Chemistry is known as the branch of science that deals with molecules and their transformations. This is central to understanding natural phenomena and human advancements. This topic explores all thefoundational concepts such as the nature of matter, states of matter, classification of matter, and the mole concept. Those who are studying in CBSE board need to practice NCERT solutions of some basic concepts of chemistry Class 11 chapter.
- Nature of Matter
- States of Matter
- Classification of Matter
- Elements and Compounds
- Mole Concept
- Molar Mass
- Avogadro's Law
- Formula Mass
- Percentage Composition
- Conclusion
Nature of Matter
As per NCERT, anything which has mass and occupies space is called matter. Everything around us, for example, book, pen, pencil, water, air, all living beings, etc., are composed of matter.In simple words, matter is anything that possesses mass and occupies space, encompassing all physical substances in the universe, such as air, water, and living organisms.
Do note that this topic helps in building the foundation of chemistry which makes it of importance for JEE main exam aspirants as well as NEET exam aspirant.
States of Matter
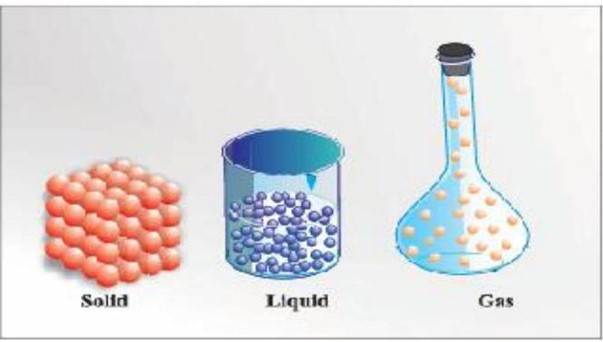
Matter exists in three physical states-solid, liquid, and gas-determined by the arrangement and movement of constituent particles, which can interconvert through temperature and pressure changes.
As per NCERT:
"Matter can exist in three physical states viz. solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have definite volume and shape; liquids have definite volume but not definite shape; gases have neither definite volume nor shape."
Figure 1: Arrangement of particles in solid, liquid, and gaseous states.
Classification of Matter
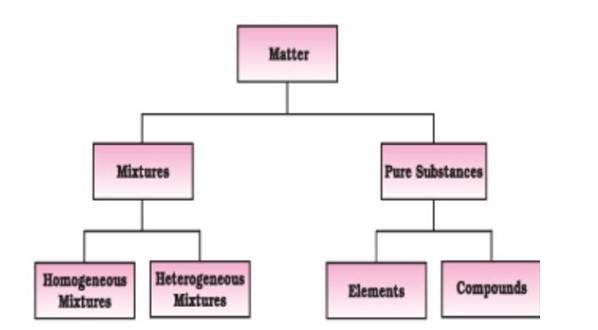
Matter is classified at the macroscopic level into mixtures (homogeneous or heterogeneous) and pure substances (elements or compounds), based on the uniformity and composition of particles.
As per NCERT:
"At the macroscopic or bulk level, matter can be classified as mixture or pure substance. A mixture contains many types of particles in variable composition, while a pure substance has fixed composition. Pure substances are further classified into elements and compounds."
Figure 2: Classification of matter (NCERT, Fig. 1.2, p. 5).
Elements and Compounds
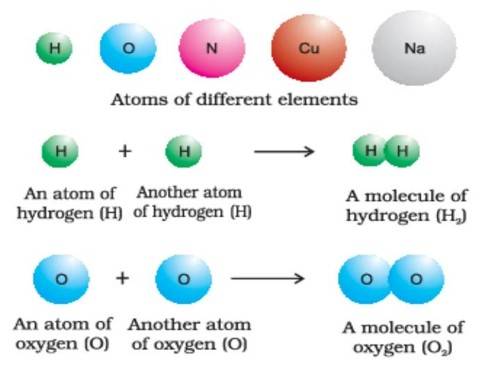
An element consists of only one type of atom, while a compound is formed by two or more elements combined in a fixed ratio.
As per NCERT:
"Particles of an element consist of only one type of atoms. When two or more atoms of different elements combine together in a definite ratio, the molecule of a compound is obtained."
Figure 1 given below represents atoms and molecules of elements, while Figure 2 depicts molecules of water and carbon dioxide.
Figure 3: Representation of atoms and molecules (NCERT, Fig. 1.3, p. 6).
Water molecule ( ) Carbon dioxide molecule ( )
Figure 4: Depiction of molecules of water and carbon dioxide (NCERT, Fig. 1.4, p. 6).
Mole Concept
The mole is a unit representing a specific number of particles (atoms, molecules, etc.), facilitating the handling of large quantities of microscopic entities in chemical calculations.
As per NCERT:
"The mole, symbol mol, is the SI unit of amount of substance. One mole contains exactly elementary entities. This number is the fixed numerical value of the Avogadro constant, , when expressed in the unit and is called the Avogadro number."
Molar Mass
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole, numerically equal to its atomic or molecular mass in unified mass units
(u).
As per NCERT:
"The mass of one mole of a substance in grams is called its molar mass. The molar mass in grams is numerically equal to atomic/molecular/formula mass in u."
Example: Calculate the molecular mass of glucose (C6H12O6).
Molecular mass
Avogadro's Law
Avogadro's law states that equal volumes of all gases, under identical temperature and pressure, contain an equal number of molecules, foundational for understanding gas reactions.
As per NCERT:
"Equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure should contain equal number of molecules."
Formula Mass
Percentage Composition
Conclusion
Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics