Adverbs are one of the most crucial components of English Grammar. It is important to understand Adverbs to get a hold of the basic English grammar. An Adverb is a word or expression that modifies a verb, an adjective, other adverb, a preposition, a clause, or a sentence. There are six main types of Adverbs. They are categorized into several types as per their function and what they describe. These are Adverbs of Manner, Adverbs of Place Adverbs of Time, Adverbs of Degree, Adverbs of Frequency, and Conjunctive Adverb.
Questions in Adverbs in English are relevant in many English language proficiency tests such as IELTS, TOEFL, PTE, etc. Here is a comprehensive guide for students to understand Adverbs in English. From this page, students can learn what are adverbs, the types of adverbs, common mistakes, practice questions, etc.
How do I identify an Adverb?
Adverb is a word that describes or modifies a Verb, Adjective, or another Adverb. Generally, it provides more information about when, how, where, how much, or to what extent something happens. A few of the Adverb examples are He has small dog, The movie was really interesting, It was a very sunny day. The common types of Adverbs are listed below:
- Adverb of Manner
- Adverb of Place
- Adverb of Time
- Adverb of Frequency
- Adverb of Degree
- Conjunctive Adverbs
How to explain Adverb to a child?
To explain an Adverb to a child, it is important to keep the concept simple while explaining. Make it relatable by citing fun examples from everyday life:
Simple definition for kids: An Adverb is a word that tells more about the action. It tells how, where, or when something happens.
Explanation: Think of a Verb as the action (like eat, run, or play) and an Adverb is a world that tells how, when, or where that action happens
A few examples of Adverbs are:
1. He eats: Just an action | He eats slowly: Adverbs tells how she eats
2. I will play: Just an action | I will play tomorrow: Tomorrow tells when
3. The dog barked: Basic action | The dog barked loudly: Loudly here tells how
Small tip to remember them: May Adverbs end in –ly, like slowly, happily, quickly
- What is an Adverb?
- English Adverbs: Definition
- Types of Adverbs in English
- How Adverbs Modify Parts of Speeches and Sentences?
- Rules of Adverbs in English Grammar
- Importance of Adverbs in English
- Difference between Adjective and Adverb
- Preparation Tips to Master Adverbs in English Grammar
- How to Identify Adverbs in a sentence?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Adverbs
- Examples of Adverbs in English Grammar
- Best Books to Prepare for Adverbs in English
- Adverbs Exercises with Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- FAQs of Adverbs
What is an Adverb?
An Adverb is a word that modifies an adjective, a verb, another adverb, a sentence or a preposition. In simple words, the main purpose of Adverbs is to provide additional context to something such as when, how, where, and to what extent. These can be categorized into various types according to their functions such as time, duration, frequency, place, degree, etc.
A simple way to understand an Adverb and what it denotes is given below:
| What is an Adverb? |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| An Adverb is a word that modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It tells the context about when, how, where, how much, or how often something happens. |
||||
| When? |
How? |
Where? |
How Much? |
How Often? |
| Already |
Carefully |
Away |
Barely |
Annually |
| Afterward |
Badly |
Away |
Almost |
Always |
| Eventually |
Closely |
Behind |
Entirely |
Hardly |
| Early |
Cheerfully |
Down |
Completely |
Frequently |
| Later |
Fast |
Far |
Fairly |
Often |
| Recently |
Easily |
Here |
Slightly |
Occasionally |
| Soon |
Loudly |
There |
Too |
Rarely |
Also Read:
Commonly asked questions
How do you identify adverbs in a sentence?
To identify an Adverbs in a sentence, here is a step-by-step guide to spot an Adverb:
- First of all, find the main verb in a sentence
- Then, ask questions about the verb such as How? When? Where? To what extent? How often?
- Lastly, look for the words that answer those questions. These words are called as Adverbs
Some examples of Adverbs are:
- She sings beautifully. Verb here is sings and Beautifully is an Adverb
- She arrived late. Verb here is arrived and Late is an Adverb
- He almost won the race. Here, almost is an Adverb
What is the difference between a Verb and an Adverb?
Adverbs and Verbs are different parts of speech that have different function in a sentence. Verbs express an action or state of being, while Adverbs modify Verbs, Adjectives or other Adverbs, proving detail about when, how, where, to what extent something is done.
Basic difference is:
Parameters | Verbs | Adverbs |
|---|---|---|
Function | Verbs are the main action or state | Adverbs modify other words |
Ending | No such role for Verbs | Many Adverbs end in –ly, though not this |
Examples | She runs every morning | She quickly ran |
English Adverbs: Definition
As per the Oxford Dictionary, Adverbs is “a word that adds more information about place, time, manner, cause or degree to a verb, an adjective, a phrase or another adverb”
Pronunciation: /ˈædvɜːrb/
Word Origin: Late Middle English: from Latin adverbium , from ad- ‘to’ (expressing addition) + verbum ‘word, verb’.
Adverb Example:
My grandmother visited my house yesterday. (Here, yesterday depicts when something happened. So, yesterday is the Adverb of Time)
Adverb: Definition according to Collins Dictionary
According to Collins Dictionary, “An Adverb is a word such as ‘slowly’, ‘now’, ‘very’, ‘politically’ or ‘fortunately’ which adds information about the action, event, or situation mentioned in a clause”.
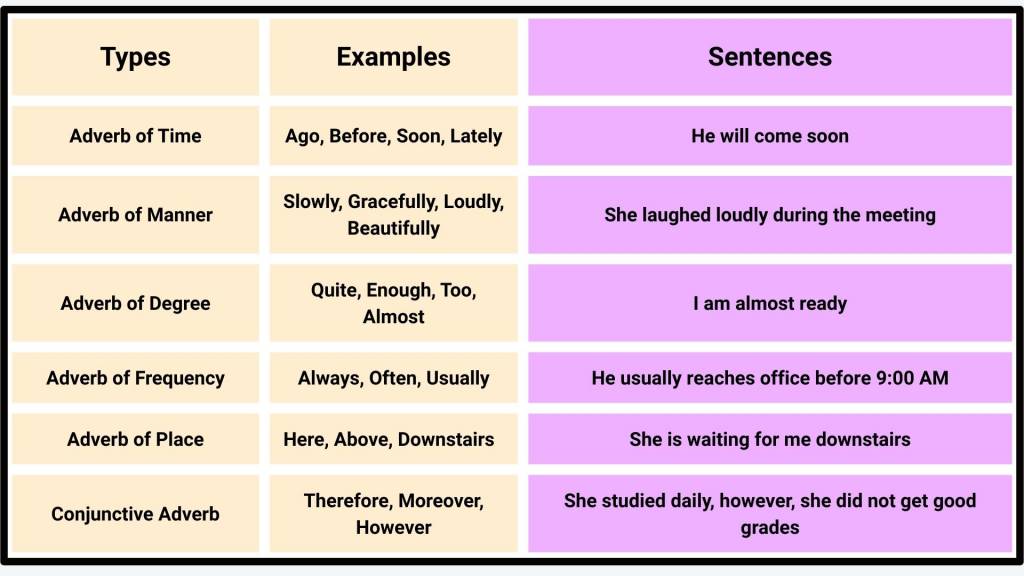
Types of Adverbs in English
Broadly, Adverbs in English can be divided into six categories as per what kind of details they are providing. The six common types of Adverbs are Adverbs of Manner, Adverbs of Time, Adverbs of Place, Adverbs of Degree, Adverbs of Frequency, and Conjunctive Adverbs. The types of adverbs are categorized below in detail:
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of Manner basically describe the manner in which an action is done. It primarily answers the question ‘how’.
Examples: Clearly, Quickly, Gradually, Rapidly, Instantly, etc.
- Rachel bravely rescued a kitten from a tree
- The fire spread rapidly in the room
- She crossed the road carefully
- He spoke loudly to make his point
Adverbs of Time
In simple words, Adverbs of Time describes when an action or situation has happened. These could include words that describe the specific time or general time periods.
Examples: Yesterday, Tomorrow, Soon, Tonight, Since, Recently, Today, etc.
- We will reach Rishikesh tomorrow
- Tonight, I have a Doctor’s appointment
- Yesterday, I went to the market
- Chandler moved to a new city recently
Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of Frequency can be used to describe how often an action has been performed or is happening. These adverbs can be recognized by asking the question ‘how often’.
Examples: Rarely, Seldom, Monthly, Weekly, Annually, Usually, Sometimes, etc.
- My mother and I often go out for dinner
- Leonard occasionally eats junk food
- Amy seldom read the newspaper
- I rarely practice my piano lessons in the morning
Adverbs of Degree
Usually, Adverbs of Degree describe the intensity of an action or quality. They could be used as intensifiers to describe adjectives and other adverbs.
Examples: Really, Very, Extremely, Fairly, Somewhat, Too, Much, Quite, etc.
- He is very excited about the Manali trip
- The management at the concert was extremely helpful
- It is very hot outside today
- Monica is quite satisfied with her CAT results
Adverbs of Place
As the name suggests, the Adverbs of Place are used to indicate where the mentioned action is taking place or has taken place. These adverbs can be identified by asking the question ‘where’.
Examples: Outside, Inside, Somewhere, North, South, Somewhere, Left, Right, East, West, etc.
- Samantha is not able to find her keys anywhere
- She is waiting for you outside
- The dog hid underneath the bed
- The children are playing upstairs
Conjunctive Adverbs
A Conjunctive Adverb is an adverb that links different clauses or sentences, to show cause and effect, sequence, and contrast between the two clauses or sentences. It has a characteristic of a conjunction.
Examples:
- She was sick, therefore, she stayed home
- He wanted to go, however, it was raining
- All of us cleaned the house, then, we went shopping
- Nitin has to work hard, otherwise, he will not be able to score good marks
Here is a table depicting the Types of Adverbs along with their functions and examples.
| Type of Adverb |
Function |
Examples in Sentences |
|---|---|---|
| Adverb of Manner |
How something happens |
Divya sings beautifully |
| Adverb of Place |
Where something happens |
My parents are sitting outside |
| Adverb of Time |
When something happens |
She arrived yesterday |
| Adverb of Frequency |
How often something happens |
He always prays before going to sleep |
| Adverb of Degree |
To what extent does something happens |
It is raining heavily |
| Conjunctive Adverb |
Connects two independent clauses or sentences |
She was tired, still, she completed her deadlines |
How Adverbs Modify Parts of Speeches and Sentences?
Given below are the details as to how Adverbs modify adjectives, verbs, other adverbs, and sentences:
- Verb: An adverb describes when, how, where, and to what extent the action happens (Example: He runs quickly)
- Adjective: An adverb adds degree or intensity to an adjective. (Example: That painting is very beautiful)
- Adverb: When an adverb modifies another adverb, it intensifies or clarifies it. (Example: She sings very beautifully)
- Sentence: An adverb used in a sentence expresses or conveys the speaker’s attitude or provides a general perspective on the statement (Example: The weather report is almost always right)
Also Read:
Rules of Adverbs in English Grammar
There are some of the basic rules that a student must know to use Adverbs correctly in English Grammar. These are:
- Most Adverbs End in –ly
Several Adverbs are formed by adding –ly to adjectives.
| Adjective |
Adverb |
|---|---|
| Happy |
Happily |
| Quick |
Quickly |
| Slow |
Slowly |
| Careful |
Carefully |
Example:
- He runs quickly
- Samantha spoke softly in the assembly
- Adverbs answer significant questions
The types of Adverbs basically answer the questions like how, when, where, how often, and to what extent.
| Types of Adverbs |
Question Answered |
|---|---|
| Place |
Where? |
| Manner |
How? |
| Time |
When? |
| Frequency |
How often? |
| Degree / intensity |
To what extent? |
Example:
- He completed the task happily
- My parents live nearby
- She arrived late
- She is always on time
- Rahul is extremely tired
- Position of Adverbs in Sentences
A. Adverbs of Manner, Place, and Time generally go after the verb or are placed at the end of the sentence
Examples:
- Rekha danced gracefully
- She goes to bed late
B. Adverbs of Frequency are placed before the main verb, but, after ‘be’ verbs
Examples:
- She is never late to the office
- He always wakes up early
C. Adverbs of Degree usually go before adjectives or other adverbs
Examples:
- It is extremely hot today
- She worked very hard during her CAT preparation
Also Read: English Tenses
Importance of Adverbs in English
Adverbs in English grammar provide the context in a sentence by describing when, how, where, and to what extent something happens. They are used to modify adjectives, verbs, and even other adverbs. Majorly, Adverbs in English Grammar are used for the following purposes:
To add detail and precision to something: Adverbs tell about how something happens, where it happens, when it happens, how often, and to what extent. This makes the communication clearer and more specific.
Examples:
- Sanya laughed loudly
- Joe is extremely talented
- She ran very quickly
They modify various parts of speech: Adverbs can modify adjectives, verbs, and other adverbs. This makes adverbs important for expressing complicated ideas.
Examples:
- Reema sings beautifully
- Both of them travel often during holidays
- She will leave tomorrow
Adverbs express emotion, tone, or attitude: Many adverbs can help express the opinion or tone of the speaker. This adds emotion and depth to both speech and writing.
Examples:
- Unfortunately, I cannot come to the office today
- Reena is probably right
- I am extremely disappointed with her behavior
Adverbs improve style and fluency: A depth and rhythm to sentences can be added with the help of Adverbs. This can make any speech or writing more engaging.
Examples:
- Basic: He walked
- More expressive: He walked confidently and gracefully out of the interview
In all, Adverbs are important for better storytelling, precise descriptions, clearer instructions, and more natural conversations. Adverbs in English are important while reading, writing, speaking, and listening.
Also Read: English Grammar: Conjunctions
Difference between Adjective and Adverb
The major difference between an Adjective and an Adverb is the type of words they describe. Adjectives describe Nouns and Pronouns, whereas Adverbs describe Verbs, Other Adverbs, and Adjectives.
The table given below can be referred to know the basic difference between an Adverb in English Grammar and an Adjective.
| Particulars |
Adverb |
Adjective |
|---|---|---|
| What it describes |
An adjective, verb, or other adverb |
A noun or pronoun |
| What it tells |
When, how, where, how often, to what extent |
Which one, what kind, how many, etc. |
| Examples |
She danced beautifully |
The cake was delicious |
Preparation Tips to Master Adverbs in English Grammar
How to Identify Adverbs in a sentence?
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Adverbs
Examples of Adverbs in English Grammar
Best Books to Prepare for Adverbs in English
Adverbs Exercises with Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
FAQs of Adverbs
Commonly asked questions
What is an Adverb in Grammar with examples?
Adverbs in English is a word that describes or modifies an adjective, a verb, another adverb, or maybe a whole sentence. Usually, Adverbs answer the questions such as when, where, how, to what extent, how much, etc. A few examples of Adverbs are:
- The roads in my area are very steep
- The election in Delhi is coming soon
- They participated in the annual function happily
- Yesterday, I went to the market
- We will leave tomorrow for Bhutan
What are the most common types of Adverbs?
The most common types of adverbs are Adverbs of Manner, Adverbs of Place, Adverbs of Time, Adverbs of Frequency, Adverbs of Degree, and Conjunctive Adverb. The details of the types of Adverbs are given as follows:
Type of Adverb | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Adverbs of Manner | Tell how something happens | Slowly, quickly, loudly, carefully |
Adverbs of Place | Tell where something happens | Outside, here, there, inside |
Adverbs of Time | Tell when something happens | Now, soon, yesterday |
Adverbs of Frequency | Tell how often something happens | Often, always, sometimes, rarely |
Adverbs of Degree | Tell how much or to what extent | Too, Quite, Very, Extremely, Very |
Conjunctive Adverb | Connect clauses | Moreover, however, therefore |
What are the uses of adverbs?
Some of the uses of Adverbs in English are:
- Adds detail and clarity
- Help show emotion, tone, or attitude
- Provides important context by telling where, when, how, how often, something happens
- Boosts writing and speaking skills. By using Adverbs in English grammar, the language can make more dynamic, expressive, and descriptive
- Helps in exams and standardized tests
How can Adverbs help in standardized tests?
Knowledge of Adverbs can help students in English language proficiency tests such as IELTS, TOEFL, PTE or other exams. Since proficiency tests check the grammar skills, a knowledge of Adverbs can help one understand sentence structure, word placement, etc. Also, while writing essays, which are an integral part of applications, a knowledge of Adverbs can help add detail and clarity and make sentences more descriptive. Additionally, a knowledge of Adverbs can help in Reading Comprehension passages too. Adverbs in a passage can help one understand attitude, cause and effect, tone, frequency, and time. Furthermore, Adverbs in these proficiency tests appear in Grammar and Vocabulary questions.
Which books I can use to learn about Adverbs in English Grammar?
Here are some of the books that a student can refer to learn about Adverbs in English:
Books | Author / Publication |
|---|---|
Adjectives and Adverbs | Louise McNally |
Adverbs | Keshab Pradhan |
Reading Fundamentals – Verbs and Adverbs | Carolyn Hurst |
Adverbs and Verbs | Maggie Rock |
Dictionary of Adverbs: Vocabulary Building | Manik Joshi |
Adverbs: Things You Should Know | Rumi Michael Leigh |
Study of Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions & Interjections | Mr. Peter |
English Adverbs Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds