Inverse trigonometric functions, also known as inverse trig functions or arcus functions, are the inverses of the standard trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent, etc.). They are used to find the angle when the value of the trigonometric function is known. Inverse trigonometric functions define integrals making them important for calculus as well with various applications in science and engineering. Even entrance examinations such as JEE Main and IIT JAM ask questions based on the conceptual applications of these topics. The following table gives inverse trigonometric functions along with their range and domain:
| Function | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Formula
- What is Arc sine function or Inverse sine function?
- What is Arc cosine function or Inverse cosine function?
- Understanding Arc tangent function or Inverse Tangent Function
- Arc co-tangent function or Inverse co-tangent function
- What is Arc secant function or Inverse secant function?
- Understanding Arc cosecant function or Inverse cosecant function
- Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- What are the Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions?
- Important Points Related to Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Inverse Trigonometric Functions Formula
The following table provides the inverse triginometric functions formula for users to learn. These are essential for entrance exams like NEET and CUET since they are used in different questions asked.
| Inverse Trigonometric Function | Formula |
|---|---|
| Arccosine | |
| Arctangent | |
| Arcsine | |
| Arcsecant | |
| Arccotangent | |
| Arccosecant |
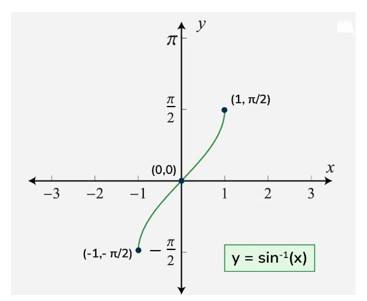
What is Arc sine function or Inverse sine function?
(a) The inverse sine function, also known as arcsine, is the inverse of the sine function. It is denoted as sin⁻¹ or arcsin. The inverse sine function takes a ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle and returns the corresponding angle.
(b) Inverse sine function is written as .
(c) Domain of is .
(d) Range of is .
(e) The inverse sine function "undoes" the sine function, meaning sin(arcsin(x)) = x for all x in the domain of arcsin.
(f) The graph of is shown in fig.
Some relevant reads:
| NCERT solutions | |
| NCERT Class 12 Maths Notes for CBSE |
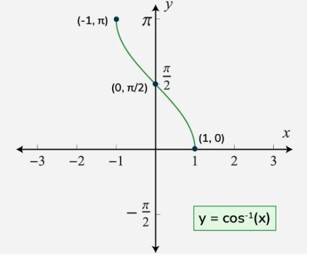
What is Arc cosine function or Inverse cosine function?
(a) The inverse cosine function, also known as arccosine, is denoted as cos⁻¹(x) or arccos(x). It's the inverse of the standard cosine function and is used to find the angle (in radians or degrees) whose cosine is equal to a given value. Essentially, if cos(θ) = x, then θ = cos⁻¹(x).
(b) Inverse cosine function is written as .
(c) Domain of is .
(d) Range of is .
(e) The inverse of a function "undoes" the original function. If f(a) = b, then f⁻¹(b) = a.
(f) The graph of is shown in fig.
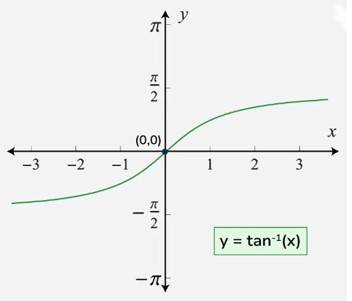
Understanding Arc tangent function or Inverse Tangent Function
(a) The tan inverse function, also known as arctan or tan⁻¹(x), is the inverse of the tangent function. It takes a ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side in a right triangle and returns the angle in radians or degrees. The inverse tangent function is denoted by tan⁻¹x or arctan(x). This is an important function for those who are planning to take IISER exam.
(b) Inverse tangent function is written as .
(c) Domain of is R.
(d) Range of is .
(e) The tan inverse function reverses the relationship of the tangent function. If tan(θ) = x, then θ = tan⁻¹(x).
(f) The graph of is shown in fig.
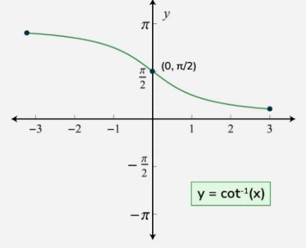
Arc co-tangent function or Inverse co-tangent function
(a) The inverse cotangent function, also known as arccotangent or arccot, is the inverse of the cotangent function. It is denoted as arccot(x) or cot⁻¹(x). The arccot function takes a real number 'x' as input and returns the angle whose cotangent is equal to 'x'.
(b) Inverse co-tangent function is written as .
(c) Domain of is R.
(d) Range of is .
(e) The inverse of a function "undoes" the operation of the original function. So, if cot(θ) = x, then arccot(x) = θ.
(f) The graph of is shown in fig.
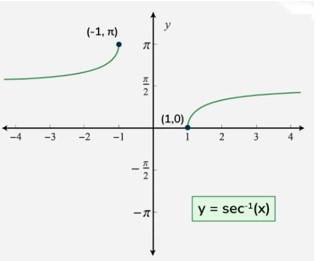
What is Arc secant function or Inverse secant function?
(a) It is the inverse of the secant function. It returns the angle whose secant is equal to x.
(b) Inverse secant function is written as .
(c) Domain of is R .
(d) Range of is or .
(e) The graph of is shown in fig.
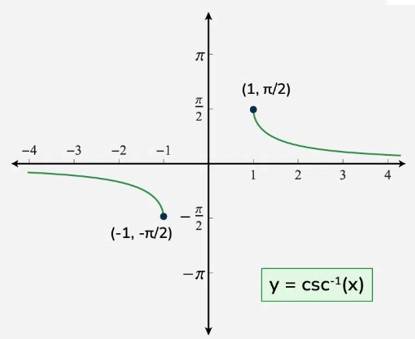
Understanding Arc cosecant function or Inverse cosecant function
(a) The arccosecant function takes a cosecant value (which is a ratio of the hypotenuse to the opposite side in a right triangle) and returns the angle whose cosecant is that value.
(b) The inverse of the cosecant function, often denoted as cosec⁻¹(x) or arccsc(x), is the arccosecant function. It is also known as the inverse cosecant.
(c) Inverse cosecant function is written as .
(d) Domain of is R .
(e) Range of is or .
(f) The graph of is shown in fig.
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
What are the Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions?
Important Points Related to Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Explore exams which ask questions on Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Select your preferred stream
Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Maths Chapters
- Quantitative Aptitude Prep Tips for MBA
- Maths Integrals
- Maths Differential Equations
- Maths Vector Algebra
- Maths Matrices
- Maths Determinants
- Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Maths Differentiation
- NCERT Class 12 Maths
- Maths Continuity and Differentiability
- Maths Applications of Derivatives
- Maths Application of Integrals
- Maths Linear Programming
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test