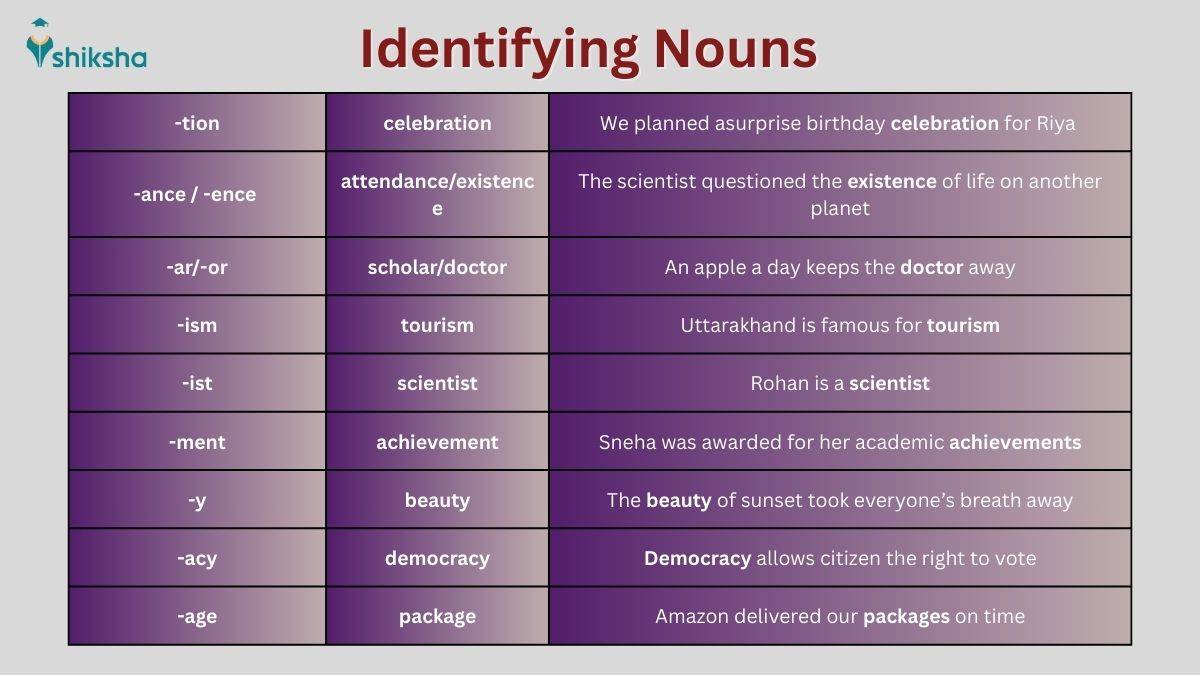
A noun is a word used as a name of a place, person, or thing. It is essential to understand Nouns for improving written and spoken English Grammar and Communication. Nouns are everywhere, in identifying people, places or things. Nouns help in conveying thoughts and structuring our thoughts to express ourselves. In this article, we will learn the definition of nouns, types, illustrative examples, rules to form a sentence, preparation tips and so forth.
What is difference between uncountabel and countable noun?
- Countable nouns are things that can be counted as seperate items like two books, three pencils, five students. Whereas, uncountable nouns are nouncs which cannot be counted like water, hair, milk, etc.
- Countable nouns have both singular and plural forms, whereas, uncountable nouns does not have singular or plural forms.
Why is nouns important?
Nouns are important because they talk about people, place, things or ideas. Nouns acts as foundation in a sentence by acting as subject, verb and more. Without a noun in a sentence, it would look vague and incomplete. Nouns gives identification, builds sentence, acts as subject, and provides clarity.
What are compound nouns?
A compound noun is a noun formed by combination of two or more nouns to create a new meaning. For example, when we combine two nouns 'air' and 'plane' it forms a compound noun 'airplane'. Other examples are:
- Bookshop: book and shop
- Rainbow: rain and bow
- Sunflower: sun and flower
- What is Noun?
- Definition of a Noun
- Types of Nouns in English
- English Nouns Rules in Grammar
- Nouns in Grammar: Special Cases and Exceptions
- Nouns Vs Pronouns
- Noun Vs Verb
- Multifunctional Nouns
- Preparation Tips to Master Nouns
- How to Identify Nouns in a Sentence?
- Common Errors to Avoid
- Best Books for Nouns
- Nouns Exercises with Grammar
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- FAQs on English Nouns
What is Noun?
A noun is a naming word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. It is one of the fundamental parts of speech in English grammar and is used in almost every sentence to convey or express anything.
- Person: Rahul, teacher, doctor, Prime Minister, men, women
- Place: Delhi, school, beach, badminton court, classroom, college
- Thing: book, car, computer, mouse, bottle, earphones
- Idea: freedom, happiness, justice, argument, evolution
Examples:
- The cat sat on the mat (cat and mat are nouns because they name things and places, respectively).
- Riya is going to school (School is a noun depicting a place)
- Shyam bought a new car (Here, car is a noun representing things)
- Honesty is the best policy. (honesty is a noun representing an abstract idea)
Commonly asked questions
What are 20 examples of nouns?
Nouns are the naming words which are used in place of name, place, animal or things. Refer the list of nouns examples below:
- Delhi
- India
- Shyam
- Saumya
- herd of sheep
- pride of lion
- girls
- boys
- beautiful
- love
- happiness
- chair
- dog
- elephant
- table
- mouse
- children
- cow
- music
- group of students
What are 5 rules of nouns?
Check some of the rules of nouns below:
- Some nouns, while singular in meaning, are always treated as plural and take plural verbs.
- Certain nouns always appear in the plural form and require plural verbs.
- When nouns refer to measurements (such as weight, length, time, or money), and are preceded by a specific number, their form remains unchanged.
- Abstract or uncountable nouns always take singular verbs.
- Collective nouns may take either singular or plural verbs, depending on whether the group is seen as a single unit or as individuals.
What is the difference between singular and plural nouns?
A singular noun refers to one person, place, thing or idea, whereas, plural noun refers to more than one person, place, idea or things. For example 'cat', 'house', 'book' presents singular form and to indictae more than one thing or plural form, it will be written as 'cats', 'houses' and 'books'. While forming the plural form of singular nouns, candidates must abide with the grammatical rules.
Definition of a Noun
According to the Oxford Dictionary, a noun is “a word that refers to a person (such as ‘Ram’ or ‘teacher’), a place (such as ‘India’ or ‘school’), a thing (such as ‘table’ or ‘book’), or an idea (such as ‘happiness’ or ‘freedom’). Nouns can be used as the subject or object of a verb.”
According to the Collins Dictionary, a noun is “a word or group of words that refers to a person, place, or thing or any syntactically similar word.”
Pronounced as /naʊn/
Example, air, India, man, airplane etc. are nouns.
Types of Nouns in English
In English grammar, there are nine types of nouns. Read below to know the types of nouns:
1. Proper Nouns
A Proper Noun refers to a name given to specific people, places, or organisations. Proper nouns are always written with a capital letter at the beginning.
Example:
Mount Everest is the highest mountain in the world
2. Common Nouns
A Common Noun is a name shared by every person or thing of the same class and kind. In a sentence, proper nouns are sometimes used as common nouns. Check the examples below:
Example:
Mayank is the Shakespeare of our class. (‘Shakespeare’ is a proper used as a common noun)
3. Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns are the nouns which describe the physical sense of something. An object which can be touched, seen, heard, smelled or tasted as tagged as concrete nouns.
Example:
The baby is playing with a toy. (Toy is a concrete noun)
4. Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns are the opposite of concrete nouns. They are used to describe things that cannot be seen or sensed, such as ideas, emotions, or intangible things.
Example:
Honesty is the best policy. (Honesty is an Abstract noun)
5. Collective Nouns
Collective nouns refer to a naming word used for a group of animals, things or people.
Example:
The boy spotted a herd of sheep in the farm.
Tourists were excited to spot the pride of lions during the safari.
6. Countable Nouns
Countable nouns refer to nouns which can be measured or counted.
Example:
I have a pen
Shyam bought four cupcakes for his friends
7. Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns refer to nouns which cannot be measured or counted
Example:
Is there any water in bottle?
I have some information on new education policy
8. Singular Nouns
Singular nouns are used to name a single person, place or thing.
Example:
There is a cat in front of the house
I have a mango in my bag
9. Plural Nouns
Plural nouns are used to refer number of people, places or things. Plural nouns are formed by adding ‘s’, ‘es’, ‘ies’ or ‘ves’.
Example:
| Singular Noun |
Plural Noun |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Most nouns |
Add -s |
cat → cats, book → books |
| Nouns ending in -s, -ss, -sh, -ch, -x, -z |
Add -es |
bus → buses, box → boxes |
| Nouns ending in consonant + y |
Drop -y, add -ies |
baby → babies, city → cities |
| Nouns ending in vowel + y |
Just add -s |
boy → boys, key → keys |
| Some nouns ending in -f or -fe |
Replace with -ves |
knife → knives, leaf → leaves |
| Some -f/-fe nouns |
Just add -s |
roof → roofs, belief → beliefs |
| No fixed rule |
Change word form |
man → men, child → children |
| Some animals, fish, etc. |
No change |
deer → deer, sheep → sheep |
| Some nouns ending in -o |
Add -es |
tomato → tomatoes, hero → heroes |
| Some nouns ending in -o |
Add -s |
photo → photos, piano → pianos |
| Latin/Greek origin |
Use original plural form |
cactus → cacti, criterion → criteria |
English Nouns Rules in Grammar
There are some exceptions and rules of nouns in English grammar. Some of the common rules or exceptions for Nouns with examples are mentioned below:
Rule 1: Some nouns, though singular in meaning, are always treated as plural and take plural verbs.
Examples: people, police, cattle, government, audience.
- The police have arrived at the scene.
- People are becoming more health-conscious nowadays.
Rule 2: Certain nouns are always used in the plural form and require plural verbs.
Examples: trousers, scissors, spectacles, jeans.
- These jeans are too tight for me.
- My spectacles are on the table.
Rule 3: When nouns denote measurement (weight, length, time, money, etc.), they remain unchanged in form if preceded by a definite numeral.
Examples:
- He purchased 10 dozen eggs.
- My school is 3 kilometers away from home.
Rule 4: Some abstract or uncountable nouns always take singular verbs.
Examples: furniture, information, advice, knowledge, mathematics.
- The information you provided is useful.
- Mathematics is his favorite subject.
Rule 5: Collective nouns can take either singular or plural verbs based on whether the group is acting as one unit or as individuals.
Examples: team, committee, family, audience, staff.
- The jury has reached its verdict. (acting as one)
- The jury are discussing their opinions. (acting individually)
Rule 6: Material nouns typically don’t take articles like a, an, or the unless used in a specific or metaphorical sense.
- She bought a silver from the market. (incorrect)
- She bought silver from the market. (correct)
Also Read:
| Subject Verb Agreement Questions and Answers | Examples of Articles |
Rule 7: Some nouns have different meanings in their singular and plural forms.
Examples:
- Work (Singular): A task or job
Works (Plural): Factories or artistic compositions - Quarter (Singular): One-fourth
Quarters (Plural): Living accommodations
Rule 8: Neuter nouns (non-living things) may be referred to with masculine or feminine pronouns depending on qualities:
- Use feminine for beauty/grace (e.g. ships, nature)
- Use masculine for strength/power (e.g. cars, machines)
Example:
- The ship set sail; she was a sight to behold.
- The train roared as he sped through the valley.
Rule 9: Collective nouns and names of small creatures or babies are treated as neuter gender, even if they refer to living beings.
Example:
- The baby is sleeping peacefully.
- The ant crawled across the floor.
Rule 10: Titles of books, movies, or artworks are considered singular, even if they appear plural.
Example:
- The Chronicles of Narnia is a popular fantasy series.
- The Beatles is my dad’s favorite band. (referring to the name)
Nouns in Grammar: Special Cases and Exceptions
There are some exceptions or special cases to nouns.
- Plural nouns are formed by adding ‘s’, ‘es’, ‘ves’, ‘oes’, and so forth. Whereas, some irregular nouns do not follow the pluarisation rule.
For example:
- Child is changed to children
- Mouse is changed to mice
- Some nouns do not change their form. They are the same in singular and plural forms.
Example:
- Singular: There is a sheep in a field
- Plural: There are 20 sheep in the field
- Some uncountable nouns are written in singular form.
Example:
- Rohini gave me some advices on exam preparation. (wrong)
- Rohini gave me some advice on exam preparation. (correct)
Nouns Vs Pronouns
This table outlines the key differences between nouns and pronouns in English grammar. While nouns are naming words for people, places, animals, and things, pronouns are used to avoid repetition by replacing nouns.
| Features |
Nouns |
Pronouns |
|---|---|---|
| Definition |
Noun is a naming word for person, place, animal and thing |
Pronouns replaces noun to avoid repition |
| Example |
Kritika, Jaipur, Tiger, Pencil box |
He, she, it, them, they, etc |
| Function in a sentence |
Acts as a subject of a verb or preposition |
It replaces the noun as object or subject |
| Modified by |
It can be modified by articles, adjectives, quantifiers like some and many Example: Many students are attending the online webinar |
Not modified |
| Can it be a Subject/Object? |
Yes |
Yes |
| Form change |
Changes with as singular, plural or possessive noun |
Changes as per the subject form (she/he/them) |
Also Read: English Grammar: Conjunctions
Noun Vs Verb
This table highlights the fundamental differences between nouns and verbs in English grammar. Nouns represent names of things, while verbs express actions or states of being.
| Features |
Nouns |
Verb |
|---|---|---|
| Definition |
Noun is a naming word for person, place, animal and thing |
It is an action word. Describing the action or state of being |
| Example |
Kritika, Jaipur, Tiger, Pencil box |
Sleep, run, walk, eat |
| Function in a sentence |
Acts as a subject of a verb or preposition |
Tells what the subject is or does |
| Modified by |
It can be modified by articles, adjectives, quantifiers like some and many Example: Many students are attending the online webinar |
Modified by adverbs Example:
|
| Can it be a Subject/Object? |
Yes |
No |
| Form change |
Changes with as singular, plural or possessive noun |
Changes as per the tenses Example: Run, ran, running |
Also Read: English Tenses
Multifunctional Nouns
Preparation Tips to Master Nouns
How to Identify Nouns in a Sentence?
Common Errors to Avoid
Best Books for Nouns
Nouns Exercises with Grammar
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
FAQs on English Nouns
Commonly asked questions
How to identify a noun in a sentence?
To identify a noun in a sentence, students must apply the below rules:
- Look for words that name a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Find the subject or verb to spot connected nouns.
Example: She is writing – “She” is a noun, “is writing” is the verb. - Check for articles (a, an, the) – they usually come before nouns.
Example: The competition was held – “competition” is a noun. - Look for capitalized words – they might be proper nouns.
Example: Shakespeare wrote books – “Shakespeare” is a noun. - Words following “a lot, ” “some, ” or specific numbers are often nouns.
Example: Some pencils are on the table – “pencils"
What are the types of Nouns?
There are nine types of nouns:
- Proper Nouns: A proper noun is a noun that refers to specific person, place, animar or thing.
- Common Nouns: A Common Noun is a name shared by every person or thing of the same class and kind.
- Concrete Nouns: It is a noun which describe physical sense of something. An object which can be touched, seen, heard, smelled or tasted as tagged as concrete nouns.
- Abstract Nouns: These nouns are used to tell about things which cannot be seen or sensed. These are ideas, emotions, or any intangible things.
- Collective Nouns: Collective nouns refers to naming word used for a group of animal, things or person.
- Countable Nouns: These nouns refer to nouns which can be measured or counted.
- Uncountable Nouns: Uncountable nouns refer to nouns which cannot be measures or counted
- Singular Nouns: Singular nouns are used to name a single person, place or thing.
- Plural Nouns: These are used to refer number of people, places or things. Plural nouns are formed by adding 's', 'es', 'ies' or 'ves'.
What is collective noun in English Grammar?
A collective noun is a word given to group of people, things or animals. Example: herd, family, flock, government and so forth.
These nouns are usually treated as a singular noun even though it refers to a group of animal, thing or people.
English Nouns Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds