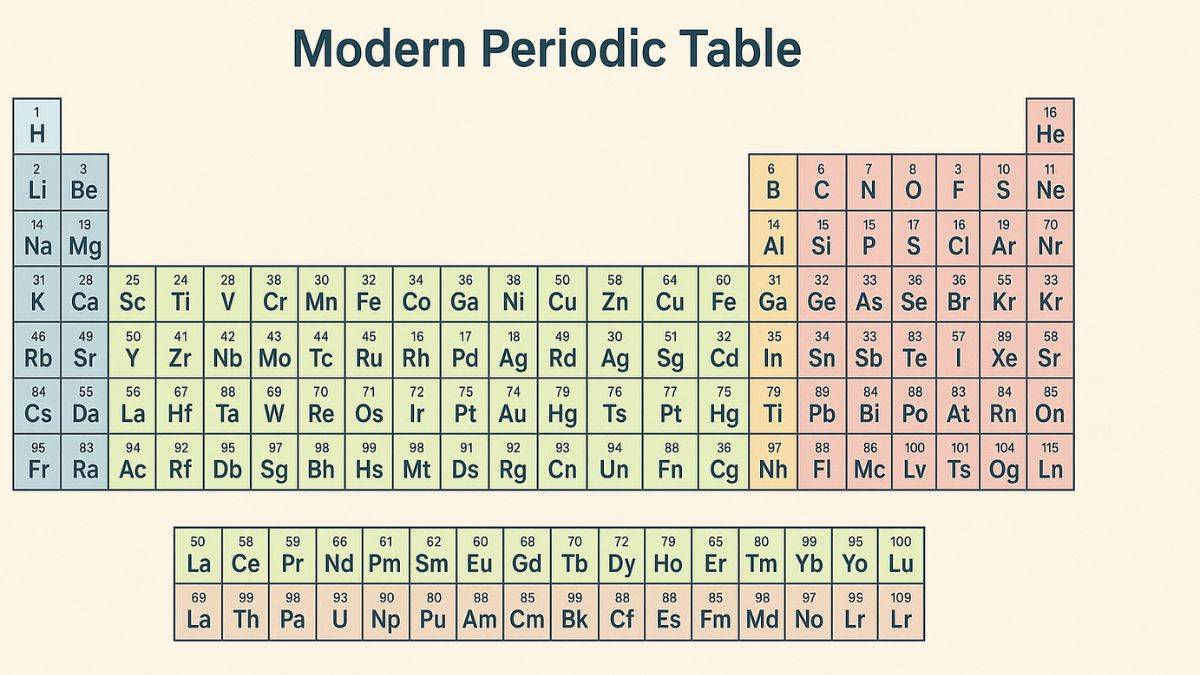
Mendeleevs Periodic Table
Modern Periodic Table and Moseleys Contribution
Illustration
Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Classification of Elements
- Electronic Configuration Types of Elements
- Why do we need to classify elements
- Periodic Trends in Properties of Elements
- Genesis of Periodic Classification
- Present Form of Periodic Table
- Nomenclature of Elements with Atomic Numbers
- Periodic Table Electronic Configuration of Element
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics