Imagine you are trying to describe your day without saying what you did. Impossible, right? That's where English Verbs come to the rescue. Whether you are singing, listening, running a marathon, drawing a sketch, reading a novel, or simply ‘being’, you are using verbs. In English grammar, verbs are one of the most essential parts of speech that we use in our daily lives by helping us express actions, states, or occurrences.
With this article, Shiksha aims to help you understand verbs in English Grammar in detail. Know about the meaning of verbs, types of verbs, verb forms, and verb examples. Find helpful tips to master English Verbs with the help of some engaging verb exercises with answers to strengthen your English speaking and writing skills.
- What is a Verb?
- Definition of Verb
- Types of Verbs in English Grammar
- List of Verbs in English
- Verb Forms
- Tenses and Verbs in Grammar
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Verb: Uses with Examples
- Special Cases and Exceptions in Verbs
- How to Identify Verbs in a Sentence?
- Common Mistakes in Verbs
- Best Grammar Books to Prepare for Verbs
- Verb Examples
- Verb Exercises with Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Verbs
What is a Verb?
A verb is a word that describes an action, a feeling, a state of being or existence, or possession. Simply put, it is a word in a sentence that shows what the subject is doing or what is happening. Verbs can be in different forms, including base form, past simple form, past participle form, and present participle form. Verbs build a relationship between the subject and other parts of an English sentence.
A verb in a sentence expresses:
1. Physical Actions: Some verbs describe the actions performed by the body or using tools.
Examples of Physical Action Verbs:
- I smell something cooking in the kitchen.
- She heard weird noises from the building.
2. Mental Actions: Some English verbs define the internal process of a human being. These include thinking, knowing, etc.
Examples of Mental Action Verbs:
- I know who won the game.
- I got her number from my friend.
3. State of Being Actions: Some verbs describe conditions or situations without showing action. These verbs often use forms of "to be" like "am" or "is,".
Examples of State of Being Action Verbs:
- I am a student.
- He is a Management Professor.
Definition of Verb
Verb Definition: Oxford Dictionary
As per the Oxford Dictionary, a verb is "a word used to describe an action, state, or occurrence, and forming the main part of the predicate of a sentence."
Pronunciation: /vɜːb/ (British) | /vɝːb/ (American)
Verb Example:
- She runs fast.
- He goes to the school by bus.
Verb Definition: Collins Dictionary
As per the Collins Dictionary, a verb is “ a word such as ' sing', ' feel', or ' die' which is used with a subject to say what someone or something does or what happens to them, or to give information about them.”
Also Read:
| Definition of Prepositions | Conjunction Definition in English | Definition of English Synonyms |
Types of Verbs in English Grammar
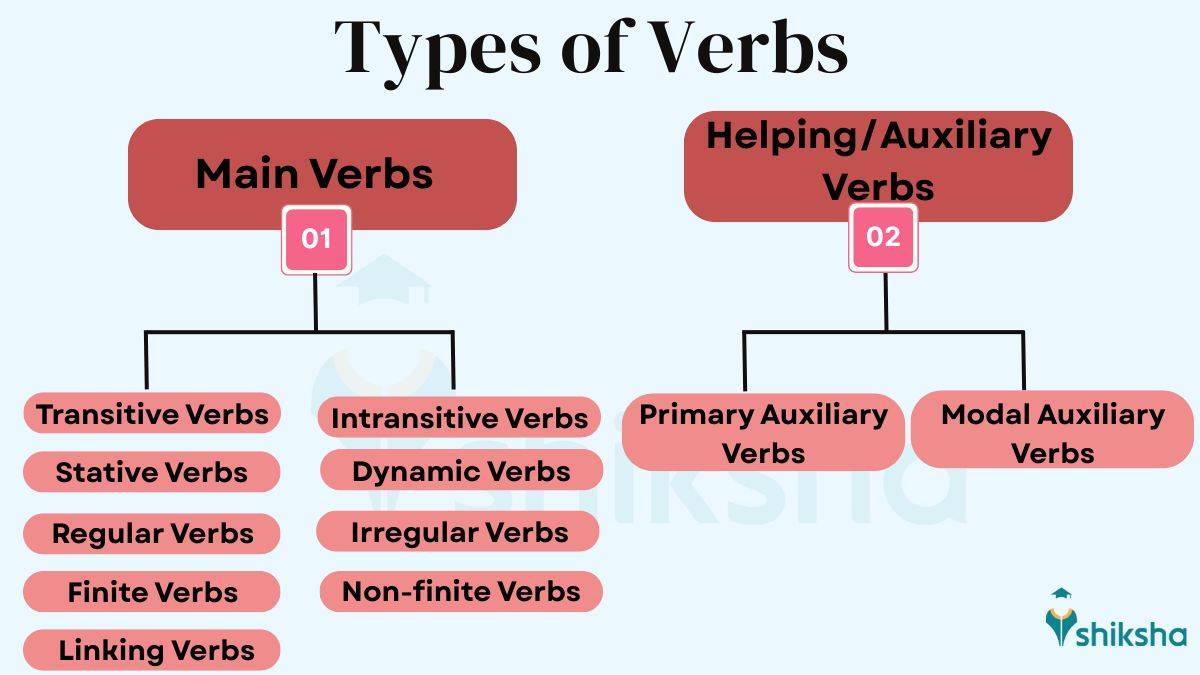
Verbs in English Grammar are crucial to write a meaningful sentence. Verbs help express actions and show feelings, conditions, time, and state. There are two main types of verbs. These are main (or principal) verbs and helping (or auxiliary) verbs.
I. Main Verbs/ Principle Verbs
Main verbs also known as principle verbs. They are the primary verbs in a sentence. The main verbs shows us the core meaning of the sentence, i.e., what the subject is doing or experiencing. These verbs can appear alone or along with a helping verb.
Main verbs are of nine types:
1. Transitive Verbs
A transitive verb is a types of verb that requires an object to complete its meaning. The action passes from the subject to the object. Without the object, the sentence is incomplete. This object could be a noun, pronoun, or phrase.
Examples of Transitive Verbs:
- The boy kicked the ball.
- She wrote a letter.
- I gave my sister a gift.
How do you know if it is a transitive verb?
If a sentence has a verb + object, then it is a transitive verb.
For example, Shreya is baking a cake. (“baking” is the verb; “cake” is object)
2. Intransitive Verbs
An intransitive verb does not take an object. The action remains with the subject and does not transfer to anything else. However, these verbs still make complete sense on their own.
Examples of Intransitive Verbs:
- The baby cried loudly.
- Birds fly high.
- He sleeps peacefully.
3. Linking Verbs/Copular Verbs
Linking verbs are also known as copular verbs. These verbs do not show action, but connect the subject to additional information about itself. These verbs usually link the subject to a subject complement (a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes or identifies the subject).
Common linking verbs include: be (am, is, are, was, were), seem, appear, become, look, feel, sound, and taste.
Examples of Linking Verbs:
- She is a doctor.
- The soup smells delicious.
- They were excited about the trip.
4. Dynamic Verbs
In English grammar, dynamic verb (also known as action verbs) describe actions or processes that are changeable or moving. These verbs can be used in progressive tenses to show the ongoing actions.
Structure of Dynamic Verbs:
| Subject + Action Verb + The rest of the sentence |
Examples of Dynamic Verbs:
- Arpit is painting a picture.
- The kids ran across the field.
- Suhani writes in her journal every day.
5. Stative Verbs
Stative verbs describe a condition or state rather than an actual action. These verbs typically refer to emotions, thoughts, senses, relationships, or possession. Stative Verbs are rarely used in continuous forms.
Note: Stative verbs can be found in a sentence where the subject is doing something without any action.
Examples of Stative Verbs:
- I believe in honesty.
- She owns two houses.
- We feel tired after the hike.
6. Regular Verbs
Regular verbs follow a consistent rule. They form both their past tense and past participle by adding -ed or -d to the base form.
| Base Form |
Past Simple |
Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| arrive |
arrived |
arrived |
| marry |
married |
married |
| play |
played |
played |
| work |
worked |
worked |
| call |
called |
called |
| lie |
lied |
lied |
Examples of Regular Verbs:
- He cleaned his room.
- They watched a movie.
- I played chess with my brother.
7. Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs are those that do not follow the standard -ed ending rule. Their past tense and past participle forms vary.
Examples of Irregular Verbs:
- She went to the market.
- They have eaten lunch already.
- Our car cost a lot of money.
8. Finite Verbs
A finite verb agrees with the subject in person and number, and it clearly shows tense. It can act as the main verb in a sentence.
Examples of Finite Verbs:
- He drives to work.
- They watched a play.
- I am reading a book.
9. Non-finite Verbs
Non-finite verbs are those that do not indicate tense or subject agreement. These verbs cannot serve as the main verb of a sentence. There are three types of non-finite verbs; gerunds, infinitives, and participles.
- Gerunds: A gerund is the present participle form of a verb that functions as a noun. It always ends in –ing.
Example: Writing is tough.
- Infinitives: An infinitive is the base form of a verb. It is usually preceded by “to”.
Example: She wants to dance.
- Participles: Participles are verb forms that function as adjectives. They are of three types, present participle (-ing form), past participle (usually -ed or irregular), and perfect participle (having + past participle).
Examples: running water (present), broken vase (past), having finished work (perfect).
Examples of Non-finite Verbs:
- Typing is hard on my wrists.
- I like to read before bed.
- Bored by the lecture, he left early.
Also Read:
Meaning of Paraphrasing in English
II. Helping Verbs/Auxiliary Verbs
Helping verbs, also known as auxiliary verbs, support the main verb in forming tense, mood, or voice. These verbs do not stand alone as the main verb. However, they are essential for creating different verb structures. The major auxiliary verbs are: be, have, and do.
Helping verbs are divided into Primary Auxiliaries and Modal Auxiliaries.
1. Primary Helping Verbs (Primary Auxiliary Verbs)
These include the verbs be, have, and do, along with their various forms:
- Forms of be: am, is, are, was, were, being, been
- Forms of have: has, have, had
- Forms of do: do, does, did
These help form continuous tenses, perfect tenses, and negative or interrogative structures.
Examples of Primary Auxiliary Verbs:
- She is singing a song.
- I have eaten already.
- Do you know the answer?
2. Modal Helping Verbs (Modal Auxiliary Verbs)
Modal verbs express ideas such as possibility, ability, permission, obligation, or necessity. Common modal verbs include: can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, ought to, dare, need, used to
Examples of Modal Auxiliary Verbs:
- You must finish your homework.
- I can solve this easily.
- May I come in?
List of Verbs in English
Verbs tell us what a person is doing or what is happening around us. There are some verbs that we use in our everyday conversation. Here is a list of some commonly used verbs in English:
| Verbs |
|
|---|---|
| go |
eat |
| come |
say |
| do |
get |
| make |
have |
| take |
run |
| read |
play |
| give |
like |
| tell |
walk |
| bring |
talk |
| see |
think |
Regular & Irregular Verbs
In English grammar, all verbs are divided into two main types: Regular Verbs and Irregular Verbs. This classification is based on how the verb changes when used in the past tense and past participle forms.
- Regular verbs follow a fixed rule. You simply add -ed or -d to the base form of the verb to make the past forms.
- Irregular verbs do not follow a standard rule. They change differently.
Here is a quick difference table between Regular and Irregular Verbs:
| Regular Verbs |
Irregular Verbs |
|---|---|
| Add -ed or -d to form past tenses |
Change form entirely or do not follow a pattern |
| Easy to learn and follow a rule |
Must be memorized individually |
| Example: play → played |
Example: go → went → gone |
There are about 200 irregular verbs in English. We can divide these into four types:
1. Same Base Form, Past Simple Form, and Past Participle Form
- Cut → cut → cut
- Put → put → put
- Hit → hit → hit
2. Same Past Simple Form and Past Participle Form
- Keep → kept → kept
- Sleep → slept → slept
- Feel → felt → felt
3. Same Base Form and Past Participle Form
- Come → came → come
- Run → ran → run
- Become → became → become
4. Different Base Form, Past Simple Form, and Past Participle Form
- Go → went → gone
- See → saw → seen
- Drink → drank → drunk
Examples of Regular Verbs
Check out the table below for some commonly used regular verbs:
| Base Form |
Past Simple Form |
Past Participle Form |
|---|---|---|
| walk |
walked |
walked |
| play |
played |
played |
| call |
called |
called |
| watch |
watched |
watched |
| clean |
cleaned |
cleaned |
| jump |
jumped |
jumped |
| open |
opened |
opened |
| close |
closed |
closed |
| work |
worked |
worked |
| smile |
smiled |
smiled |
| dance |
danced |
danced |
| climb |
climbed |
climbed |
| cook |
cooked |
cooked |
| laugh |
laughed |
laughed |
| talk |
talked |
talked |
Examples of Irregular Verbs
Check out the table below for some commonly used irregular verbs:
| Base Form |
Past Simple Form |
Past Participle Form |
|---|---|---|
| go |
went |
gone |
| eat |
ate |
eaten |
| write |
wrote |
written |
| speak |
spoke |
spoken |
| take |
took |
taken |
| give |
gave |
given |
| see |
saw |
seen |
| come |
came |
come |
| begin |
began |
begun |
| drink |
drank |
drunk |
| break |
broke |
broken |
| fly |
flew |
flown |
| know |
knew |
known |
| drive |
drove |
driven |
| sing |
sang |
sung |
Also Read: Articles in English Grammar
Verb Forms
Verbs are present in different forms in a sentence, depending on their function. To better understand the use of tense in a sentence, it is essential to know about the forms of verbs. In English, there are four major verb forms—Base Form (V1), Past Simple Form (V2), Past Participle Form (V3), and Present Participle Form (V4).
1. Base Form (V1)
The base form of verb is also known as the root verb. It is the simplest form of the verb and does not have any prefixes. When we look for a word in dictionary, it is in the base form. The base verb form is used in the present tense, imperatives, and infinitives.
Examples of Base Form of Verb:
- I play football every evening.
- She wants to learn Spanish.
2. Past Simple Form (V2)
The second form of the verb is past simple form. It is used in a sentence to describe an action that has already happened in the past. These actions are finished at present. In case of regular verbs, the past simple form means a verb ending with '-ed'. In case of irregular verbs, we have unique past simple verb forms.
Examples:
- He watched a movie last night.
- They went to the zoo yesterday.
3. Past Participle Form (V3)
The past participle form of verb is usually used in perfect tenses and passive voice. Just like past simple verb form, in this form of verb also, the regular verbs eds with '-ed' and irregular verbs have different verb forms. The past participle verb forms are often used with the helping verbs (has, had, have, been).
Examples:
- She has finished her homework.
- The cake was eaten by the children.
4. Present Participle Form (V4/Gerund)
The present participle form of verb is made by adding '-ing' to the base verb form. With the help of present participle verb form, continuous tenses are framed. However, sometimes this verb form also acts as an adjective or gerund.
Examples:
- He is running in the park. (continuous tense)
- The shining stars lit up the sky. (adjective)
Tenses and Verbs in Grammar
Tenses are a fundamental part of English grammar. They inform us when an action occurs, what stage it is in, and whether it’s ongoing, completed, or still pending. Since verbs are the words that express actions, feelings, or states of being, tenses and verbs are connected. Without the right verb tense, it’s difficult to understand the time and meaning of a sentence.
There are three main types of tenses in English:
1. Present Tense
Tenses that describes actions happening now or things that happen regularly are known as present tenses. In English, present tenses are classified into four types, namely, Simple Present Tense, Present Perfect Tense, Present Continuous Tense, and Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Example:
- She plays the guitar every day.
- I work on my project daily for an hour.
2. Past Tense
Tenses that talks about actions that have already happened are known as past tense. In layman terms, if we want to talk about an action or event that has already happened in the past, we will use English past tense. These tenses are further classified into four types; Simple Past Tense, Past Perfect Tense, Past Continuous Tense, and Past Perfect Continuous Tense.
Example:
- They watched a movie yesterday.
- I went to National Craft Musuem with my friends yesterday.
3. Future Tense
The future tenses refers to actions that will happen later. The future tense in English is divided into four types; Simple Future Tense, Future Perfect Tense, Future Continuous Tense, and Future Perfect Continous Tense.
Example:
- I will call you tomorrow.
- We will go for shopping on next Sunday.
Why are Verb Tenses important?
Using correct verb tense is important because of the reasons mentioned as follows:
1. Verbs change their form to reflect the time of the action, i.e., past, present, or future. The correct verb form help the listener or reader understand when something happened.
Example:
-
She walks to school. (present)
-
She walked to school. (past)
2. The correct tense helps show the correct order of actions or events. This is important when we are describing multiple actions in a sentence or paragraph.
Example:
-
After I had eaten, I went to bed.
-
We went for a walk after having lunch.
3. Using the correct verb tense helps others understand exactly what you mean. Whether you're writing a school essay, telling a story, or having a chat with someone, the right tense shows when something happened.
Example:
-
I am going to the market.
-
I went to the market.
4. Use of correct tense in a sentence help convey the required message to the listener or reader. It allows to have a proper conversation with others without creating any confusion.
-
She will goes to the market yesterday. (Wrong tense: fuure used instead of past)
-
She went to the market yesterday. (Correct: past tense 'went' matches the time expression yesterday)
Also Read: Nouns in English Grammar
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-Verb Agreement means that the verb must match the subject in number (singular or plural) and sometimes in person. If the subject is singular, the verb must also be singular. If the subject is plural, the verb must be plural, too. This rule helps make sentences grammatically correct and easy to understand. It’s one of the most important rules in English grammar because every sentence needs a subject and a verb that go together correctly.
Sometimes, it’s easy to follow this rule, but in longer or more complex sentences, students often make mistakes. That’s why learning subject-verb agreement is important.
A Few Helpful Rules:
- Add -s or -es to the verb when the subject is a singular noun or he/she/it (in the present tense).
Example: She runs - Do not add -s or -es when the subject is plural or when using I or you.
Example: They run. - Be careful with subjects that may sound plural but are actually singular, like "each," "everyone," or "the team."
Example: Everyone wants to win.
Examples:
- The boy reads a book every night.
(‘Boy’ is singular, so the verb ‘reads’ is singular.)
- My cousins are waiting for me.
(‘Cousins’ is plural, so we use the plural verb ‘are’.)
- The list of items is on the table.
(‘List’ is singular, even though ‘items’ is plural. The verb agrees with ‘list’.)
Verb: Uses with Examples
Special Cases and Exceptions in Verbs
How to Identify Verbs in a Sentence?
Common Mistakes in Verbs
Best Grammar Books to Prepare for Verbs
Verb Examples
Verb Exercises with Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Verbs
Commonly asked questions
Verbs are divided into different types based on how they function in a sentence. Here are the 11 important types of verbs you should know:
- Action Verbs
- Transitive Verbs
- Intransitive Verbs
- Linking Verbs
- Regular Verbs
- Irregular Verbs
- Finite Verbs
- Non-finite Verbs
- Stative Verbs
- Primary Helping Verbs
- Modal Helping Verbs
A verb is a word that shows an action or a state of being. It tells what the subject of a sentence is doing (like run, eat, write) or what is happening (like is, seems, feels). Verbs are one of the most important parts of a sentence because they give life to the subject.
Without verbs, we wouldn't know what is happening or what someone is doing in a sentence. They help us understand time, mood, and condition too.
Yes, there can be two main verbs in a sentence. For example,
- Samiksha laughed and danced all night at the party.
- He cooked dinner and washed the dishes.
- Aradhna read the book and wrote a summary.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, a verb is “a word used to describe an action, state, or occurrence, and forming the main part of the predicate of a sentence.”
In simpler terms, a verb shows what someone is doing (like run, read, eat) or what is happening (like is, seems, feels). Verbs are necessary for making complete sentences because they tell us what is happening, when it happens, and who is doing it. They can also change form depending on the tense, subject, and number.
Here is the list of 10 commonly used regular verbs:
Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
help | helped | helped |
look | looked | looked |
wait | waited | waited |
start | started | started |
visit | visited | visited |
paint | painted | painted |
shout | shouted | shouted |
arrive | arrived | arrived |
repeat | repeated | repeated |
love | loved | loved |
Linking verbs connect the subject to more information about the subject. They do not show action but tell us what something is or how it feels. Example: Shruti is happy. ("is" links "shruti" to "happy")
Helping verbs (also called auxiliary verbs) are used with main verbs to show tense, voice, or mood. They help form questions, negatives, and other verb tenses. Example: She is running fast. ("is" helps the verb "running")
English Verbs Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds