
The Rotational Motion Class 11 covers the understanding of the motion of extended bodies, defined as a system of particles. The motion of the system is considered as a whole. The key concept of the Class 11 Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion is the centre of mass of a system of particles. System of Particles and Rotational Motion discusses the usefulness of this concept and the motion of the centre of mass of a system of particles. When the extended body is considered as a rigid body, i.e., with a perfectly defined and unchanging shape, the distance between such pairs of particles does not change.
The system of particles and rotational motion class 11 NCERT solutions has been created to help students understand the concepts properly to get good marks in the Class 11 exams, CBSE Board exam, and other competitive exams like NEET and JEE Mains.
If you are looking for the Class 11 Physics important topics, PDFs of each chapter, and weightage information, check here - Class 11 Physics Notes.
- Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 System of Particles and Rotational Motion: Key Topics, Weightage
- NCERT Physics Class11th Solution PDF for System of Particles and Rotational Motion Chapter
- NCERT Physics Class11th Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion Solutions
Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 System of Particles and Rotational Motion: Key Topics, Weightage
While preparing for System of Particles and Rotational motion, students must focus on Moment of inertia, Torque, basic concepts of rotational motion, rotational kinetic energy, angular momentum, parallel and perpendicular axis theorems, and understanding the relationship between translational motion and rotational motion. See below the topics covered in this chapter:
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 6.1 | Introduction |
| 6.2 | Centre of Mass |
| 6.3 | Motion of Centre of Mass |
| 6.4 | Linear Momentum of a system of particles |
| 6.5 | Vector Product of Two Vectors |
| 6.6 | Angular Velocity and its Relation with Linear Velocity |
| 6.7 | Torque and Angular Momentum |
| 6.8 | Equilibrium of a Rigid Body |
| 6.9 | Moment of Inertia |
| 6.10 | Kinematics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis |
| 6.11 | Dynamics of Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis |
| 6.12 | Angular Momentum in case of Rotation About a Fixed Axis |
System of Particles and Rotational Motion Class 11 Weightage in JEE Mains, NEET
| Exam | Number of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| NEET | 1-2 questions | 4-8% |
| JEE Main | 2-3 questions | 4-6% |
NCERT Physics Class11th Solution PDF for System of Particles and Rotational Motion Chapter
Find below the link to download the free System of Particles and Rotational Motion Class 11 PDF. Once the students download the PDF, they can access it anytime from anywhere without the need for an internet connection. It is an effective study material for exam preparation.
Download Here: NCERT Solution for Class XI Physics Chapter System of Particles and Rotational Motion PDF
More Links
| NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 | NCERT Solutions Physics Class 11th | NCERT Solutions Class 11 and 12 |
NCERT Physics Class11th Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion Solutions
| Q.7.1 Give the location of the centre of mass of a (i) Sphere (ii) Cylinder (iii) Ring and (iv) Cube each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body? |
| Ans.7.1 All the structures specified are symmetric bodies with uniform mass density. For all these bodies, their centre of mass will lie in their geometric centres. Not necessarily, the centre of gravity of a circular ring is at the imaginary centre of the ring. |
| Q.7.2 In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 Å (1 Å = 10-10 m). Find the approximate location of the CM of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. |
| Ans.7.2 If mass of the H atom = m, mass of the Cl atom = 35.5m Given x + y = 1,27 À Let us assume that the centre of mass of the given molecule lies at the origin. Therefore, We can have,: (my+35.5mx)/(m+35.5m) = 0 mx + 35.5my = 0 x = 35.5 (1.27 – x) x = 1.24 À So the centre of mass lies 1.24 À from H atom |
| Q.7.3 A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with a speed V on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system? |
| Ans.7.3 The child is sitting on the trolley and there is no external force, hence it is a single system. The velocity of the centre of mass will not change, irrespective of any internal motion. |
| Q,7.4 Show that the area of the triangle contained between the vectors a and b is one half of the magnitude of a × b. |
| Ans.7.4 Let AB is equal to the vector a and AC be equal to the vector b. Consider two vectors = = = inclined at an angle MN = | | = | | | The area of ΔABC, we can write the relation Area of Δ ABC = AB = |
Commonly asked questions
7.1 Give the location of the centre of mass of a (i) Sphere (ii) Cylinder (iii) Ring and (iv) Cube each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body?
All the structures specified are symmetric bodies with uniform mass density. For all these bodies, their centre of mass will lie in their geometric centres.
Not necessarily, the centre of gravity of a circular ring is at the imaginary centre of the ring.
7.9 A car weighs 1800 kg. The distance between its front and back axles is 1.8 m. Its centre of gravity is 1.05 m behind the front axle. Determine the force exerted by the level ground on each front wheel and each back wheel.
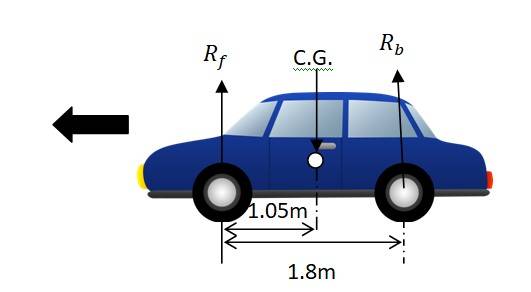
Mass of the car, m = 1800 kg
Distance between the front and rear axles, d = 1.8 m
Distance between C.G. and the front axle = 1.05 m
Let Rf and Rb be the force exerted from ground at front and rear axles respectively.
Rf + Rb = mg = 1800 x 9.8 N = 17640 N ……. (i)
For rotational equilibrium around C.G. we have Rf x 1.05 = Rb x (1.8 – 1.05)
Rf x 1.05 = Rb x 0.75
Rf/Rb = 0.75 / 1.05
Rf = 0.71 Rb ……. (ii)
From equation (i), we get
0.71 Rb + Rb = 17640
Rb = 10316 N
Rf = 7324 N
Therefore, force exerted on each front wheel = Rf/2 =7324/2 = 3662 N
Force exerted on each rear wheel, Rb/2 = 10316 / 2= 5158 N
7.16 From a uniform disk of radius R, a circular hole of radius R/2 is cut out. The centre of the hole is at R/2 from the centre of the original disc. Locate the centre of gravity of the resulting flat body
Radius of the original disc = R
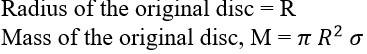
Mass of the smaller disc = = (1/4) = M/4
Let O and O’ be the respective centers of the original disc and the cut out disc respectively. As per the definition of the centre of mass, the centre of mass of the original disc is supposed to be concentrated at O, while that of the smaller disc is supposed to be concentrated at O’.
It is given, OO’ = R/2
After the smaller disc has been cut from the original, the remaining portion is considered to be a system of two masses. The two masses are
M – concentrated at O and M/4 concentrated at O’
Let x be the distance through which the centers of masses of two masses shifts from O.
The relation between the centers of masses is given as
x = (m1r1 + m2r2)/ (m1 +m2)
= = = x =
7.19 A hoop of radius 2 m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor so that its centre of mass has a speed of 20 cm/s. How much work has to be done to stop it?
Radius of the hoop, r = 2 m, mass of the hoop, m = 100 kg, velocity of the hoop, v = 20 cm /s = 0.2 m/s
Total energy of the hoop = Translational KE + Rotational KE = m +
Moment of inertia about the centre, I = mr2
So the total energy = m +
Since v = r we get
Total energy = m + =
Required work to be done = 100 x 0.2 x 0.2 J = 4 J
7.21 A solid cylinder rolls up an inclined plane of angle of inclination 30°. At the bottom of the inclined plane the centre of mass of the cylinder has a speed of 5 m/s.
(a) How far will the cylinder go up the plane?
(b) How long will it take to return to the bottom?
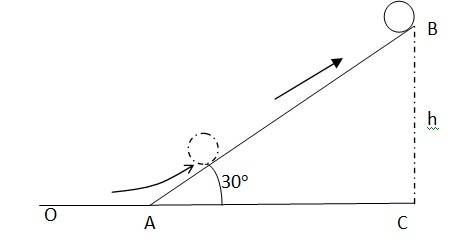
Initial velocity of the cylinder, v = 5 m/s
Angle of inclination, = 30
Height reached by the cylinder = h
Energy of the cylinder at point A:
KE rot + KEtrans
(1/2) I + (1/2) m
Energy of the cylinder at point B = mgh
Using the law of conservation of energy
(1/2) I + (1/2) m = mgh
Moment of inertia of the solid cylinder I = (1/2) mr2
Hence (1/2)(1/2)mr2 + (1/2) m = mgh
We also know v = r
(1/4)m + (1/2) m = mgh
(3/4) = gh
h = (3/4)( = (3/4)(25/9.81) = 1.91 m
In Δ ABC, = , AB = BC / = 3.82 m
Hence the cylinder will travel 3.82 m on the inclined plane
For radius of gyration K, the velocity of the cylinder at the instance when it rolls back to bottom is given by the relation
v = = )
for solid cylinder, =
v = ) = g AB )
The time taken to return to the bottom is :
t = = AB/ ( = ( = = 0.764 s
Therefore, the total time taken by the cylinder to return to the bottom is 2 x 0.764 = 1.53 s
7.3 A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with a speed V on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system?
The child is sitting on the trolley and there is no external force, hence it is a single system. The velocity of the centre of mass will not change, irrespective of any internal motion.
7.4 Show that the area of the triangle contained between the vectors a and b is one half of the magnitude of a × b.
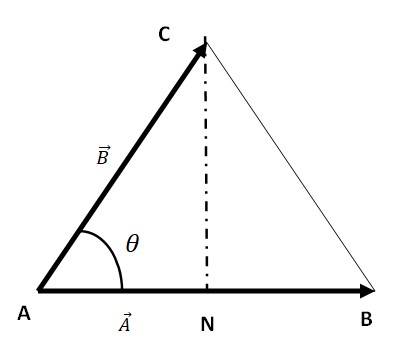
Let AB is equal to the vector a and AC be equal to the vector b.
Consider two vectors = =
= inclined at an angle
MN =
| | = | | |
The area of ΔABC, we can write the relation
Area of Δ ABC = AB =
7.2 In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 Å (1 Å = 10-10 m). Find the approximate location of the CM of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus.
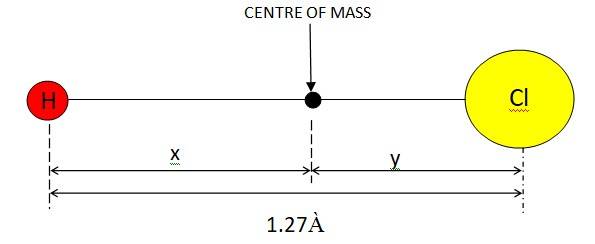
If mass of the H atom = m, mass of the Cl atom = 35.5m
Given x + y = 1,27 À
Let us assume that the centre of mass of the given molecule lies at the origin. Therefore,
We can have, : (my+35.5mx)/ (m+35.5m) = 0
mx + 35.5my = 0
x = 35.5 (1.27 – x)
x = 1.24 À
So the centre of mass lies 1.24 À from H atom
7.5 Show that a. (b × c) is equal in magnitude to the volume of the parallelepiped formed on the three vectors, a, b and c.
Let = , = , =
Let be a unit vector perpendicular to both b and c. Hence and a have the same direction
Now = bc
= bc = bc
Now )= a. (bc ) = abccos ? = abccos0° = abc = Volume of the parallelepiped
7.7 Two particles, each of mass m and speed v, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance d. Show that the angular momentum vector of the two particle system is the same whatever be the point about which the angular momentum is taken.
Let at certain instant two particles be at points P and Q, as shown in the figure.
Angular momentum of the system about point P
= mv x 0 + mv x d = mvd ……. (i)
Angular momentum of the system about point Q
= mv x d + mv x 0 = mvd ……. (ii)
Consider a point R, which is at a distance y from point Q such that QR = y
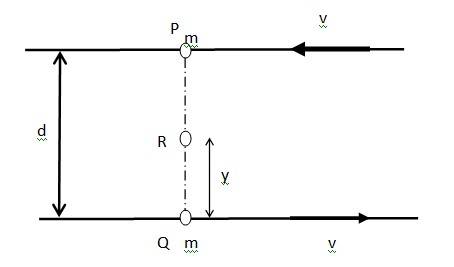
PR = d – y
Angular momentum of the system about point R
= mv x (d – y) + mv x y = mvd – mvy + mvy = mvd ……. (iii)
Comparing equations (i), (ii) and (iii) we get
= = …… (iv)
7.8 A non-uniform bar of weight W is suspended at rest by two strings of negligible weight as shown in Fig.7.39. The angles made by the strings with the vertical are 36.9° and 53.1° respectively. The bar is 2 m long. Calculate the distance d of the centre of gravity of the bar from its left end.
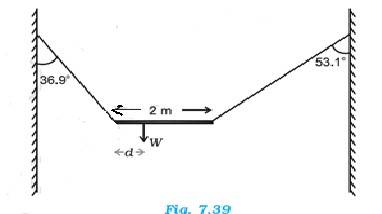
A free body diagram needs to be drawn.
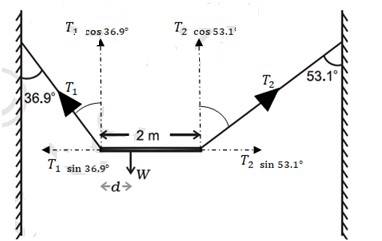
The length of the bar, l = 2 m
T1 and T2
At translational equilibrium, we have =
(T1 / T2) = ( / = 4/3
T1 = (4/3)T2
For rotational equilibrium, on taking the torque about the centre of gravity, we have
T1 x d = T2 (2-d)
T1 x 0.8d = T2 x 0.6 (2-d)
(4/3)T2 x 0.8d = T2 x 0.6 (2-d)
(4/3) x 0.8d = 0.6 (2-d)
1.07d = 1.2 – 0.6d
d = 0.72
So the c.g. of the given bar lies at 0.72 m from its left end.
7.10 (a) Find the moment of inertia of a sphere about a tangent to the sphere, given the moment of inertia of the sphere about any of its diameters to be 2MR 2/5, where M is the mass of the sphere and R is the radius of the sphere.
(b) Given the moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius R about any of its diameters to be MR 2/4, find its moment of inertia about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge.
(a)
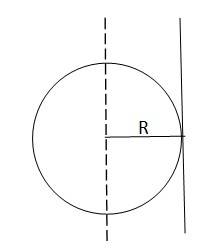
The moment of Inertia of a sphere about its diameter = 2MR 2/5
According to the theorem of parallel axis, the moment of inertia of a body about any axis is equal to the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about a parallel axis passing through its centre of mass and the product of its mass and square of the distance between two parallel axes
Hence the moment of inertia about a tangent of the sphere = 2MR 2/5 + MR2 = 7MR 2/5
(b)
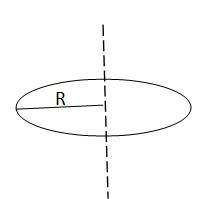
The moment of inertia of a disc about its diameter = MR 2/4
According to the theorem of perpendicular axis, the moment of inertia of a planar body about an axis perpendicular to its plane is equal to the sum of its moments of inertia about two perpendicular axes concurrent with perpendicular axis and lying in the plane of the body.
The M.I. of the disc about its centre = MR 2/4 + MR 2/4 = MR 2/2
Applying the theorem of parallel axis,
The M.I. about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge
= MR 2/2 + MR2 = 3MR 2/2
7.11 Torques of equal magnitude are applied to a hollow cylinder and a solid sphere, both having the same mass and radius. The cylinder is free to rotate about its standard axis of symmetry, and the sphere is free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre. Which of the two will acquire a greater angular speed after a given time.
Let m and r be the mass and radius of the hollow cylinder and solid sphere.
The moment of inertia of the hollow cylinder about its standard axis, =I
The MI of the solid sphere about an axis passing through its centre, Is = (2/5) mr2
We know the relation = I , where
= angular acceleration
= torque
I = moment of inertia
For the hollow cylinder, =
For the solid sphere, =
Since the torque applied is same, = , we get
= = (mr2) /( (2/5) mr2 )) = 5/2
Hence ……(i)
Now using the relation
+ where
= initial angular velocity
t = time of rotation
= final angular velocity
We get is proportional to
So we can write
>
7.12 A solid cylinder of mass 20 kg rotates about its axis with angular speed 100 rad s-1. The radius of the cylinder is 0.25 m. What is the kinetic energy associated with the rotation of the cylinder? What is the magnitude of angular momentum of the cylinder about its axis?
Mass of the cylinder, m = 20 kg
Angular speed, = 100 rad/s
Radius of the cylinder, r = 0.25 m
The moment of inertia of the solid cylinder
I = (1/2) mr2 = (1/2) x 20 x (0.25)2 = 0.625 m2
Kinetic energy = (1/2)I 2 = (1/2) x 0.625 x (100)2 = 3125 J
Angular momentum, L = I = 0.625 x 100 = 62.5 Js
7.13 (a) A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rev/min. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to 2/5 times the initial value ? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction.
(b) Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
(a) Initial angular velocity, = 40 rev/min, let the final angular velocity be
Let the moment of inertia of the boy with hands stretched be I1 and
M.I. with folded hands be I2
Given I2 = (2/5) I1
Since no external force acts on the boy, the angular momentum will remain constant.
Hence I1 = I2 , I1/I2) x = (5/2) x 40 = 100 rev/min
(b) Kinetic energy Ev = (1/2)I
Hence ( Final KE / Initial KE ) = (I2 )/ (I1 ) = { (2/5) I1 x 100 x 100 } / { I1 x 40 x 40 }
= 2.5
7.14 A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N ? What is the linear acceleration of the rope ? Assume that there is no slipping.
Mass of the hollow cylinder, m = 3 kg
Radius of the hollow cylinder, r = 40 cm = 0.4 m
Applied force, F = 30 N
The MI of the hollow cylinder about its axis,
I = = 3 x 0.4 x 0.4 = 0.48 kgm2
Torque, = 30 x 0.4 = 12 Nm
For angular acceleration , torque is given by
= I x or
/ I = 12 / 0.48 = 25 rad/s
Linear acceleration = r x = 0.4 x 25 = 10 m/s2
7.15 To maintain a rotor at a uniform angular speed of 200 rad s-1, an engine needs to transmit a torque of 180 N m. What is the power required by the engine ?
(Note: uniform angular velocity in the absence of friction implies zero torque. In practice, applied torque is needed to counter frictional torque). Assume that the engine is 100% efficient.
Angular speed of the rotor, = 200 rad/s
Torque, = 180 Nm
Power required, P = x = 180 x 200 = 36 x103 W = 36 kW
7.17 A meter stick is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coins, each of mass 5 g are put one on top of the other at the 12.0 cm mark, the stick is found to be balanced at 45.0 cm. What is the mass of the meter stick?
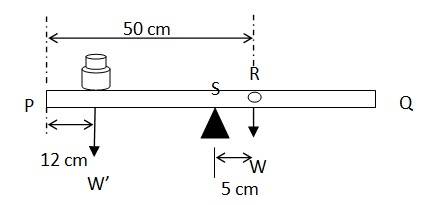
Mass of the meter stick = W
Mass of each coin = 5 g
When the coins are placed 12 cm away from the end P, the centre of mass gets shifted by 5 cm from point R towards the end P. The centre of mass is located at a distance of 45 cm from point P.
The net torque will be conserved for rotational equilibrium about point R,
10 x (45-12) – W' (50-45) = 0
W' = (10 x 33)/5 = 66 g
7.18 A solid sphere rolls down two different inclined planes of the same heights but different angles of inclination. (a) Will it reach the bottom with the same speed in each case? (b) Will it take longer to roll down one plane than the other? (c) If so, which one and why?
(a) Let the mass of the sphere = m
Height of the plane = h
Velocity of the sphere at the bottom of the plane = v
At the top of the plane, the total energy of the sphere = potential energy = mgh
At the bottom of the plane, the sphere has both translational and rotational energies.
Hence, total energy = (1/2)mv2 + (1/2)I
Using the law of conservation of energy, we can write: (1/2)mv2+ (1/2)I = mgh …(1)
For a solid sphere, the moment of inertia, I = (2/5)mr2
The equation (1) becomes (1/2)mv2 + (1/2)( (2/5)mr2 = mgh
(1/2) v2 + (1/5)r2 = gh
From the relation v = , we get
(1/2) v2+ (1/5) v2= gh
v =
Since v depends only on g (constant) and h (height = constant), the velocity at the bottom remains same from whichever plane the sphere rolled.
(b) Yes
(c)
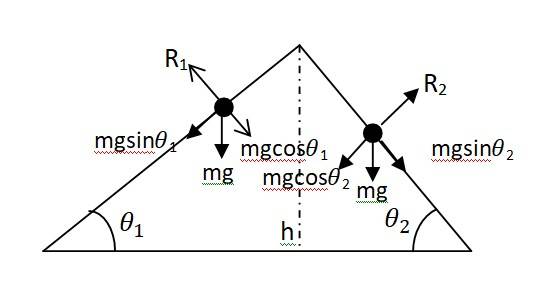
Consider two inclined planes with inclinations and related as > .
The acceleration produced in the sphere where it rolls down the plane inclined at is given as g sin . Similarly for the plane with inclination is given as g sin
Let R1 and R2 be the normal reaction to the sphere on these two planes
Since > , > sin …..(i)
> …….(ii)
From the equation v = u +at where u = 0 and v = constant, we get t (1/a)
For inclination ,t1 (1/a1) and t2 (1/a2)
Therefore t2 < t1
So the sphere will take a longer time to reach plane with smaller inclination.
7.20 The oxygen molecule has a mass of 5.30 × 10-26 kg and a moment of inertia of 1.94×10-46 kg m2 about an axis through its centre perpendicular to the lines joining the two atoms. Suppose the mean speed of such a molecule in a gas is 500 m/s and that its kinetic energy of rotation is two thirds of its kinetic energy of translation. Find the average angular velocity of the molecule.
Mass of the oxygen molecule, m = 5.30 × 10-26 kg
Moment of inertia, I = 1.94×10-46 kg m2
Velocity of the oxygen molecule, v = 500 m/s
the separation of atoms in oxygen molecule = 2r.
the mass of each oxygen atom = (m/2)
Moment of inertia I can be calculated as I = (m/2)r2 + (m/2)r2
hence r =
r = sqrt (1.94×10-46 / 5.30 × 10-26 = 6.05 x 10-11
It is given that KErotation = KEtranslation
(1/2)I = (2/3) (1/2)mv2
= (v/r)
= 6.8 x 1012 rad/s
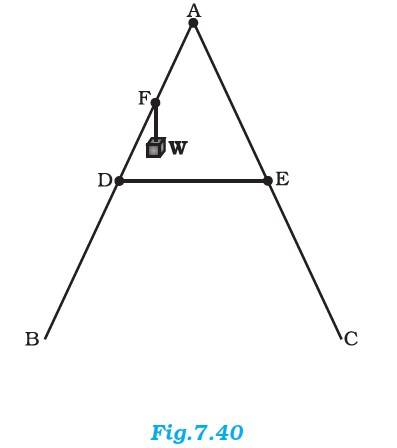
7.22 As shown in Fig.7.40, the two sides of a step ladder BA and CA are 1.6 m long and hinged at A. A rope DE, 0.5 m is tied half way up. A weight 40 kg is suspended from a point F, 1.2 m from B along the ladder BA. Assuming the floor to be frictionless and neglecting the weight of the ladder, find the tension in the rope and forces exerted by the floor on the ladder. (Take g = 9.8 m/s2)
(Hint: Consider the equilibrium of each side of the ladder separately.)
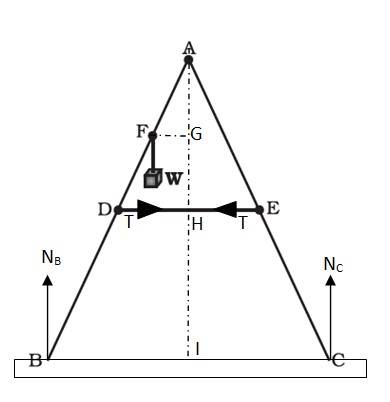
The given situation can be shown as
NB = force exerted on the ladder by the floor point B
NB = force exerted on the ladder by the floor point B
T = Tension in the rope
BA = CA = 1.6 m, DE = 0.5 m and BF = 1.2 m
Mass of the weight, m = 40 kg
The perpendicular drawn from point A on the floor BC, this intersects DE at mid-point H.
Δ ABI and ΔACI are congruent. Therefore BI = IC, I is the mid-point of BC. DE is parallel to BC.
BC = 2 x DE = 1 m and AF = BA – BF = 0.4 m…… (i)
D is the mid-point of AB, hence we can write
AD = (1/2) x BA = 0.8 ……. (ii)
Using equation (i) and (ii), we get FE = 0.4 m
Hence, F is the mid-point of AD.
Hence G will also be the midpoint of AH.
ΔAFG and ΔADH are similar
FG = (1/2)DH = (1/2) X 0.25 = 0.125 M
In ΔADH, AH = - ) = – ) = 0.76 m
For translational equilibrium of the ladder, the upward force should be equal to the downward force, NC + NB = mg = 392 …… (iii)
For rotational equilibrium of the ladder, the net moment about A is
NB x BI +mg x FG + NC x CI + T x AG – T x AG = 0
NB x 0.5 +40 x g + 0.125 x NC x 0.5 = 0
(NC - NB) x 0.5 = 49
NC - NB = 98 ………. (iv)
Adding equation (iii) and (iv) we get
NC = 245 N, NB = 147 N
For rotational equilibrium of the side AB, considering the moment about A
NB x BI + mg x FG + T x AG = 0
245 x 0.5 + 40 x 9.8 + T x AG = 0
T = 96.7 N
7.23 A man stands on a rotating platform, with his arms stretched horizontally holding a 5 kg weight in each hand. The angular speed of the platform is 30 revolutions per minute. The man then brings his arms close to his body with the distance of each weight from the axis changing from 90cm to 20cm. The moment of inertia of the man together with the platform may be taken to be constant and equal to 7.6 kg m2.
(a) What is his new angular speed? (Neglect friction)
(b) Is kinetic energy conserved in the process? If not, from where does the change come about?
(a)
Moment of Inertia of the man-platform system = 7.6 kg-m2
Moment of inertia when the man stretches his hands to a distance 90 cm
= 2 x mr2 = 2 x 5 x (0.9)2 = 8.1 kg-m2
Initial moment of inertia of the system, = 7.6 + 8.1 = 15.7 kg-m2
Angular speed = 30 rev/min
Angular momentum, = = 15.7 x 30 …… (i)
Moment of inertia when the man folds his hands to a distance of 20 cm
= 2 x mmr2= 2 x 5 x (0.2)2 = 0.4 kg-m2
Final moment of inertia, = 7.6 + 0.4 = 8 kg-m2
Final angular speed = and final angular of momentum, = = 8 …… (ii)
From the conservation of angular momentum, we have =
= = 58.88 rev/min
(b) Kinetic energy is not conserved in the given process. In fact, with the decrease in the moment of inertia, kinetic energy increases. The additional kinetic energy comes from the work done by the man to fold his hands towards himself.
Explore exams which ask questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th
Select your preferred stream
physics ncert solutions class 11th Exam
Student Forum
Other Similar chapters for you
- NCERT Physics 11th
- Physical World
- Units and Measurements
- Motion in a Straight Line
- Motion in a Plane
- Laws of Motion
- Work, Energy, and Power
- System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Gravitation
- Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Thermal Properties of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Kinetic Theory
- Oscillations
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test
