
Tenses are one of the most important components of English Grammar. There are about 12 tenses in English. To establish effective English communication and master the language, it is important to learn tenses. Tenses are also a topic included in various entrance exams, such as CAT, IPMAT, and CUET. The inclusion of this topic in the top competitive exams indicates that Tenses in English are an important topic to focus on. There are mainly three types of tenses, i.e. Present Tense, Past Tense and Future Tense.
Shiksha has presented a comprehensive guide to help the students master the Tense in English Grammar, which includes what is a tense, common mistakes in tenses, grammar rules, verb and conjugation, the importance of tenses, tenses exercises and answers, and more. Read below to know what are tenses, types, rules, usage, how to prepare, common mistakes, tenses exercises with answers, etc.
Are all tenses equally important in competitive exams?
Yes, all the tenses hold equal importance in competitive and entrance exams. While some tenses such as the Present Tense and Past Tense appear more frequently in English grammar questions, understanding and studying all the 12 types of tenses in English ensure better comprehension and accuracy. Various questions on fill in the blanks and setence correction, include questions on tenses.
What are the 20 examples of present tense?
The 20 examples of different types of present tense are as follows:
- The jury has not reached a verdict yet.
- She has already worked on it.
- I am working on a project.
- He is going to London today.
- Ujjwal is learning English.
- Have you been sleeping since morning?
- The servant is waiting for the master.
- The kids play outside.
- He loves adventure sports.
- Manish watches the television at 10 PM.
- I am going to the market.
- Rahul goes to bed early.
- I am visiting Mount Carmel today.
- We do not speak Spanish.
- The train is moving, come on!
- She is my mother.
- I have not been singing.
- Frieda is listening to soothing music.
- I am painting a picture of a dog.
- Nora wakes up at 8 AM.
What are five examples for future perfect tense?
Find below some examples of future perfect tense in English:
- By next month, I will have finished this project.
- By 2028, the band will have toured across the globe.
- Mr. Kim will have cooked for his friend by the time they arrive.
- I won't have made this dish by dinner.
- I will not have saved enough money to buy concert tickets by next yest.
- What are Tenses in English?
- Tenses in Grammar: Definition
- Types of Tenses: 12 Tenses in English Explained
- Grammar Rules for Tenses
- Importance of Tenses in English
- Special Cases and Exceptions in English Grammar Tenses
- Tenses in Grammar: Difference Between Written and Spoken English
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Tenses
- Tenses in English Grammar with Examples
- Preparation Tips to Master Tenses
- Best Books to Prepare for Tenses in English
- Tenses Exercises with Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on Tenses
What are Tenses in English?
A Tense or verb tense is a form of the verb that allows an individual or person to express the time of action (present, past and/or future). The English Verb Tenses describe when an event or something existed or when a person did something. Different types and forms of tenses are used at all times in life. Another way of understanding the tenses is that tenses are the additions to the verb form to indicate the time of action.
Tenses act as the backbone of clear communication in English and help writers and speakers express themselves clearly and precisely.
Commonly asked questions
What are the four types of Present Tense?
The four types of Present Tense in the English language are Simple Present, Present Perfect, Present Perfect Continuous, and Present Continuous.
- The Simple Present is used for general truths, habits, and regular actions.
- Present Continuous is used for actions happening now or for planned future actions.
- Present Perfect tense is used for actions that started in the past and continued to the present.
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used for actions that started in the past and are still continuing in the present.
Which tense is used to describe habits?
Two tenses in English Grammar are used to describe habits. These are Simple Present Tense and Simple Past Tense.
Simple Present Tense is used to describe current habits.
For Example:
- She drinks coffee everyday.
- He goes to the temple daily.
Simple Past Tense is used to describe habits of the past. For example.
He used to jog every morning.
- She walked to school everyday when she was a little girl.
Tenses in Grammar: Definition
Tenses Definition According to the Oxford Dictionary
As per the Oxford Dictionary tenses is – “any of the forms of a verb that may be used to show the time of the action or state expressed by the verb”
Pronunciation- /tens/
Word Origin- noun Middle English (in the general sense ‘time’): from Old French tens, from Latin tempus meaning ‘time’.
Tense Example: I fed the dog. (Fed is the form of the verb which expresses the time of action and is the tense in this sentence)
Tenses Definition According to Collins Dictionary
As per the Collins Dictionary, tenses is – "a category of the verb or verbal inflexions, such as present, past, and future, that expresses the temporal relations between what is reported in a sentence and the time of its utterance."
Types of Tenses: 12 Tenses in English Explained
Typically, there are three types of tenses, which are further divided into four parts each to describe the degree of completeness of an action or situation, thus giving a total of 12 types of tenses:
-
Present Tense
The present tense is used to indicate the current time of being. In other words, it is used to tell the present time of action or current activity. It talks about what is happening right now, in this very moment. There are various types of tenses, each indicating different times of action. Present Tense in English is further classified into four types. The types of Present Tense are:
- Simple Present Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Examples of Present Tense:
- She lives in Delhi.
- I play the guitar.
- The bus is moving now.
- Tom is chasing the mice.
-
Past Tense
The past tense is used to describe an action or event which has happened in the past or a past state of being. The Past Tense is the type of tense that can be used to talk about or represent any action or event that has happened in the past. That is, the Past tense in English is a form of the verb that indicates an action that has already occurred before it was talked or written about.
Example:
- Ritu met Rohan yesterday.
- Ravi visited his grandmother in the morning.
- I was preparing for my project last night.
Also Read:
| Simple Past Tense Exercises with Answers | Past Perfect Tense: Examples and Exercises with Answers | Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Meaning, Rules, and Examples |
-
Future Tense
As the name indicates, the Future Tense is the verb tense where the action will happen in the future. The English Future Tense is used to describe an action or event which is expected to happen in the future and has not yet happened. The future tense is also divided into four subcategories, i.e.
Examples of Future Tense
- Pooja will be here soon.
- I will watch a movie tonight.
- She will be eating her dinner at 10 PM.
- Suresh will be getting lunch for Heena.
Tenses Sub-Types
As mentioned above, the three main tenses are further divided into four subparts each. The 12 English tenses are:
| 12 Tenses in English |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Types of Tenses |
Present Tense |
Past Tense |
Future Tense |
| Indefinite/Simple |
Present Indefinite Tense |
Past Indefinite Tense |
Future Indefinite Tense |
| Continuous |
Present Continuous Tense |
Past Continuous Tense |
Future Continuous Tense |
| Perfect |
Present Perfect Tense |
Past Perfect Tense |
Future Perfect Tense |
| Perfect Continuous |
Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
Future Perfect Continuous Tense |
Tenses in English are categorized among the above-mentioned types. Whether one is talking about a daily routine, past experience or future plans, these are the types of tenses which are used to describe the time of action. By understanding the structure, usage, and time references of each tense—present, past, and future, along with their simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms—one can improve his/her English fluency and avoid common grammar mistakes in tenses.
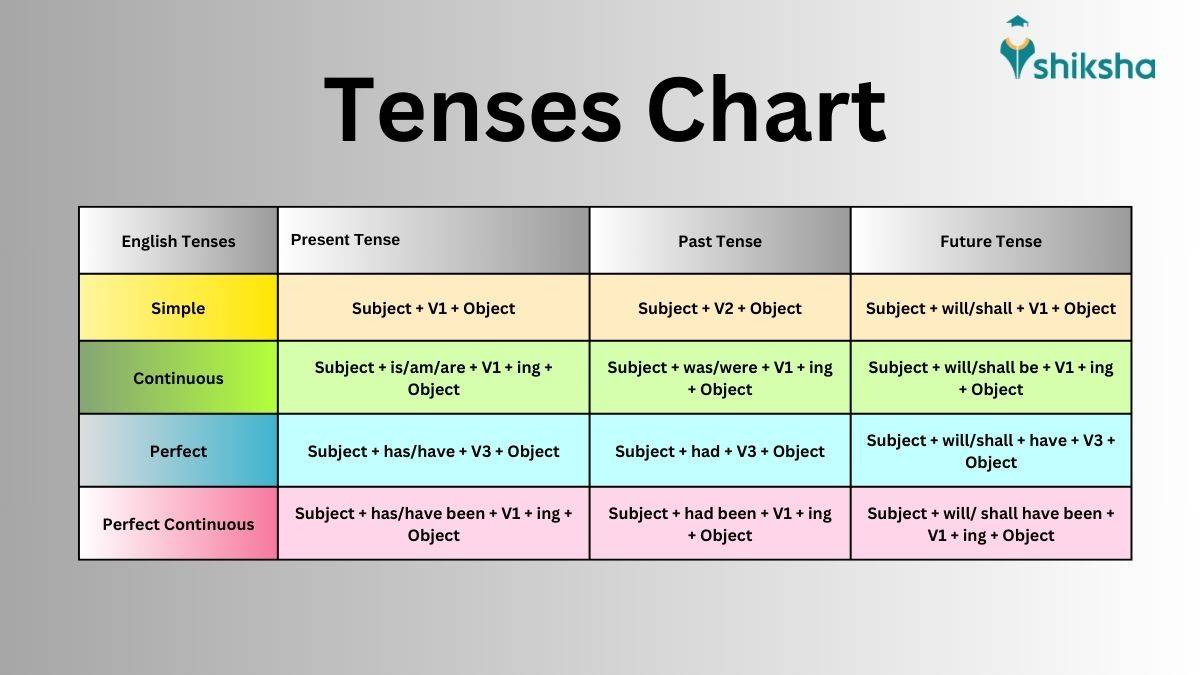
Chart of Tenses
Here is a visual representation of the rules of tenses in grammar, as the chart on tenses:
Commonly asked questions
What is the structure for future perfect tense?
Future Perfect Tense rule is simple. Check out the future perfect tense structure explained below with the help of examples:
| Structure | Example |
|---|---|
| Subject + will/ shall + have + past participle (V3) |
|
What is the rule for Present Tense?
The rule for the Present Tense depends on the type of present tense. The rule and structure of the Present Tense is:
- Simple Present Tense:
Subject + V1 or third person plural + Object
- Present Continuous Tense:
Subject + to be verb form + V1+ ing + Object
- Present Perfect Tense:
Subject + have/has + past participle of V1 + Object
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Subject + have/has+ V1+ ing + Object
Grammar Rules for Tenses
Rules for Tenses or English Tense Rules are important to understand as they help one to correctly use the different forms of tenses in a sentence without making grammatical mistakes and clearly communicating what one has to say. Mentioned below are the grammar tenses rules:
Rules for Present Tense
As mentioned before, the present tense is used to describe an event which is currently happening. The rules for the types of present tenses are mentioned below:
Rules for Simple Present Tense
The rule for the simple present tense is:
Subject + V1 + s/es + Object
Example: She lives in Delhi
(Subject- She, Verb- Live + s/es, Object- Delhi)
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Rule: Subject + V1 + s/es + Object | Rule: Subject + V1 + Object |
| Example: She plays basketball (Subject- She, V1- play + s/es, Object- Basketball) |
Example: The girls play basketball (Subject- Girls, V1- Play, Object- Basketball) |
Rules for Present Continuous Tense
The rule for present continuous tense is:
Subject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + Object
Example: He is eating fruits.
(Subject- He, is/am/are, Verb- eat + ing, Object- Fruits)
| Present Continuous |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + Object |
| Example: She is reading a novel (Subject- She, is/am/are, Verb- Read, ing, Object- Novel) |
Rules for Present Perfect Tense
The rule for present perfect tense is:
Subject + has + V3 + Object
Example: He has cleaned the room.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Rule: Subject + has + V3 + Object | Rule: Subject + have + V3 + object |
| Example: He has watched this movie (Subject- He, has, third form of verb- watch, object- movie) |
Example: They have planted trees. (Subject- They, have, third form of verb- plant, object- trees) |
Rules for Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The rule for present perfect continuous tense is:
Subject + has been + V1 + ing + object
Example: Sunita has been practicing since morning.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Rule: Subject + has been + V1 + ing + Object | Rule: Subject + have been + V1 + ing + object |
| Example: He has been watching this movie (Subject- He, has been, v1- watch, ing, object- movie) |
Example: They have been planting trees. (Subject- They, have been, V1- plant, ing, object- trees) |
Rules for Past Tense
As mentioned before, the past tense is used to describe an event has happened in the past. The rules for the types of past tenses are mentioned below:
Rules for Simple Past Tense
The rule for simple past tense states:
Subject + V2 + Object
| Simple Past Tense |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + V2 + Object |
| Example: Rohini bought a dress for me. (Subject- Rohini, V2- Bring, Object- Dress) |
Rules for Past Continuous Tense
The rule for past continuous tense states:
Subject + was/were + V1 + ing + Object
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Rule: Subject + was + V1 + ing + Object | Rule: Subject + were + V1 + ing + Object |
| Example: He was playing in the park. (Subject- He, was, V1- Play, ing, Object- Park) |
Example: They were going to the theatre. (Subject- They, were, V1- go, ing, Object- theatre) |
Rules for Past Perfect Tense
The rule for the past perfect tense states:
Subject + had + V3 + Object
| Past Perfect Tense |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + had + V3 + Object |
| Example: Shruti had watched a comedy movie. (Subject- Shruti, had, v3- watch, Object- Movie) |
Rules for Past Perfect Continuous
The rule for the past perfect continuous tense is:
Subject + had been + V1 + ing + Object
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + had been + V1 + Object |
| Example: Priya had been preparing for her presentation for one week. (Subject- Priya, had been, V1- prepare, Object- Presentation) |
Rules for Future Tense
The future tense represents the actions which are yet to happen. The tenses rules for future tenses are:
Rules for Simple Future Tense
The rule for the simple future tense is:
Subject + will/ shall + V1 + Object
| Simple Future Tense |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object |
| Example: I will study English tomorrow. (Subject- I, will, V1- study, Object- English) |
Rules for Future Continuous Tense
The rule for the future continuous tense is:
Subject + will be/ shall be + V1 + ing + Object
| Future Continuous Tense |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + will/shall be + V1 + ing + Object |
| Example: I will be reaching the office at 9 AM tomorrow. (Subject- I, will be + V1- Reach, ing, Object- Office) |
Rules for Future Perfect Tense
The rule for the future perfect tense is:
Subject + will have/ shall have + V3 + Object
| Future Perfect Tense |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + will/shall have + V3 + Object |
| Example: John will have returned home when the party is over. (Subject- John, will have, V3- return, object- home) |
Rules for Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The rules for the future perfect continuous tense are:
Subject + will have been + V1 + ing + object
| Future Perfect Tense |
|---|
| Rule: Subject + will have been + V1 + ing + Object |
| Example: By next year, they will have been going to London for two years. (Subject- They, will have been, V1- go, ing, object- London) |
Importance of Tenses in English
The tenses in grammar act as a backbone of the English language. Tenses in English play a crucial role in helping people express the time and meaning of their sentences accurately. Tenses are important in speaking English, writing and/or preparing for the exams, as learning tenses increases clarity and improves communication. Read below to know why are tenses important in English:
There are various reasons why are tenses important such as:
- Tenses Help in Expressing Time Clearly: Tenses indicate the time of action. In other words, they help in showing at what time did an action or event happen- past, present or future. This helps in clear and precise communication.
Example:
-
- Rita studied for the exam. (Past Tense)
- Rita is studying for the exam. (Present Tense)
- Rita will study for the exam. (Future Tense)
- Tenses Improve the Structure of the Sentence: To make a grammatically correct sentence, tenses are important. Grammatically correct sentences are easier to understand and ensure clear conversations. Incorrect use of tenses can confuse the readers and listeners.
Example:
-
-
He will cleaned the room tomorrow. (Incorrect)
- He will clean the room tomorrow (Correct)
-
Also Read:
| Subject Verb Agreement Questions and Answers | Articles: Meaning, Examples and Exercises with Answers |
- Tenses are Important for Academic and Professional Writing: Stronghold over tenses is important not only in the academic sphere but also the professional sphere. To write emails, reports, research papers, etc., good tense usage is important. It is crucial to know how to use tenses as poor tense usage can make writing unclear, unprofessional and confusing.
Example:
-
- Sumit has achieved his sales target this month. (Present Perfect Tense)
- Sumit achieved his sales target this month. (Simple Past Tense)
- Tenses Enhance Storytelling and Narration Experience: English tenses are important in narration and storytelling as they give a structure to the events happening and clarify the time relations in the narration or story. Writers use tenses to establish the sequences, provide background, and highlight time durations and/ or interruptions. Consistent use of tenses in a narrative maintains coherence.
Example:
-
- Ronald was watching a show when it started raining. (Past continuous tense and past simple tense is used in the background and the main event, i.e. it started raining. )
- Essential for Competitive Exams and Language Proficiency Exams: Tenses is an important topic in most of competitive exams including MBA exams, Government Exams, IELTS, TOEFL, BBA exams, etc. Grammar plays a major role for students to score well in such exams.
Example:
-
- If Johnny had studied, he would have passed the exam. (Third conditional- unreal past situations).
Special Cases and Exceptions in English Grammar Tenses
Tenses in English follow a step of rules as mentioned before. But, for the language to be clear, natural, and logical, there are some exceptions or special cases which are taken into consideration which help people to express ideas correctly. Sometimes tenses in English grammar are used in subordinate clauses, particularly when referring to future events or unrealistic situations. Some special cases and exceptions of English tenses include:
Case 1: Simple Present Continuous Tense in Subordinate Clause of Time
This kind is introduced by certain conjunctions such as, when, before, after, as soon as, etc. to talk about future events.
Example:
- I will call you as soon as I am ready.
- We will leave after we finish the food.
Case 2: Simple Present Tense Instead of Future Tense
This kind is introduced during scheduled events, especially relating to travel, transport, timetables, and/or fixed plans.
Example:
- The bus leaves at 5 PM (instead of will leave)
- The meeting with the manager starts at noon (instead of will start)
Case 3: Simple Present Tense in Subordinate Clauses of Condition (Conditional Tense)
This kind is introduced by the word ‘if’ to describe a hypothetical situation.
Example:
- If Riya studies hard, she will score well.
- If it rains, we stay inside.
Also Read: Types of Clauses
Case 4: Past Tense in Unreal Situation
This is used to express an unrealistic or improbable future situation. ‘If’ clause if used with ‘would + infinitive’
Example:
- If I had more time, I would travel the world.
Case 5: Present Perfect Instead of Past Simple Tense
This kind is introduced with experiences (with ‘ever’ or ‘never’), an unfinished time period (this week, this month, etc.), and/or with ‘just’, ‘already’, ‘yet’, etc.
Example:
- I have never seen such a beautiful dress (Not, “I never saw”)
- She has read two books this month. (Not “She read”)
- He has just finished reading the newspaper.
Case 6: Past Continuous Instead of Simple Past
This kind is often used to portray politeness and describe background action.
Example:
- I was thinking if you could help me (Instead of “I thought”)
- I was driving when I saw a deer (Instead of “I drove”)
Also Read: Adverbs: Examples and Exercises with Answers
Tenses in Grammar: Difference Between Written and Spoken English
While tenses are very important in all kinds of communication, there are some key differences between the verbal form and the written form of communication in regards to tenses. Usually, in spoken English, the Present Tense is favoured, while in written communication, we generally use the past tense or the future tense (particularly in academic or fiction writing). The table below depicts some of the key differences in the usage of tenses in written and spoken English:
| Feature | Written English | Spoken English |
|---|---|---|
| Formality | High | Low |
| Planning | Planned | Spontaneous |
| Tense Usage | Past Tense more common | Predominately Present Tense |
| Contractions | Uncommon | Common |
| Vocabulary | Formal | Informal, Usage of Slang |
| Sentence Structure | Complete sentence | Often incomplete |
| Emphasis | Punctuation and Structure | Tonality, Rhythm, Pauses |
Contractions are common in spoken English. We often use 'can't' instead of cannot when speaking. In spoken English, the usage of slang and colloquialisms is very common, which is not the case in written English. The individuals usually focus on pauses, tone and rhythm of their communication in spoken English to convey what they want to express, whereas in written communication, writers focus more on complex sentence structures and punctuation for detailed and nuanced expressions.
Also Read:
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Tenses
Tenses in English Grammar with Examples
Preparation Tips to Master Tenses
Best Books to Prepare for Tenses in English
Tenses Exercises with Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on Tenses
Commonly asked questions
The rule of the simple present tense is as follows:
- Positive Sentence or Affirmative Sentence: Subject + verb (base form) + object (e.g., "He plays football").
- Negative Sentence: Subject + does not/do not + verb (base form) + object (e.g., "She does not like coffee").
- Questions or Interrogative Sentences: Do/Does + subject + verb (base form) + object? (e.g., "Does he work here?").
How can I use tenses correctly?
Using the tenses correctly is important to make proper grammatically correct sentences. To know how to use tenses, understand the time they indicate when an action has happened or is about to happen.
In English, there are three main types of tenses, i.e. Present, Past and Future. Each of these tenses have different forms to indicate how is the action occuring or its relation with time.
How to identify tenses in an English sentence?
Knowing how to identify tenses is important to complete understand what are tenses. Focusing on the verb form and how it relates to the action's time (past, present or future) can help in identifying the tenses in a sentence. Auxiliary verbs such as have, be, will, etc. help in identifying the tense and its aspect -simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous.
The '-ing' form of a verb is called the present participle. It can act as:
- A gerund (noun)
- A participle (adjective)
- Part of a continuous tense
Examples:
Cooking is relaxing. (Gerund)
The boiling water is hot. (Present Participle)
She is cooking dinner now. (Continuous Verb)
Which is the best book to refer to learn and practice tenses?
The following table depicts the best books for tense which the students can refer to:
Books | Author/ Publication |
|---|---|
All About Tenses for Beginners | Ramandeep Kaur |
English Tenses Practical Grammar Guide | Phil Williams |
English Grammar and Composition | Wren and Martin |
The Book of English Grammar Tenses | Mamta Mehrotra |
Story Tense | Nilam Pathak and Anshuman Sharma |
The Big Book of Words You Should Know | David Olsen, Michelle Bevilacqua and Justin Cord Hayes |
Essential English Grammar | Raymond Murphy |
Word Power Made Easy | Norman Lewis |
How many tenses are there in the English language?
There are three main tenses, Present, Past and Future. These tenses are further divided into four sub categories each. Hence, making the total to 12 tenses. These are:
Present Tense:
- Simple Present
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Past Tense:
- Simple Past
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
Future Tense:
- Simple Future
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
English Tenses Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds



What is the structure of Present Perfect Tense and its rules?