Has anyone ever praised you? Or have you ever, in a conversation, given particular features to anyone or anything? Every day, around us, we knowingly and unknowingly speak, listen to, and read many words that are used to give meaning or describe the features of any person, place, animal, or thing. What kind of sky do you see? Is it Clear, Cloudy or Sunny? What kind of restaurant do you like? A fancy one or a local one?
These words not only help us speak and write the attributes of a noun, but they also give us more clarity. Such words are one of the most essential elements of the parts of speech called “Adjectives.”
Adjectives have always been a hot topic when it comes to undergraduate or postgraduate exams, banking exams, government exams and other competitive exams demanding verbal aptitude from the students. Understanding of adjectives along with other parts of speech also forms the basis of English language tests for students planning to study abroad.
Through this article, Shiksha aims to help students understand adjectives from beginner to advanced levels. We will be covering Adjectives, meaning of Adjectives, Types, Degree of Adjectives, Exercises on Adjectives with Answers, etc. Read the full article to master English Adjectives with us.
What is the definition of Adjective?
An Adjective is a word that describes a Noun or Pronoun or adds meaning to it. It is that part of speech that describes, quantifies, or modifies a noun or pronoun. It gives more details about the noun by giving information about what kind, which one, how many, etc.
- What is Adjectives?
- Adjectives Definition
- Types of Adjectives and Examples in English Grammar
- Formation of Adjectives
- Comparison of Adjectives
- Preparation Tips to Master Adjectives
- How to identify Adjectives in a Sentence?
- Best Books for Adjectives
- Examples of Adjectives
- Adjectives in English Worksheet with Answers
- Frequently Asked Questions on Adjectives
What is Adjectives?
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or a pronoun. The main function of using adjectives in grammar in a sentence is to describe the nouns or pronouns, giving more information about their qualities, quantities, and identities. This description can be of features, attributes, or numbers. By adding such a description, the sentences become more specific and expressive. Without adjectives, the sentences would be vague and would lack clarity.
Check out the following examples to clearly understand the meaning of Adjectives.
1. She wore a beautiful frock.
("Beautiful" describes the noun frock.)
2. We visited an ancient temple.
("Ancient" gives more detail about the temple.)
3. There are five muskmelons on the table.
("Five" tells the number of muskmelons.)
4. He adopted a stray cat.
("Stray" describes the type of cat.)
5. The sky is clear today.
("Clear" describes the condition of the sky.)
Also Read:
| Types of Sentences in English: Comprehensive Guide | English Composition: Meaning, Types, Preparation Guide with Examples |
Adjectives Definition
Collins Dictionary – Definition of Adjective
An adjective is a word, such as big, dead, or financial, that describes a person or thing or gives extra information about them. Adjectives usually come before a noun or after linking verbs such as be, become, seem, etc.
Oxford Dictionary – Definition of Adjective
Pronunciation: /ˈædʒɪktɪv/
A word that describes a noun or pronoun. For example, in the phrases tall building and blue sky, tall and blue are adjectives.
Pronunciation: /ˈædʒɪktɪv/
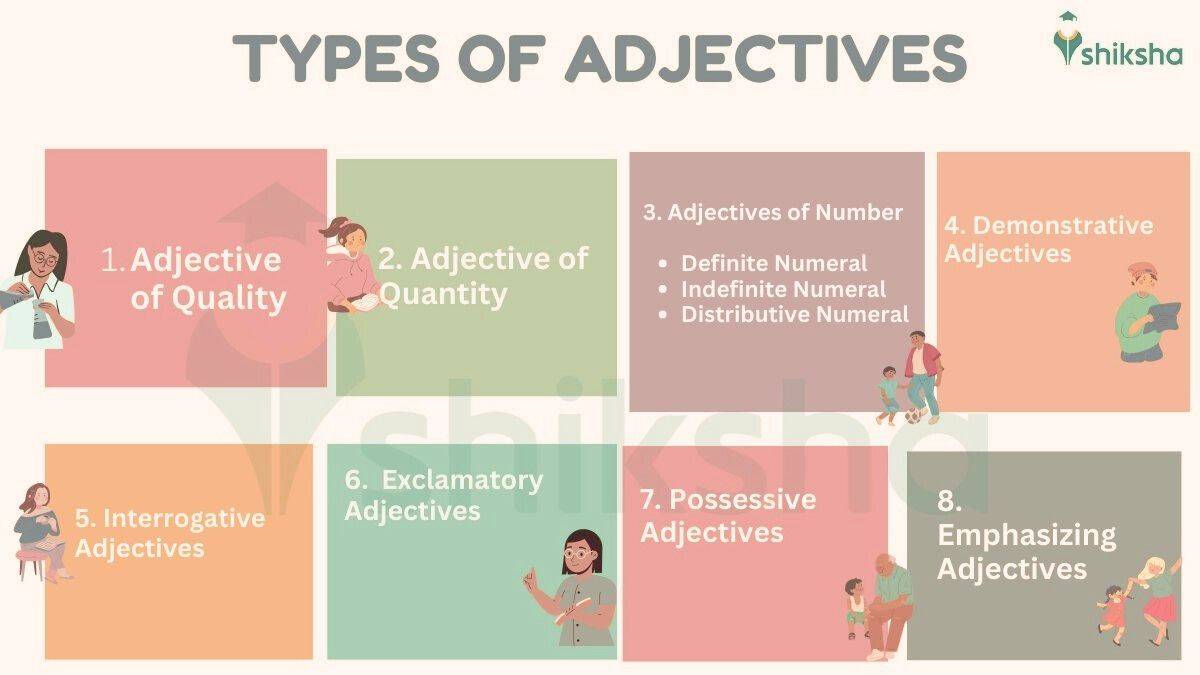
Types of Adjectives and Examples in English Grammar
There are eight main kinds of adjectives in English. The kinds of Adjectives with examples are as follows:
1. Adjectives of Quality
The Adjectives of Quality are also known as Descriptive Adjectives. They describe the kind, quality or characteristics of a person, place, animal, or thing. The sentences with Adjectives of Quality will have words like big, small, beautiful, foolish, fat, etc.
Example:
- She is a clever witch.
- Lord is an honest man.
2. Adjectives of Quantity
These adjectives indicate or tell us how much of a thing is meant, but they do not tell the exact quantity. They do not give any information in the definite terms. The sentences with such adjectives will always have words like some, much, little, half, etc.
Example:
- Much clay is needed for this pottery class.
- He ate some candies.
3. Adjectives of Number
These can also be called Numeral Adjectives. These indicate how many persons or things are meant or in what order a person or things stand. They are of three types:
i) Definite Numeral Adjectives: They indicate the exact number.
Example:
- Two parrots are sitting on a tree.
- He has four fingers.
ii) Indefinite Numeral Adjectives: These types of adjectives do not indicate the exact number.
Example:
- There are many rooms in this hotel.
- The advertisement was displayed at several places.
iii) Distributive Numeral Adjectives: These adjectives refer to each single person or thing in a group.
Example:
- Every soldier should be ready to fight for the country.
- Either laptop will do.
Also Read:
| Synonyms for common words | Preparation tips to master English prepositions |
4. Demonstrative Adjectives
These adjectives indicate or point out which person or thing is meant
Example:
- Bring that cup.
- This boy is injured.
5. Interrogative Adjectives
These adjectives are used with nouns to ask questions. Words like what, which, whose, when, etc., are used to ask questions.
Example:
- Who will book the movie tickets?
- Which train shall we take?
6. Exclamatory Adjectives
Under exclamatory adjectives, the word what is used.
Example:
- What a fine dining it was!
- What a curious girl!
7. Possessive Adjectives
These adjectives indicate possession.
Example:
- He is my friend.
- He is mine.
8. Emphasizing Adjectives
Under emphasizing adjectives, words like very and own are used to give more emphasis.
Example:
- I saw him cheating in the exam with my own eyes.
- She is her own boss.
Formation of Adjectives
Adjectives as formed from Nouns, Verbs, and other Adjectives. Some Adjectives are formed from Nouns, some are formed from verbs, and many are formed from other adjectives.
1. Many Adjectives are formed from Nouns.
The following table gives some examples of Adjectives that are formed using Nouns:
| Noun |
Adjectives |
|---|---|
| Girl |
Girlish |
| Dirt |
Dirty |
| Man |
Manly |
| Hope |
Hopeful |
| Envy |
Envious |
2. Some of the Adjectives are formed from Verbs.
The following table gives some examples of adjectives that are formed using verbs:
| Verb |
Adjectives |
|---|---|
| Talk |
Talkative |
| Move |
Movable |
| Sleep |
Sleepless |
| Break |
Breakable |
| Create |
Creative |
3. Some Adjectives are also formed from other Adjectives.
The following table gives some examples of adjectives that are formed using other adjectives:
| Adjectives |
Adjectives |
|---|---|
| White |
Whitish |
| Happy |
Unhappy |
| Dark |
Darker |
| Soft |
Softer |
| Red |
Reddish |
Also Read:
Comparison of Adjectives
Adjectives have three degrees of comparison to show differences in quality, quantity, or condition. In order to show the comparison, the Adjectives change forms. These are called the Degree of Comparison.
1. Positive Degree
When an Adjective is in its simple form, it is known as the Positive Degree. Such a degree is used to denote the mere existence of some quality that we speak about. In this, no comparison is made.
Example: The questions in the test are easy.
2. Comparative Degree
Comparative degree is used to denote a higher degree of the quality than the positive degree. It is used when we have to make a comparison between two things.
Example: The questions in this test are easier than the last one.
3. Superlative Degree
Superlative Degree is used to denote the highest degree of quantity. It is used when we have to make a comparison when more than two things are involved.
Example: The questions in this test are the easiest of all the tests.
| Degree of Comparison |
Comparison |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Degree |
No comparison is made. |
He is tall. |
| Comparative Degree |
Comparison is made between two things. |
He is taller than Kareem. |
| Superlative Degree |
Comparison is made between many. |
He is the tallest of all. |
Examples of Comparison of Adjectives
The following table gives examples of Comparison of Adjectives:
| Positive Degree |
Comparative Degree |
Superlative Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Bold |
Bolder |
Boldest |
| Young |
Younger |
Youngest |
| Noble |
Nobler |
Noblest |
| Merry |
Merrier |
Merriest |
| Fat |
Fatter |
Fattest |
| Sad |
Sadder |
Saddest |
| Industrious |
More industrious |
Most industrious |
| Courageous |
More courageous |
Most courageous |
| Polite |
Politer/ More Polite |
Politest/Most Polite |
| In |
Inner |
Inmost |
Also read:
| Auxiliaries and Modal Verbs with Examples and Exercises | Tenses in English Grammar |
Preparation Tips to Master Adjectives
The following tips can help to master adjectives. Go through them and try to inculcate them in your lives.
- Work on Basics: Start with knowing about Adjectives, its rules, degrees, usage, etc. Understand how adjectives are used with nouns, pronouns, in sentences, etc. For example, when to use the positive degree and when to use the comparative degree.
- Practice daily: The best way to master your adjectives is to practice daily. Use them in your daily life conversation. Try to learn new vocabulary, practice them, and use them with different situations and conditions of the Adjectives given above. By this, you can learn how to use adjectives easily, and it will also build confidence.
- Read Newspaper: Reading an English newspaper daily works like magic. It will not only help to improve your adjectives but also improve your English overall. To begin with, read the section in which you are interested. Some of the popular newspapers are The Indian Express, The Times of India, Hindustan Times, The Hindu, etc. These newspapers are also available online.
- Play Online Games and Quizzes: Many online games and Quizzes are available online, which are very interesting. You can learn while playing in no time. Simon Says, Sentence Building game, Bingo, Grammar Charades, etc., are some of the popular games.
How to identify Adjectives in a Sentence?
To identify adjectives in a sentence, the following tips or rules can be helpful:
1. Identify the Words that Describe Nouns or Pronouns
Adjectives give more detail or describe the nouns and pronouns. They give details about kind, numbers, how many, how much, which one, etc.
Example: The car is clean.
Here, the word clean describes the car. So clean is an adjective here.
2. Position of the Adjectives
Always keep an eye on the position of the adjectives. They usually appear before nouns or after the linking verbs. Words like is, seems, becomes are linking verbs.
Example: She is wearing a beautiful suit.
Here, the word beautiful (Adjective) comes before the noun.
Example: The question paper was difficult.
Here, the word difficult comes after the linking verb.
3. Ask Questions about Noun/Pronoun
Always ask questions about nouns and pronouns to know about the describing words (adjectives). Ask questions related to their kind, quantity, quality, numbers, etc.
Example: A ceramic bowl.
The question for this will be: What kind of bowls? And the answer for this will be ‘A ceramic bowl’. So ceramic is an adjective here.
4. Pay Attention to Comparative and Superlative Forms
Always check on words ending with –er or –est, more, most, as they are often objective. Words like happier, happiest, easier, easiest, more beautiful, and most beautiful.
Examples: She is happier than before.
5. Pay Attention to Suffixes
Always check on words ending with –ous, -able,-ive,-ic, etc. These words are adjectives most of the time.
Examples: curious, nervous, readable, understandable, attractive, historic, aesthetic
Example: I’m curious about the last scene of this movie.
Best Books for Adjectives
Examples of Adjectives
Adjectives in English Worksheet with Answers
Frequently Asked Questions on Adjectives
Commonly asked questions
How to identify an adjective?
The following steps will help to identify the Adjectives:
- Identify the Words that Describe Noun or Pronouns
- Pay attention to the Position of the Adjectives
- Ask questions about noun and pronoun to know the details
- Pay Attention to Comparative and Superlative Forms
- Pay Attention to Suffixes
What is the definition of Adjective?
An Adjective is a word that describes a Noun or Pronoun or adds meaning to it. It is that part of speech that describes, quantifies, or modifies a noun or pronoun. It gives more details about the noun by giving information about what kind, which one, how many, etc.
What is the difference between adverb and adjective?
Adverbs are the word that modifies the meaning of a verb, an adjective or another adverb. They tell us about how much, in what manner, how far, in what degree and to what extent. E.g. all, very, probably, very, etc.
- Example: She learns quickly.
Adjectives are the words that add meaning to the nouns or pronouns. They simply make noun and pronoun more descriptive. E.g. beautiful, honest, brave, wealthy.
- Example: She is a quick learner.
What are 10 examples of Adjectives?
The examples of Adjectives are:
- Bangalore is a large city.
- Ram is an honest man.
- I ate some pudding.
- You have no time.
- Have a good day!
- Most girls like Barbie dolls.
- Don't be in such a hurry.
- The CAT is lazy.
- I don't like that cafe.
- There are five mangoes in the fridge.
What are the types of Adjectives?
The Adjetives are of following types:
Type of Adjective | Function / Usage | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Descriptive Adjectives | Tells about quality or kind of a person/thing | tall, beautiful, soft |
Quantitative Adjectives/Adjectives of Quantity | Tell us about the quantity of a thing | many, few, some |
Demonstrative Adjectives | Tell us about a specific thing or person which is meant | this, that, these, those |
Possessive Adjectives | Show ownership or possession | my, your, his, their |
Interrogative Adjectives | Asks questions about nouns | which, what, whose |
Distributive Adjectives | Refer to individual members of a group separately | each, every, either, neither |
Comparative & Superlative Adjectives | Show comparisons between two or more nouns | bigger, best, more intelligent |
English Adjectives Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds