A Phrase is a group of words that has a definite meaning when used together. In other words, they are a group of two or more words functioning as a meaningful unit within a sentence. They cannot stand on their own and are without a subject and a verb. Often, phrases are used for descriptions of things, people, or events. In English Grammar, knowing about Phrases in English is important for students to improve their fluency, speak confidently, and sound more natural while conversing with others. In standardized tests like IELTS, TOEFL, SAT, GRE, etc. phrases are tested in sections like reading, writing, speaking, and grammar.
What is a Phrase in grammar?
In simple language, a Phrase is a group of words that work together as a single unit in a sentence. It does not contain a subject and a verb. It communicates a concept but is not a full sentence. Phrases are used in everyday English. They make the sentences richer by giving the words context, clarity, and details.
Example of a Phrase is given below:
- It is nice of you to say so
- How old are you?
- It is next to the bank
- Have a nice day
- How can I help you?
- Keep up the good work!
How are Phrases useful in writing?
Phrases are an important part of writing because they add flow, clarity, and emotion to a sentence. Here is how they can improve their writing:
- Can make writing appear more conversational and natural
- Improves clarity and makes the sentences precise
- They help connect ideas smoothly
- Can add style and expressions
- Phrases can help one say the same idea in a number of ways. For example: Instead of repeating “I think”, one can say “It seems to me…”, “In my opinion…”, “From my perspective…”
- What are Phrases?
- Definition of Phrases
- Types of Phrases in English Grammar
- Most Common English Phrases for Daily Use
- Difference between Phrase and Clause
- Phrases Vs Idioms: A Comparison
- How to Use Phrases? Points and Rules to Remember
- Tips to Remember English Phrases
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Phrases
- Practice Tips to Master Phrases in English Grammar
- Best Books to study Phrases
- Phrases Examples
- Phrases in English Grammar Exercises
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- FAQs on Phrases in English Grammar
What are Phrases?
A Phrase is a group of words that communicates a concept but is not a full sentence. It does not have a subject and a verb. Also, note that it cannot stand alone on its own or as a complete thought. In general, Phrases in the English language provide extra information to a sentence. Some examples of phrases in sentences are given below:
Examples:
- My black gym socks are in the hamper
- Harry has been writing an essay for an hour already
- The space under the green shed has to be cleared out
Also Read: Tenses
Commonly asked questions
How do I identify a Phrase?
To identify a Phrase, follow the steps given below:
- First of all, look for a group of words in a sentence
- Check if it has a both subject and a verb. If it has both, then it is a clause
- Check which type of Phrase it is
- Then, ask if can it stand alone?
What refers to a good phrase?
A good phrase in English is a group of words that is:
- Easy and clear to understand. It communicates an idea without confusion
- Commonly used and seem natural. It should sound natural in everyday conversation and writing
- It follows proper grammar rules
- It should be appropriate for the context. A good phrase should fir a situation
Which English phrases are useful for competitive exams?
Here is a list of Phrases that can be essential for exams like TOEFL, IELTS, UPSC, GRE, SSC, and more:
- Phrases for introducing an idea: These are useful for essays and make structured answers. Examples include It is often said that, To begin with…, There is no denying that
- Phrases for contrasting ideas: These are beneficial in argument-based writing or speaking. Examples include, On the other hand, In contrast…, Although it may seem
- Phrases for adding information: This is required at the time of writing an essay and paragraph transitions. Examples include, Besides this, In addition to that…, Not only that, but…
- Phrases for expressing opinions: These are required for essay introductions, speaking tests, and group discussions. Examples include, I strongly believe that…, In my opinion…, From my perspective…
Definition of Phrases
Phrase definition, as per some of the sources, is given below:
According to Oxford Dictionary, “A Phrase is defined as a group of words that have a particular meaning when used together.”
As per Collins Dictionary, “A Phrase is a short group of words that people often use as a way of saying something. The meaning of a phrase is often not obvious from the meaning of the individual words in it.”
Pronounced as: /freɪz/
Examples:
- My family is planning to travel to Dubai by the end of May
- The girl in the black saree is my classmate
Also Read: English Paraphrasing
Types of Phrases in English Grammar
There are main five types of Phrases in English Grammar namely Noun Phrase, Adverb Phrase, Adjective Phrase, Verb Phrase, and Prepositional Phrase. There are a few other types of phrases too such as Infinitive Phrase, Gerund Phrase, and Participial Phrase. The details of the different types of phrases in English Grammar are given below:
Noun Phrase
A Noun Phrase is a group of words that has a noun. It is basically used to modify the noun. It can be said that a noun phrase can function as a subject, an object, or a complement in a sentence.
Examples
- My sister’s friend had come to visit my family (used as a subject)
- Rita brought a beautiful silk dress (used as an object)
- She is a talented musician (used as a compliment)
Structure: Nouns + Modifiers
Adjective Phrase
An Adjective Phrase is a group of words that consists of an adjective. They describe a noun or pronoun by adding more detail to it.
Examples
- She is always ready to help her colleagues
- Ramita has silky, smooth hair
- The English movie we saw yesterday was difficult to understand without subtitles
Structure: Adjective + Modifiers
Verb Phrase
This is a phrase that is made up of a main verb plus helping verbs (auxiliary verbs).
Examples
- The dog has been barking continuously since last night
- They have been working hard on a project
- Aarushi has been writing multiplication tables for three hours
Structure: Main Verb + Helping Verbs
Adverb Phrase
An Adverb Phrase is a group of words that includes an adverb and other modifiers. This phrase type performs all the functions of an adverb.
Examples
- She drove as fast as possible
- Later this evening, my mother and I have planned to go to the mall
- The professor was teaching their students in an easy manner
Structure: Adverb + Modifiers
Prepositional Phrase
A Prepositional Phrase comprises a preposition and an object. It shows location, time, direction, cause, manner or possession and acts like an adjective or adverb in a sentence.
Examples
- The market near my house is very posh
- The keys are placed on the study table
- A baby was crying inside the classroom
Structure: Preposition + Noun / Pronoun
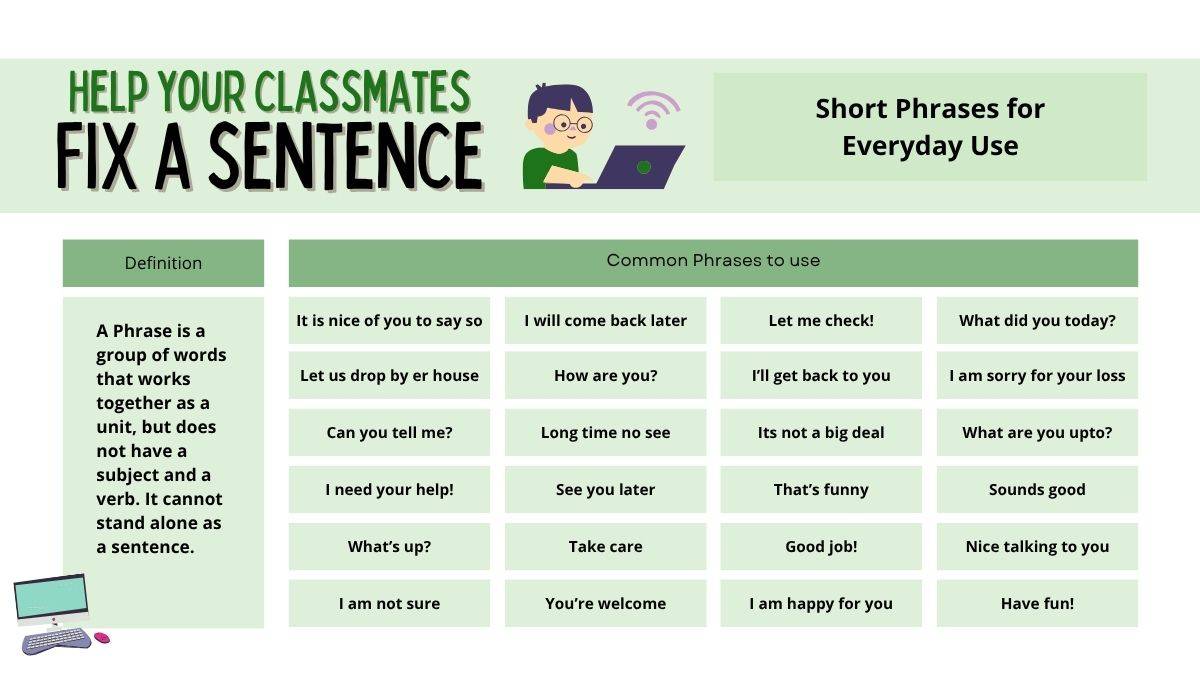
Most Common English Phrases for Daily Use
A few of examples of phrases that can be used for daily conversations are given below:
| Common Phrases |
Examples |
|---|---|
| Introductions |
|
| To keep the conversation going |
|
| Making requests |
|
| Asking and giving opinions |
|
| Ending the conversation |
|
An image showing the common phrases for daily use is given below:
Commonly asked questions
What are the Phrases for daily use?
Some of the common phrases that can be used in everyday conversations are:
Greetings
- Hi, How are you?
- How is everything going?
- Have a great day!
- Nice to meet you
Asking for Information
- How much does it cost?
- What time is it?
- How can I reach there?
- ·What does this word mean?
Making Requests
- Can you help me with this?
- Do you have a minute?
- Can I ask you something?
- I'd like some help, please
Expressing Gratitude
- I really appreciate it
- Thanks a lot
- Thank you so much!
- You're welcome
What are the most commonly used Phrases in English?
The most common English Phrases are:
- How are you?
- Nice to meet you
- What do you do?
- Can you help me
- Can you help me?
- See you later
- How much is this?
- No problem
- What time is it?
Difference between Phrase and Clause
Both Phrases and Clauses are a parts of the sentence but are different from each other. A comparison between these two is explained in the table given below:
| Phrase |
Clause |
|---|---|
| A group of words standing together as a conceptual unit without a subject and verb |
A Clause is a group of words that has both a subject and a predicate |
| A Phrase does not gives a complete meaning when standalone |
A Clause gives a complete meaning and can be a complete sentence when standalone |
| Examples:
|
Examples:
|
An easy trick to remember the difference between a Phrase and a Clause is:
- Phrase = No S + V working together
- Clause = S + V (Subject + Verb)
Phrases Vs Idioms: A Comparison
A comparison between Idioms and Phrases is given below:
| Particulars |
Phrases |
Idioms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition |
A group of words acting as a unit in a sentence |
Idioms are a group of words whose meaning is different from the actual meaning |
| Meaning |
Clear and precise |
Often non-literal and figurative |
| Function in a sentence |
Acts like a part of speech (Verb, Noun, etc.) |
Adds color or expression to speech or writing |
| Examples |
|
|
How to Use Phrases? Points and Rules to Remember
A Phrase in English Grammar is a group of related words without both a subject and a verb. It works as a single part of speech in a sentence (like an adjective, noun, or adverb). A few of the points that one should keep in mind while using Phrases are:
- Phrases are just part of a sentence and cannot be used stand-alone. They are usually used to give details about the object, subject or other components in a sentence
- Ensure a Phrase gives your sentence clarity and does not simply accumulate the sentence with information
- Use commas wherever necessary while using Phrases. Some phrases need commas. Examples of this are: After the meeting, she went home; Tired from work, she went straight to bed
- As it has been explained, a Phrase alone cannot make a complete sentence. In other words, avoid fragments.
Tips to Remember English Phrases
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Phrases
Practice Tips to Master Phrases in English Grammar
Best Books to study Phrases
Phrases Examples
Phrases in English Grammar Exercises
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
FAQs on Phrases in English Grammar
Commonly asked questions
A Phrase in English grammar is a group of words that work together as a unit in a sentence. It does not have both a subject and a verb, does not express a complete thought, and can act as a single part of speech. Phrases help add detail, function, description to a sentence. Some of the examples of Phrases are given below:
- He goes jogging in the morning
- On the way to Parliament house, we caught sight of Prime Minister's car
- They have been sleeping all day
- The girl with curly hair is my cousin
There are main five Phrase types namely Noun Phrase, Adjective Phrase, Verb Phrase, Adverb Phrase, and Prepositional Phrase. A brief chart of types of Phrases is given below:
Phrase Type | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Noun Phrase | Acts as a noun | The black dog is sitting on the mat |
Verb Phrase | Shows state or action | He has been working since morning |
Adjective Phrase | Describes a noun | That girl is full of energy when it comes to learning new skills |
Adverb Phrase | Describes where, how, when, why | She painted the wall with great enthusiasm |
Prepositional Phrase | Shows relationship (place / time) | The CAT is hiding under the table |
A few of the books to study about the phrases are given below:
Book Name | Author |
|---|---|
MTG 3001 Idioms, Proverbs, Phrases & Phrasal Verbs for English Vocabulary Enrichment | MTG Editorial Board |
Idioms and Phrases Anglo | Roshan Tolani |
3000 Idioms and Phrases (English Improvement for Success) | Sam Philips |
Oxford Learner's Pocket Phrasal Verbs and Idioms | Oxford |
Idioms and Phrases | Eric Watson |
2000 English Phrases and Sentences | Colonel Rajeev Mongia |
Idioms, Phrases & Proverbs: with Hindi Meanings & Usage | H.S. Bhatia and P.S. Bhatia |
A noun phrase is a group of words that works together as a noun in a sentence. It contains a noun and the words that modify it. It can act as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence. Some examples of Noun Phrases are given below:
- The little girl is crying
- Reema adopted a cute puppy
- A slice of chocolate cake can make me happy
A Term is a name for something and it can be more than a word. A Phrase, on the other hand, is a group of words that are used together to convey meaning. Examples of both are:
Term
- Photosynthesis is an important process of a plant life
- The internet has changed the nuances of communication
Phrases
- The CAT is hiding under the table
- He drove car with great speed
Summary
Type | Example | Explanation |
Term | She studies Physics | 'Physics' is a technical subject word |
Phrase | She studies at a university in the U.S. | A group of words that add extra detail |
English Phrases Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds