This guide will cover everything you should know about finite and infinite sets in maths. We elaborate on the NCERT definitions with practical examples and properties, differences, and applications. These will help with your JEE Mains, as the questions test your knowledge around various related concepts, including cardinality calculations for set operations and more.
Follow this article with the Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 SETS. We also have previously covered Sets and Their Representations, which might be helpful to you.
- What are Finite Sets?
- What are Infinite Sets?
- Importance of Finite and Infinite Sets
- Key Properties of Infinite Sets
- NCERT Definition of Finite and Infinite Sets
- Finite vs Infinite Sets: A Detailed Comparison
- Illustrative Venn Diagram of Finite and Infinite Sets
- Real-Life Examples of Finite and Infinite Sets
- Important Observations for JEE Preparation
- Applications of Finite and Infinite Sets
- Misconceptions and Common Errors About Finite and Infinite Sets
- Power Sets and Cardinality
- Summary and Key Takeaways
What are Finite Sets?
A finite set contains a specific number of elements. These elements can be listed and counted.
The process of enumeration concludes after a finite number of steps. Also, every finite set has a starting and an ending point.
A set is termed finite if its elements can be completely counted using natural numbers, and the process terminates.
Examples of Finite Sets
Set of vowels in the English language:
Set of prime numbers less than 20 :
Set of colors in a rainbow:
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet
In each of these cases, the number of elements can be precisely determined and the set listing ends.
Key Properties of Finite Sets
1. Every finite set has a well-defined cardinality (the number of elements).
2. The union, intersection, and cartesian product of finite sets are themselves finite.
3. Every subset of a finite set is finite.
4. The power set (set of all subsets) of a finite set is also finite.
What are Infinite Sets?
Infinite sets, on the other hand, are collections that do not end. They continue without bound and cannot be counted entirely.
An infinite set is a set that is not finite. Its elements are unlimited in number and cannot be completely listed.
Examples of Infinite Sets
Set of natural numbers:
Set of integers:
Set of real numbers between 0 and 1
Importance of Finite and Infinite Sets
Have a deeper understanding of finite and infinite sets is useful for JEE exams.
- These are essential components of Sets in the JEE Main syllabus.
- Knowing how you can differentiate finite and infinite sets would help you solve problems on set operations.
- This is a fairly easy and conceptual section in the exams, which makes it easier to score well.
Key Properties of Infinite Sets
- Infinite sets do not have a finite cardinality
- An infinite set's subset could be finite, or it could be infinite, in its entirety.
- Infinite sets are not only countable but also can be uncountable
- Two infinite sets' union is generally infinite.
- The power set of an infinite set is also infinite, and often has a higher order of infinity.
NCERT Definition of Finite and Infinite Sets
In Chapter 1 of your NCERT textbook, the definition of finite and infinite sets is
"A set which is empty or consists of a definite number of elements is called finite otherwise, the set is called infinite. "
Basics of finite and infinite sets you should remember
- When you can count the elements, it's a finite set
- When the number is indefinite or uncountable, it's an infinite set
Finite vs Infinite Sets: A Detailed Comparison
Finite Sets:
1. Elements are limited and countable.
2. Examples:
3. Power set is finite.
4. Cardinality is a natural number.
5. Subsets are always finite.
6. Listing elements ends after finite steps.
Infinite Sets:
1. Elements are unlimited and not completely countable.
2. Examples: Set of natural numbers, set of points on a line
3. Power set is infinite.
4. Cardinality is infinite (countable or uncountable).
5. Subsets can be finite or infinite.
6. Listing elements never ends.
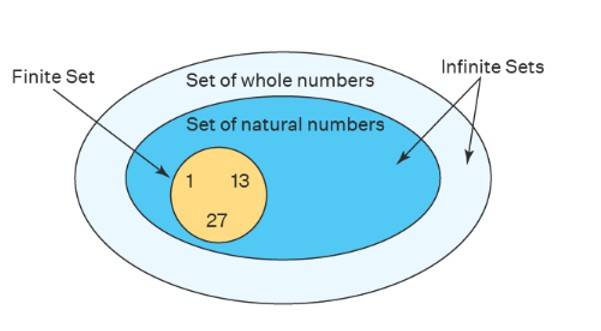
Illustrative Venn Diagram of Finite and Infinite Sets
Imagine a circle representing a finite set, like . Now, picture a larger space representing the infinite set of all natural numbers and set of whole numbers.
Real-Life Examples of Finite and Infinite Sets
Important Observations for JEE Preparation
Applications of Finite and Infinite Sets
Misconceptions and Common Errors About Finite and Infinite Sets
Power Sets and Cardinality
Summary and Key Takeaways
Maths Sets Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Maths Chapters
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test