Paraphrasing is a crucial part of the English language which is an integral part of most syllabi, courses, and even government competitive exams. English is one of the trickiest yet high-scoring exams and paraphrasing is one topic in English grammar that helps in scoring. Whether you're facing an English section at any basic school level or competitive exam, paraphrasing helps in rewriting content in your own words without altering the core meaning. This skill is vital for reading comprehension, descriptive writing, summarization, and even precise communication in competitive exams.
Mastering paraphrasing is essential for scoring well as many aspirants struggle with paraphrasing because of its varied usage and exceptions. Shiksha has presented a comprehensive guide to help students master paraphrasing in English Grammar which includes what is paraphrasing, common mistakes in paraphrasing, grammar rules, the importance of paraphrasing, etc. Along with engaging examples from day-to-day life, interactive exercises, and recommended books to help you strengthen this topic. A strong command of grammar and vocabulary can differentiate between a candidate's success and failure at the school level, or competitive exams such as SSC, Banking, Railways, or UPSC. Whether you are preparing for UPSC, SSC, IBPS, CDS, or other government exams, Read below to master paraphrasing with confidence.
Also read: English Preposition
- What is Paraphrasing?
- Types of Paraphrasing
- Grammar Rules of Paraphrasing
- How to Paraphrase?
- What are the 4 R’s of Paraphrasing?
- Paraphrasing in English: Special Cases and Exceptions
- Paraphrasing vs Summarizing
- Paraphrasing vs Quoting
- English Preparation Tips to Master Paraphrasing
- How to Identify Paraphrasing in a Sentence?
- Paraphrasing in Spoken and Written English
- Common Errors to Avoid When Paraphrasing
- Best Books to Learn Paraphrasing in English Language
- Examples of Paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing Exercises with Answers
- Additional English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- FAQs on Paraphrasing
What is Paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is the art of expressing someone else’s ideas or information in your own words while keeping the original meaning intact. In easy words, Paraphrasing is rewriting something in your own words without changing the meaning.
Some examples are -
- Original:
The sun sets in the west every evening.
Paraphrased:
Every evening, the sun goes down in the western sky.
- Original:
Avleen enjoys reading books about magic and adventure.
Paraphrased:
Avleen loves to read stories that involve magic and exciting journeys.
- Original:
Water freezes at zero degrees Celsius.
Paraphrased:
At 0°C, water turns into ice.
It shows your understanding of the content and is frequently tested in exams through reading comprehension, vocabulary improvement, and writing sections.
Types of Paraphrasing
There are several ways to paraphrase content:
| Type |
Description |
|---|---|
| Idea-level Paraphrasing |
Expressing the same idea with different examples or a completely new format Example: Original: Reading regularly improves vocabulary and comprehension skills. The idea remains the same, but the format/example is different. |
| Technical Paraphrasing |
Simplifying complex technical content Example: Original: Quantum entanglement occurs when pairs of particles become linked in such a way that the state of one particle instantly influences the state of the other, no matter the distance. Simplified version of a technical explanation. |
| Structural Paraphrasing |
Changing sentence voice (active/passive), order, or grammar Example: Original: The committee approved the new education policy. Changed from active to passive voice while retaining the same meaning. |
| Word-level Paraphrasing |
Changing synonyms of individual words Example: Original: The weather was chilly and gloomy. Synonyms are used for individual words. |
| Phrase-level Paraphrasing |
Replacing phrases while maintaining sentence structure Example: Original: She was over the moon after hearing the results. Idiomatic phrase “over the moon” is replaced with a clear alternative while keeping structure intact. |
Also read: English Verbs
Grammar Rules of Paraphrasing
While paraphrasing students must always maintain the original meaning of the sentence, this is the thumb rule and they must just rewrite the sentence in their own words. If the sentence consists of any idioms or proverbs, it must be kept intact. Change the sentence structure, replace words with synonyms, and avoid copying more than 2–3 consecutive words from the original. From the following, we have shared some rules.
- Understand the text completely.
- Don’t just change words—restructure the sentence.
- Use synonyms cautiously.
- Preserve the original meaning.
- Avoid copying phrases directly.
- Always cite sources (if required).
Also read: English Adverb
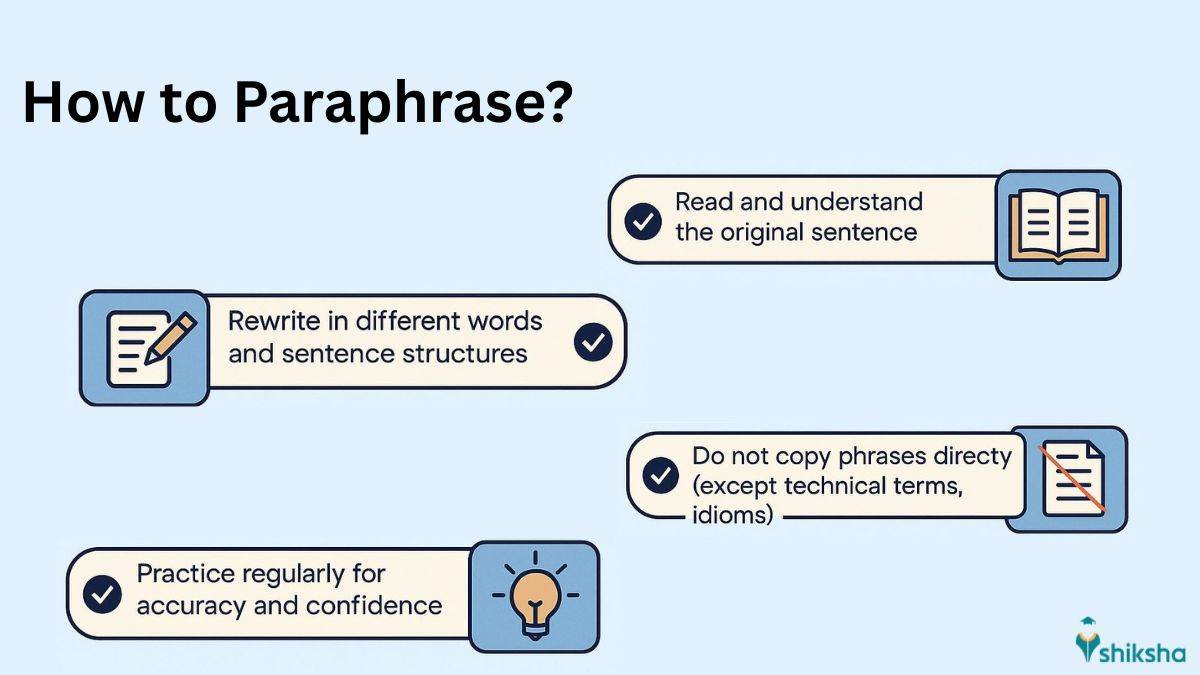
How to Paraphrase?
Paraphrasing is restating an already written sentence in your own words while not changing the original meaning. To do it paraphrasing effectively, students must first read the original sentence thoroughly and understand its core message. Then, they must rewrite it using different words and sentence structures. Students must avoid copying phrases directly unless they are technical or widely accepted such as idioms or proverbs. Compare both the versions the original and the paraphrased one to ensure it conveys the same meaning and is free from plagiarism. Students must practice regularly to become more confident and accurate in paraphrasing, especially for exams and academic writing.
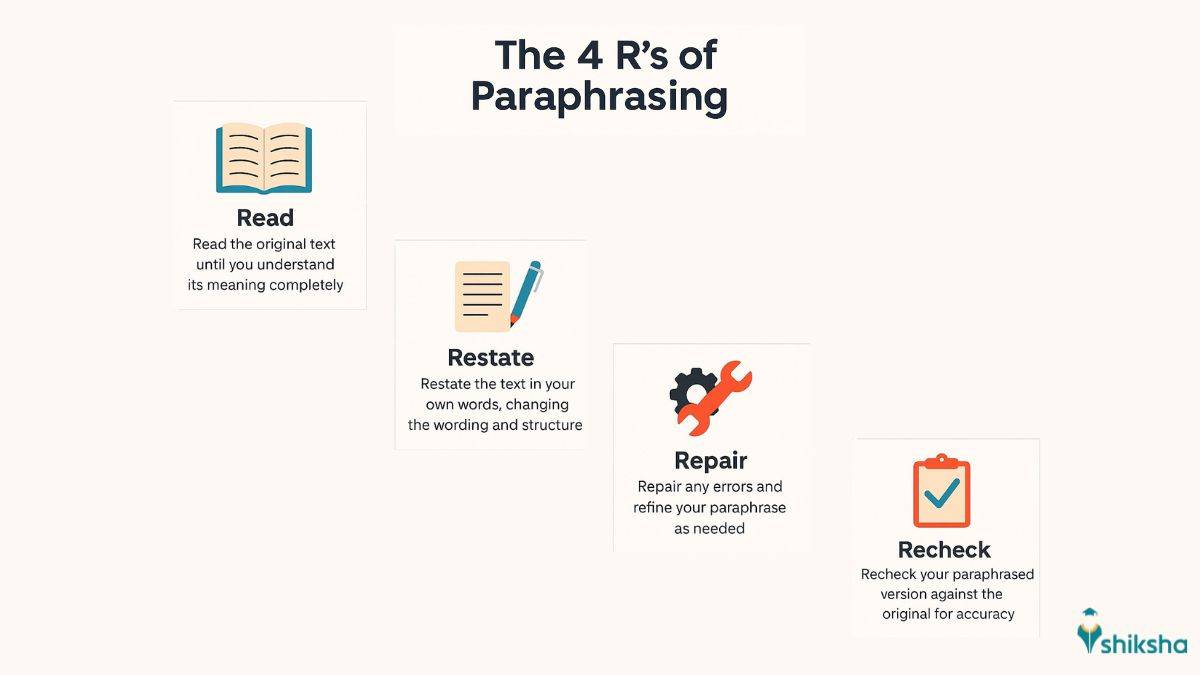
What are the 4 R’s of Paraphrasing?
The 4 R’s stand for Read, Restate, Recheck, and Repair.
- First, Read original text to understand the meaning.
- Next, Restate the idea in your own words without copying.
- Then, Recheck your version to make sure it maintains the context of the original sentence.
- Finally, Repair any parts that may still resemble the source or need clarity.
If you master these 4 steps your paraphrased content will be accurate, original, and plagiarism-free.
Paraphrasing in English: Special Cases and Exceptions
While paraphrasing students must handle the technical definitions carefully, if the context consists of any legal statements, or direct quotes they must avoid misinterpretation. Some phrases, such as idioms or cultural references, may lose meaning if changed, hence quote them or clarify them alongside.
- Idioms & Phrases: Don't paraphrase idioms literally. e.g., “Kick the bucket” ≠ or “Kick a container”
- Quotes: Preserve original words for quoted speech or use quotation marks.
- Technical Terms: Some words (e.g., “quantum mechanics”) must remain unchanged.
Also read: English Antonyms
Paraphrasing vs Summarizing
Paraphrasing rewrites a specific passage or idea without shortening it much, while summarizing shortens the content into brief, highlighting only key points. Both require understanding the original content deeply.
| Aspect |
Paraphrasing |
Summarizing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose |
To simplify or clarify |
To condense |
| Skill Tested |
Vocabulary + Grammar + Comprehension |
Comprehension + Conciseness |
| Focus |
Rewriting in your own words |
Highlighting the main idea only |
| Length |
Almost making it as long as the original |
Crisp it to make it shorter than the original |
Paraphrasing vs Quoting
English Preparation Tips to Master Paraphrasing
How to Identify Paraphrasing in a Sentence?
Paraphrasing in Spoken and Written English
Common Errors to Avoid When Paraphrasing
Best Books to Learn Paraphrasing in English Language
Examples of Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing Exercises with Answers
Additional English Grammar Topics for Preparation
FAQs on Paraphrasing
English Paraphrasing Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds