Motion in magnetic field is all about the effect of the magnetic field on the movement of a charged particle. The force exerted on a moving charge by a magnetic field affects the trajectory and motion in a circular or helical path. A detailed explanation of the motion of charged particles in magnetic field is mentioned in this article.
Motion in Magnetic Field is an important topic in moving charges and magnetism. Knowledge of motion in magnetic field will help to understand the topics such as magnetic forces, Biot-Savart law, Ampere’s circuital law, Solenoid, etc.
For a better understanding of topics, students must practice the NCERT Class 12 Physics solutions. The subject experts at Shiksha have prepared Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 NCERT solution for textbook problems. Also, this topic is important for various competitive exams such as JEE Main, NEET, etc. CBSE Board students must practice the previous year questions on motion of charged particles on magnetic field to get a good grip over the topic.
- What is the motion of a charged particle in magnetic field?
- Uses of Motion in Magnetic Field
- Motion of charged particles under the effect of magnetic force
- Helical Path
- Complete analysis
- In y-z plane
- Examples of Motion in Magnetic Field
- Motion in magnetic field in daily life
What is the motion of a charged particle in magnetic field?
Motion of charged particle in magnetic field is all about movement of particle based on the force exerted on it. When an electric current passes through the conductor, a magnetic field is generated around it.
Now, when a charged particle moves in the magnetic field, it will feel force, which might change its direction. The magnetic force will be exerted on charged particle if it is moving else no force will be affecting the particles.
Thus, the force is always toward the motion, it will change the direction of charged particles rather than slowing or boosting its speed.
If the charge particle is moving perpendicular to the magnetic field, then the particle will be in circular path. Here, the magnetic force is acting like a centripetal force, which keeps pulling towards the Centre of circle.
Now, in case, the charged particle moves in the magnetic field along with an angle, its motion will be along or across the field line. Due to these two motions, the particle will move in a spiral shape.
Why is it important?
The behavior of charged particles in magnetic field help in various ways such as:
- Understanding the space weather
- Building electric motors
- Guiding particles in scientific instruments
Uses of Motion in Magnetic Field
Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields are numerous practical and scientific.
- Medical Application
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Medical Isotope Production
- Radiation Therapy
- Technological Applications
- Magnetrons
- Hall Effect Sensors
- Cathode Ray Tubes (CRTs) - Older Technology
- Understanding Natural Phenomena
- Cosmic Ray Deflection
- Aurora Borealis and Australis (Northern and Southern Lights)
- Van Allen Radiation Belts
Motion of charged particles under the effect of magnetic force
Note :
- w, f, T are independent of velocity.
Helical Path
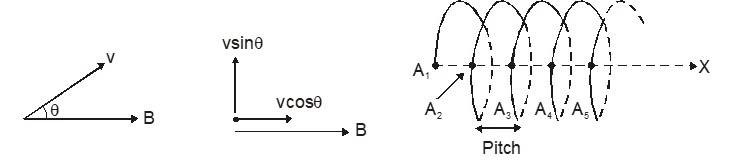
If the velocity of the charge is not perpendicular to the magnetic field, we can break the velocity in two components – v||, parallel to the field and v, perpendicular to the field. The components v|| remains unchanged as the force is perpendicular to it. In the plane perpendicular to the field, the particle traces a circle of radius as given by equation. The resultant path is helix.
Complete analysis
Let a particle have initial velocity in the plane of the paper and a constant and uniform magnetic field also in the plane of the paper.
The particle starts from point A1.
It completes its one revolution at A2 and 2nd revolution at A3 and so on. X-axis is the tangent to the helix
A1, A2, A3, ..........all are on the x-axis.
distance A1A2 = A3A4 = ............... = v cosΘ. T = pitch
where T = Time period
Let the initial position of the particle be (0, 0, 0) and v sin Θ in +y direction. Then in x :
Fx = 0, ax = 0, vx = constant = v cosΘ, x = (v cosΘ)t
In y-z plane
Examples of Motion in Magnetic Field
Below is an example of motion in magnetic field.
- Helical Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field
- Motion in a Cyclotron
- Electron Beam in a Television (CRT - older technology)
- Mass Spectrometer
- Circular Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field
Motion in magnetic field in daily life
Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter