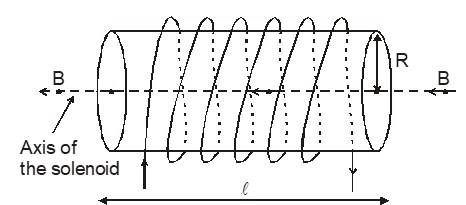
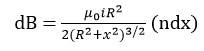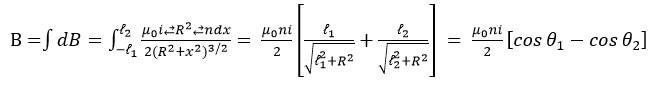A solenoid is an electromagnet that is capable of generating a controlled magnetic field. The magnetic field can be controlled by managing the supply of electric current. The right-hand thumb rule is used to identify the direction of the magnetic field.
To create a solenoid, copper wire is wound in a helix shape. Each winding of wire is tightly packed with the other. When current is passed through the wire coil, a magnetic field is generated around and within the coil. This is the basic understanding of a solenoid.
The working principle of the solenoid is used in various equipment such as MRIs, doorbells, washing machines, refrigerators, circuit breakers, etc. In this article, we focus on the definition of the solenoid, types of solenoids, the working principle of the solenoid, and applications.
Solenoid is an important topic in Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism. Additionally, students can check the Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 NCERT Solution for the textbook at Shiksha. NCERT Solutions are the best resource to prepare for the exam.
- What is Solenoid?
- Working Principle of Solenoid
- Types of Solenoids
- Application of Solenoid
What is Solenoid?
A solenoid is a coil of wire wound into a helical shape. When we pass an electric current through the solenoid, then magnetic field is generated. The solenoid acts like an electromagnet that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion.
Also Read: Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions
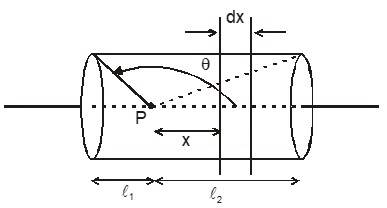
Working Principle of Solenoid
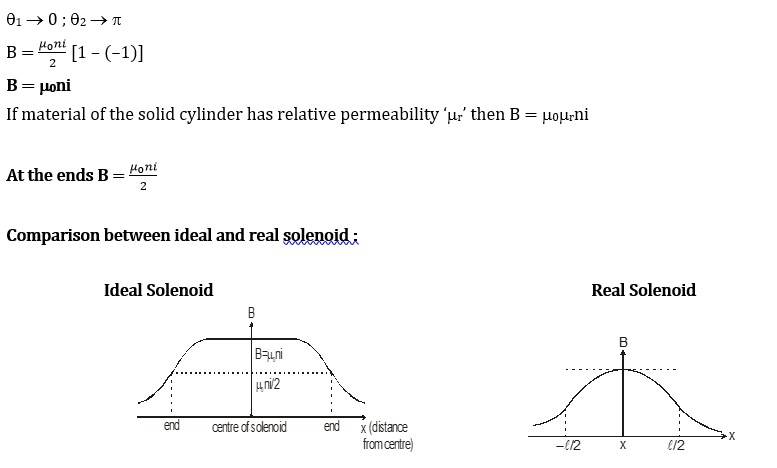
For ‘Ideal Solenoid’ B Inside (at the mid point)
l >> R or length is infinite
Types of Solenoids
The following are the types of solenoids:
- AC and DC Solenoid: Can operate with alternating current or direct current.
- Linear Solenoid: Applies push or pull force on a plunger.
- Rotary Solenoid: Used in an automatic control process.
- Valve Solenoid: Controls the flow of liquid and gas in valves.
Application of Solenoid
Solenoid is used in various devices, including:
- Household Appliances
- Automotive
- Security Systems
- Medical Devices
- Valves
- Doorbell
- Industrial equipment
Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter