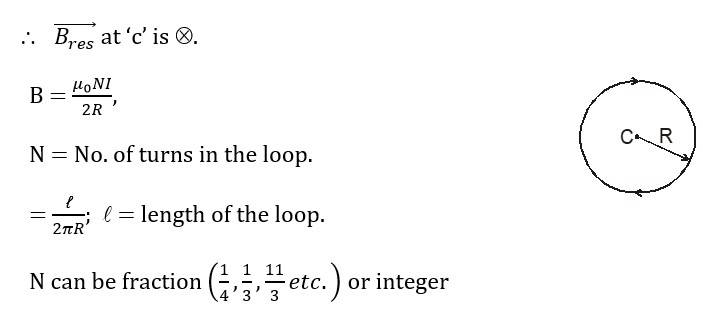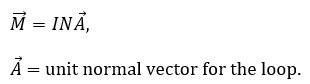Earlier, we studied that a magnetic field is generated around the conductor due to the flow of electric current. The relationship between the electric current and the magnetic field produced in space is described through the Biot-Savart Law.
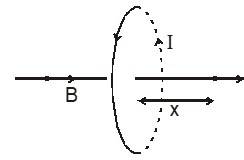
Current passing through the circular wire loop generates a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field on the axis of a circular current loop can be determined using the Biot-Savart Law.
Moving Charges and Magnetism is an important chapter in Class 12 Physics. Understanding the relation between electric current, magnetic field, and behaviour will build the foundation for topics such as Ampere’s circuital law, Solenoid, magnetic force, motion in the magnetic field, etc.
Students must attempt the question based on the magnetic field on the axis of a circular loop for better understanding of the topic. The subject experts at Shiksha have uploaded the Class 12 Physics Ch 4 NCERT solution for the textbook problem online. Class 12 Physics NCERT solutions are the best resource to prepare for the CBSE board exam. Students preparing for competitive exams such as JEE Main, NEET, etc, can refer to the NCERT Solutions for self-assessment.
- What is a Magnetic Field on the Axis of a Circular Loop?
- Magnetic Field on the Axis of a Circular Loop Derivation
- A loop as a magnet
What is a Magnetic Field on the Axis of a Circular Loop?
Magnetic Field due to a circular loop refers to the magnetic field at any point on the axis of the loop. The axis passes through the loop and is perpendicular to the plane containing the loop. This can be determined using the Biot-Savart Law and the right-hand thumb rule.
Magnetic Field on the Axis of a Circular Loop Derivation
Below is the derivation of the magnetic field due to a circular loop.
Magnetic Field on the Axis of a Circular Current Loop ( due to circular loop)
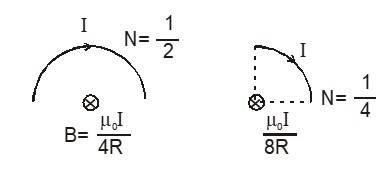
Due to each at ‘c’ is inwards (in this case).
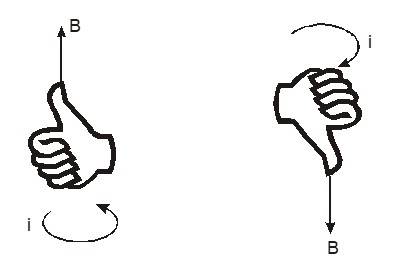
Direction of : The direction of the magnetic field at the centre of a circular wire can be obtained using the right-hand thumb rule. If the fingers are curled along the current, the stretched thumb will point towards the magnetic field (figure).
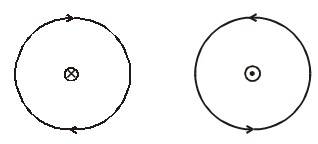
Another way to find the direction is to look into the loop along its axis. If the current is in an anticlockwise direction, the magnetic field is towards the viewer. If the current is in the clockwise direction, the field is away from the viewer.
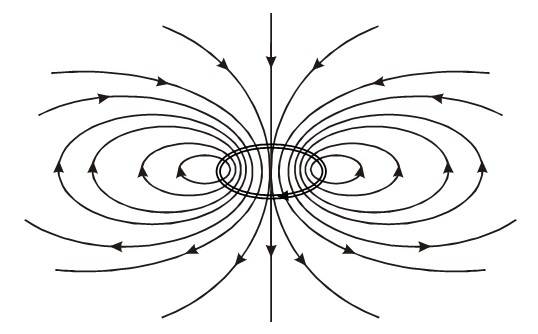
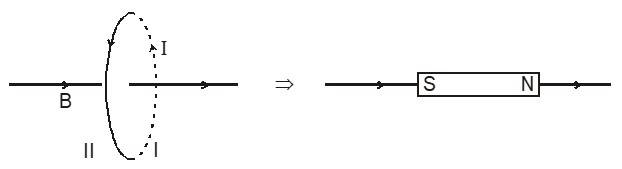
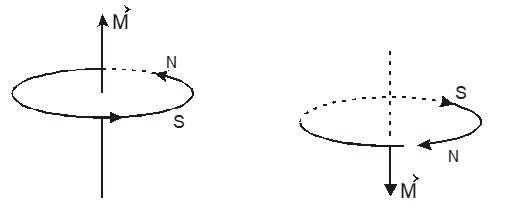
A loop as a magnet
The magnetic field pattern is comparable to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet.
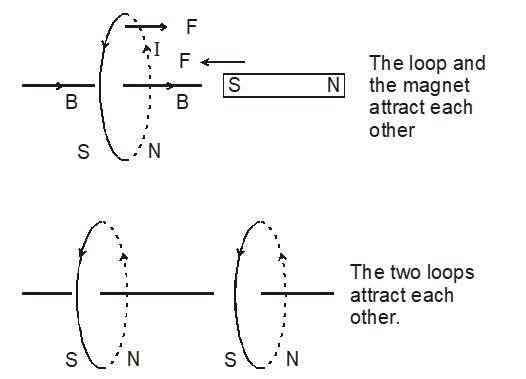
The side ‘I’ (the side from which the enters) acts as the ‘SOUTH POLE’. It can be verified by studying the force on one loop due to a magnet or another loop.
Mathematically
Baxis = for x >> R
it is similar to Baxis due to magnet = 2
Magnetic dipole moment of the loop M = INπR2
M = INA for any other shaped loop.
Unit of M is Amp. m2.
Unit of m (pole strength) = Amp. m {in magnet M = ml}
To be determined by the right-hand thumb rule, which is also used to determine direction of on the axis. It is also from the ‘S’ side to the ‘N’ side of the loop.
Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter