Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Everything around us — air, water, soil, plants, animals — is composed of matter. The understanding of the nature of matter forms the fundamental basis for the study of chemistry and physics. This document elaborates on the classification, physical and chemical properties, and structure of matter, along with relevant figures and diagrams.
The subject experts at Shiksha have also provided the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry. Students can use the NCERT solutions to prepare for the CBSE board exam and competitive exams such as JEE Mains, NEET, etc.
- Nature of Matter Definition
- Classification of Matter
- Properties of Matter
- States of Matter and Interconversion
- Atomic Theory of Matter
- Molecular Structure of Matter
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Particle Nature of Matter
- Density of Matter
- Changes in Matter
- Kinetic Theory of Matter
- Examples of Matters
- Summary Table
- Conclusion
Nature of Matter Definition
The definition of Matter as per the NCERT is, “Anything which has mass and occupies space is called matter”.
Explanation: As per the above definition, any object or substance that has mass and takes up space is called matter. For example, books, pens, pencils, water, air, all living beings, etc.
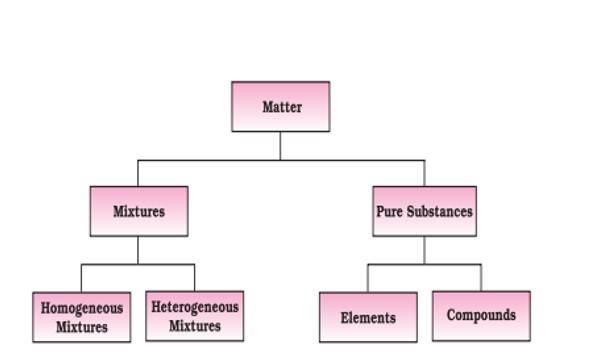
Classification of Matter
Matter is classified into two types: Physical and Chemical. The detailed classification matter is mentioned below.
Physical Classification
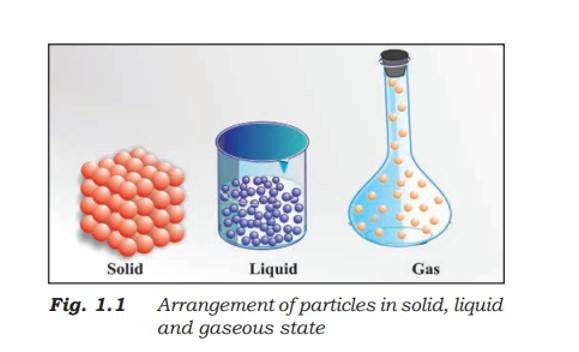
Matter can exist in three primary states:
Solids: Definite shape and volume, incompressible, particles tightly packed.
Liquids: Definite volume but no definite shape, slightly compressible, particles less tightly packed than in solids.
Gases: Neither definite shape nor volume, highly compressible, particles far apart.
Properties of Matter
Physical Properties
Can be measured without changing the composition. Examples: Density, Colour, Melting point, Boiling point.
Chemical Properties
Can only be observed when a substance undergoes a chemical change. Examples: Reactivity, Flammability.
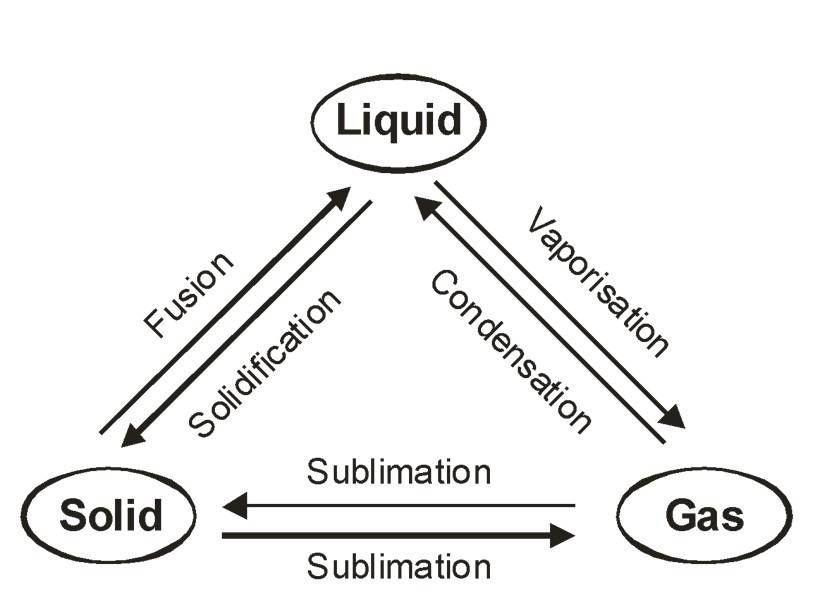
States of Matter and Interconversion
Matter can change states by changing temperature and pressure.
Melting: Solid to Liquid
Freezing: Liquid to Solid
Vaporization: Liquid to Gas
Condensation: Gas to Liquid
Sublimation: Solid to Gas directly (e.g., Camphor)
Deposition: Gas to Solid directly
Atomic Theory of Matter
Democritus (400 BC) proposed that matter is made up of small, indivisible particles called atoms. Dalton's Atomic Theory (1808) expanded on this, suggesting atoms are indivisible, identical for an element, and combine in simple ratios.
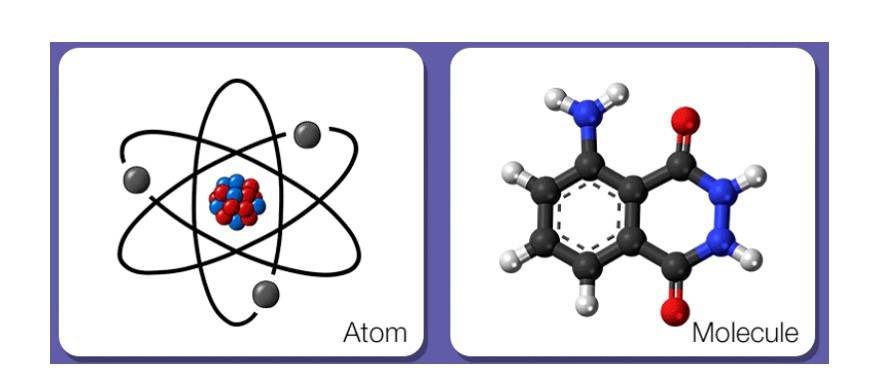
Molecular Structure of Matter
Atom: The smallest unit of an element.
Molecule: Two or more atoms bonded together.
Laws of Chemical Combination
Law of Conservation of Mass: Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.
Law of Definite Proportions: Compounds always contain elements in fixed ratios.
Law of Multiple Proportions: When two elements form multiple compounds, their mass ratios are simple whole numbers.
Gay-Lussac's Law: Gases react in simple volume ratios.
Avogadro's Law: Equal volumes of gases contain equal number of molecules.
Particle Nature of Matter
Density of Matter
Changes in Matter
Kinetic Theory of Matter
Examples of Matters
Summary Table
Conclusion
Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics