This guide will define universal set and go beyond the basics to help you crack your JEE exams with confidence!
Learning universal sets is especially helpful when you are trying to understand complement of sets, because to figure what's not in a set, it is important to know what's in it in the first place.
Below, you will find examples of universal set along with Venn diagram representations and everything in between.
- What is a Universal Set?
- NCERT Definition of Universal Set
- Complement of a Universal Set
- Examples of Universal Sets
- Properties of Universal Set
What is a Universal Set?
We define universal set as a collection that holds all the elements of the other related sets without any repetition. It provides a comprehensive boundary within which all subsets exist.
For example, if and , then the universal set that includes these sets would be .
It ensures that every element of any subset is also an element of the universal set.
Illustrative Example of Universal Set
Let's consider two sets.
- Set , consisting of even numbers.
- Set , consisting of odd numbers.
In this case, the universal set would contain all natural numbers:
Both even and odd numbers are part of natural numbers. So, U encompasses all elements of P and Q.
Importance of Universal Set (for Engineering exams)
- The JEE Mains exam usually tests on universal sets with Venn diagrams, where you may have to identify elements within various regions.
- Some questions on universal sets could be related to finite and infinite sets, or it could be around related concepts in the sets chapter of your NCERT textbook. Try going through our page on Sets and their representations, too!
NCERT Definition of Universal Set
Section 1.7 of your NCERT textbook touches upon universal sets. It briefly describes with an example.
"Usually, in a particular context, we have to deal with the elements and subsets of a basic set which is relevant to that particular context. For example, while studying the system of numbers, we are interested in the set of natural numbers and its subsets such as the set of all prime numbers, the set of all even numbers, and so forth. This basic set is called the “Universal Set”. The universal set is usually denoted by U, and all its subsets by the letters A, B, C, etc.
For example, for the set of all integers, the universal set can be the set of rational numbers or, for that matter, the set R of real numbers. For another example, in human population studies, the universal set consists of all the people in the world."
Complement of a Universal Set
For every set, a complement can be identified. That includes all the elements not in the given set but within the universal set.
But, the complement of the universal set itself is an empty set because there are no elements outside of it.
The empty set is also known as a null set. It contains no elements and is denoted by ' '. This reflects that the universal set covers all possible elements under discussion.
Examples of Universal Sets
Universal sets can be finite or infinite. When dealing with a vast or unending number of elements, ellipses (three dots '...') are often used for representation.
For example:
(infinite)
(finite)
Solved Examples of Universal Sets
Example 1:
Given three sets:
To find the universal set, combine all distinct elements:
Example 2:
Given:
(odd numbers)
(even numbers)
The universal set
includes all natural numbers:
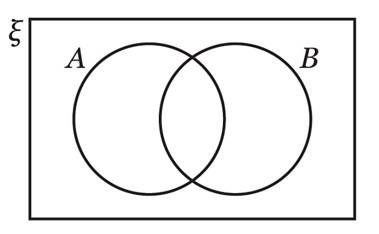
Universal Set Representation Through Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram visually represents the relationships between sets. In such diagrams, sets are shown as circles, and the universal set is depicted as a rectangle enclosing all the circles. This makes it easy to visualize the common, distinct, and complementary elements among sets.
Example of universal set.
represents the universal set.
A represents set A and B represents set B, usually a capital letter is used.
Properties of Universal Set
Consider U as the universal set and , and Z as any three finite sets. The key properties include:
1.
2.
3. If and are disjoint non-void sets, then
4.
5. The union of a set and its complement equals the universal set:
6. The complement of the universal set is the empty set, and vice-versa: and
Maths Sets Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Maths Chapters
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test