Are you the one who struggles while speaking and learning active and passive voice? Active voice and passive voice are important topics that everybody must learn, whether you are aged 10-12 or 55-60. We must understand their nuances, as active and passive voice are used in both written and spoken forms. Whether you are writing for an exam, drafting an academic paper, delivering a speech, or writing a blog post, understanding how to use active and passive voice gives you an edge over others. In this article, we will learn and explore the definition, types, grammar rules, exceptions, and practical applications of active and passive voice.
The voice of a sentence determines the relationship between the subject and the verb. Active and passive voices are the two primary options for constructing sentences. The active voice emphasizes the subject acting, while the passive voice shifts the focus to the action or the recipient. Both voices serve distinct purposes, and their effective use depends on the context and the intended message.
Also Read: What is Punctuation in English
What is the difference between active and passive voice?
Active voice occurs when the subject performs an action. While on the other hand, passive voice occurs when the subject receives the action. Normally it is recommended to use active voice in writing, as sentences get complicated in passive voice.
When should I use active voice?
In normal English it is advised to write sentences in active voice only. Since the sentence structure of active voice is simple and easy to understand for a user, unless asked, we need to prioritize writing in active voice only. It is generally preferred for straightforward communication or in Technical writing.
When should we use passive voice in writing?
The passive voice writing style is suitable for formal writing, scientific reports or any such situation where the subject is less important than the object, like the experiment was conducted. It highlights the action or result. In such style of writing object is doer instead of subject.
- Active Voice and Passive Voice Definition
- What is Active Voice and Passive Voice?
- Active Voice and Passive Voice Examples
- Types of Active Voice and Passive Voice
- Active Voice to Passive Voice Rules
- Active and Passive Voice Exceptions
- How to learn active and passive voice
- Should you write in the active voice or passive voice?
- Active and Passive Voice Practise Questions & Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- FAQs on Active and Passive Voice
Active Voice and Passive Voice Definition
Voice shows whether the subject of a verb does the action or receives it. Let’s deep dive to understand the definition of active and passive voice to get more clarity. Some of the popular active voice and passive voice definitions are mentioned below.
Active Voice Definition
The active voice definition, as per Collins Dictionary, is that
“A voice of verbs used to indicate that the subject of a sentence is performing the action or causing the event or process described by the verb.”
One such example of this is kicked in the sentence given below.
Ram kicked the ball. While here, Ram is a Noun.
Passive Voice Definition
According to the Collins Dictionary, the Passive voice definition is that
“ The passive or passive voice is formed using 'be' and the past participle of a verb. The subject of a passive clause does not perform the action expressed by the verb but is affected by it.”
For example, in 'She's been injured', the verb is in the passive. Here "She" is a Pronoun.
“If you describe someone as passive, you mean that they do not take action but instead let things happen to them.”
Commonly asked questions
What is definition of Active voice?
Active voice is a structure of a sentence where the doer is the subject that performs the action expressed by the verb. Here, the emphasis will be on the doer, making the sentence clear and direct.
For example, Siya was riding a bicycle. Here the emphasis is on Siya instead of on the bicycle.
What is the definition of Passive voice?
Passive voice is a type of sentence in which the subject receives the action instead of becoming the doer. Here, the focus will be on the object, and there will be a little focus on the subject or doer. I.e. A mango was eaten by Ram. In this sentence, the emphasis is on Mango instead of Ram.
Where will I get Active and Passive voice exercises?
To master active and passive voice, applicants are advised to practise a lot of questions. Active and passive voice exercises are given below on the page; candidates are advised to first solve the questions and then check the answers given below to it. Though it is required to practise questions, as many question as one can to gain the confidence.
What is Active Voice and Passive Voice?
Active Voice
First, understand the sentence formation of the Active voice. Active voice refers to the formation of a sentence when the subject performs the action expressed by the verb.
The active voice sentence formation structure is given below:
Subject + Verb + Object.
Let’s understand it with an example
The dog chased the cat.
This sentence clearly shows that the dog (subject) is performing the action (chased) on the cat (object).
Passive Voice
Passive voice is identified in a sentence when the subject receives the action instead of doing it. The person or thing doing the action is either left out or mentioned later. A passive voice sentence structure is given below:
Subject + helping verb (like "is" or "was") + past participle + (optional) "by" + the doer.
For example, in “The cat was chased by the dog”.
Here in this passive voice sentence, the cat receives the action, and the dog comes at the end. We use passive voice when the focus is more on the action or result than on who did it. Passive voice is useful when the action or result matters more than who performed it.
By understanding this example, we also get to know the difference between active voice and passive voice.
Also Read: Know What is Adverb
Active Voice and Passive Voice Examples
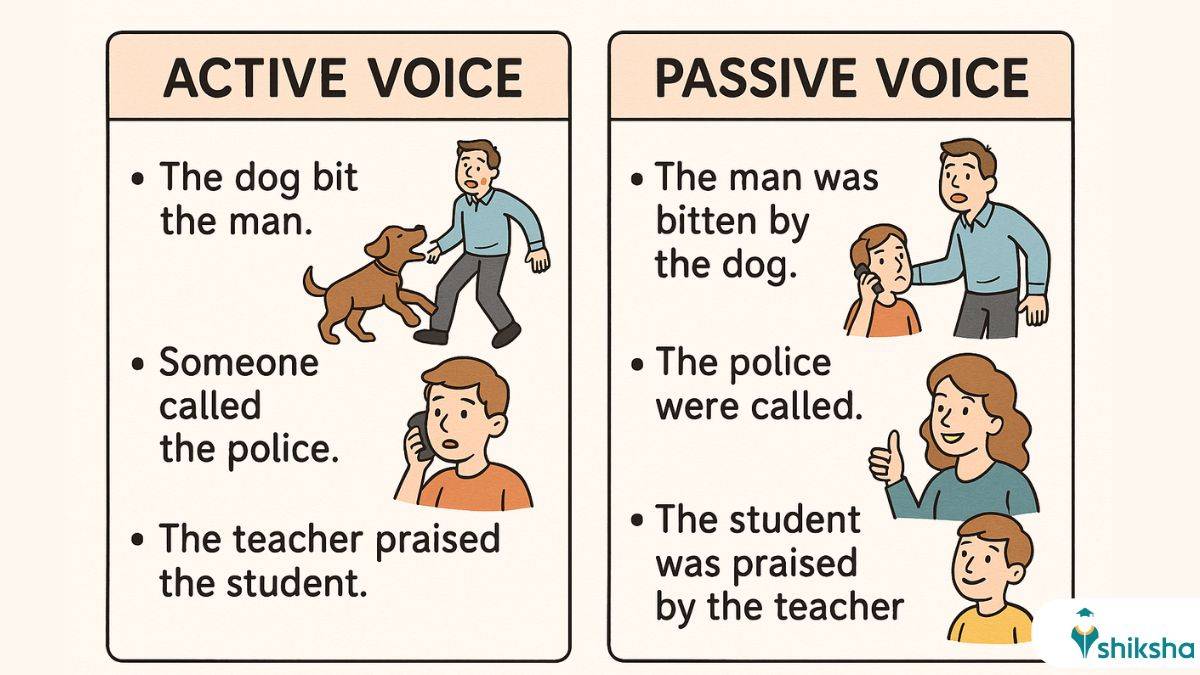
After knowing the active and passive voice definitions, students can check some of the active and passive voice examples given in the table below:
| Active Voice |
Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| The dog bit the man. |
The man was bitten by the dog. |
| Someone called the police. |
The police were called. |
| The teacher praised the student. |
The student was praised by the teacher. |
Types of Active Voice and Passive Voice
To deep dive into the concept of active and passive voice, applicants are advised to know the different types of active and passive voice separately, one by one. As per English grammar tense, the sentences are mainly divided into present, past, and future tenses; hence, we will explore active and passive voice types in a similar format.
(I). Present Tense Active & Passive Voice Types
In this type of voice-type sentence structure, we will see all the different types of present tense voices. The detailed description is given below.
1. (A) Present Active Voice
In present active voice, the subject performs an action that is happening now. It uses the present tense of the verb. The basic, simple active voice sentence structure and example are given below:
Structure: Subject + Present Verb (+ Object, if applicable)
Example: She writes a letter (present tense).
1. (B) Present Passive Voice
The conversion of passive voice is done through
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + Past Participle (+ by + Agent, if specified)
Example: A letter is written by her.
Explanation: The object "a letter" becomes the subject, receiving the action "is written", with "by her" indicating the doer (optional).
2. (A) Present Continuous Active Voice
In this present continuous active voice, the subject is actively performing an action that is ongoing or happening at the present moment. It uses the present tense of the verb "to be" (am, is, are) combined with the present participle (base verb + -ing). The present continuous active voice structure and example are given below:
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + Verb(-ing) (+ Object, if applicable)
Example: Sania is riding a scooter. (present continuous)
Here, Sania (subject) is actively performing a task (riding).
2. (B) Present Continuous Passive Voice
When the action being received by the subject is ongoing or occurring right now. It combines the past participle of the main verb with the present continuous tense of the auxiliary verb "to be" (am being, is being, are being).
Structure: Subject + am/is/are being + Past Participle (+ by + Agent, if specified)
Example: The scooter is being ridden by Sania
Explanation: Identify the subject, verb, and object in the active sentence. Make the object of the active sentence the subject of the passive sentence. Change the verb to its passive form. At last, put the original subject after the verb, preceded by "by".
3. (A) Present Perfect Active Voice
In this type of active voice, the subject has actively performed an action in the past or has relevance to the present moment. It uses the present tense of the auxiliary verb "have" (has/have) combined with the past participle of the main verb.
Structure: Subject + has/have + Past Participle (+ Object, if applicable)
Example: Nidhi has written a letter.
In this sentence, Nidhi (subject) has performed a task (writing) in the past.
Note:
- An auxiliary verb, also known as a helping verb, is a verb used along with a main verb to compose different tenses and voices in a sentence.
- A past participle is a verb form used to indicate a completed action or state, typically in perfect tenses.
3. (B) Present Perfect Passive Voice
It describes an action completed or relevant to the present moment. In this type there is emphasis on the receiver of the action rather than the doer.
Structure: has/have + been + past participle
Example: The letter has been written by Nidhi.
Explanation: The active sentence "Nidhi has written a letter" (present perfect tense) is converted by making the object "a letter" the subject and using the structure has + been + past participle ("has been written"). The doer "Nidhi" follows the verb with "by," emphasizing the action and receiver over the doer.
Also Read: Learn Subject Verb Agreement in English Grammar
(II). Past Tense Active Voice Types
The past tense voice type structure lets us explore all the different types of past tense voices. The detailed description is given below.
-
(A) Simple Past Active Voice:
A grammatical structure described as simple past active voice occurs when the subject actively carried out an activity that took place and was finished at a particular point in the past.
Structure: Subject + Auxiliary Verb (be) + Past Participle (+ by + Agent, if specified).
Example: Akhil wrote a letter.
Here, the subject “Akhil” performed an action (wrote).
-
(B) Simple Past Passive Voice
It is a grammatical form that emphasises the action or the recipient rather than the doer by giving the subject an action that was finished at a particular point in the past. It combines the past participle of the main verb with the past tense of the auxiliary verb "to be" (was/were).
Structure: Subject + was/were + Past Participle (+ by + Agent, if specified)
Example: The letter was written by Akhil.
Explanation: In this sentence, the object "a letter" is converted to the subject, and the passive structure was/were + past participle ("was written") is used. The doer "Akhil" is placed after the verb with "by", focusing on the action and receiver rather than the doer.
2. (A) Past Continuous Active Voice
Past Continuous Active voice defines a scenario in which the subject was continuously carrying out an ongoing action at a certain point in the past.
Structure: Subject + was/were + Verb(-ing) (+ Object, if applicable)
Example: Vikrant was watching a cricket match yesterday.
Here the subject is “Vikrant”, and the action is “watching”.
2. (B) Past Continuous Passive Voice
When expressing a continuous action in the past, the past continuous passive voice highlights the recipient above the doer, which is frequently the case when the doer is unknown or of lesser importance.
Structure: was/were + being + past participle
Example: A cricket match was being watched by Vikrant yesterday.
Explanation: The verb becomes "was being watched", a past continuous passive form, and the object "a cricket match" becomes the subject. At last, add by in the sentence framing.
3. (A) Past Perfect Active Voice
Past perfect active voice is a grammatical structure where the subject had actively completed an action before another action in the past.
Structure: Subject + had + Past Participle (+ Object, if applicable)
Example: Nitish had played football yesterday.
Here, the subject is “Nitish” and completed the action “play”
3. (B) Past Perfect Passive Voice
The past perfect passive voice is used to show that an action had been completed in the past by someone or something, before another past action or time.
Structure: Subject + had + been + past participle (V3) + (by + doer)
Example: Football had been played by Nitish yesterday.
Explanation: The verb takes on the past perfect passive form since the object "football" is now the subject: had been played. "By Nitish" indicates who carried out the action.
Future Active and Passive Voice Sentences
1 (A). Future Simple Active Voice
The future simple active voice is a verb tense in which the subject performs an action that will occur in the future. It conveys future facts, intents, choices, or projections.
Structure: Subject + will + base verb
Example: Nia will fly a kite tomorrow.
1 (B). Future Simple Passive Voice
The future simple passive voice is used in English grammar when an action will happen in the future, where the subject receives the action rather than performing it. It focuses more on the action or the result rather than on who or what performs it.
Structure: Subject + will be + past participle (V3) + (by + agent)
Example: A kite will be flown by Nia tomorrow.
Explanation: The object "a kite" becomes the subject, and the verb changes to the simple future passive form “will be flown”. "By Nia" shows who will do the action.
Also Read: Rules of Etymology and Roots
2. (A) Future Perfect Active Voice
The future perfect active voice is a verb tense used to describe an action that will be completed by a specific point in the future. It puts emphasis on the fact that the action will be finished before another future event or time.
Structure: Subject + will have + past participle of the main verb
Example: Manisha will have finished her homework by 9 PM.
2. (B) Future Perfect Passive Voice
The future perfect passive voice is a verb tense used to describe an action that will have been completed by a specific point in the future. In this type of passive voice the subject receives the action.
Structure: Subject + will have been + past participle of the main verb
Example: Her homework will have been finished by manisha by 9 PM.
Explanation: In this sentence, the object "her homework" becomes the subject. The verb is changed to the future perfect passive form: will have been + past participle (finished). "By Manisha" shows who will complete the action.
Active Voice to Passive Voice Rules
There are various rules to change active voice into passive and vice versa. The detailed description of active and passive voice rules is given in the table below.
| Tense |
Active |
Passive |
|---|---|---|
| Present Indefinite |
Verb 1st form + s/es e.g. Abhay plays cricket at home. |
Is/Am/Are + Verb 3rd form e.g. Cricket is played by Abhay at home. |
| Present Continuous |
Is/Am/Are + Verb 1st form + ing e.g. Avika is writing a letter. |
Is/Am/Are + being + Verb 3rd form e.g. A letter is being written by Avika. |
| Present Perfect |
Has/Have + Verb 3rd form e.g. He has cleaned the room. |
Has/Have + been + Verb 3rd form e.g. The room has been cleaned by him. |
| Past Simple |
Verb 2nd form e.g. Nidhi played a guitar. |
Was/Were + Verb 3rd form e.g. A guitar was played by Nidhi. |
| Past Continuous |
Was/Were + Verb 1st form + ing E.g. They were riding the bike since morning. |
Was/Were + being + Verb 3rd form E.g. The bike was being ridden by them since morning. |
| Past Perfect |
Had + Verb 3rd form E.g. I had done my work. |
Had been + Verb 3rd form E.g. My work had been done by me. |
| Future Simple |
Will + Verb 1st form E.g. I will watch a movie this Sunday. |
Will be + Verb 3rd form E.g. A movie will be watched by me this Sunday. |
| Future Perfect |
Will have + Verb 3rd form E.g. Sapna will have bought a car by next year. |
Will have been + Verb 3rd form E.g. A car will have been bought by Sapna next year. |
Also Read: What are Conjunctions?
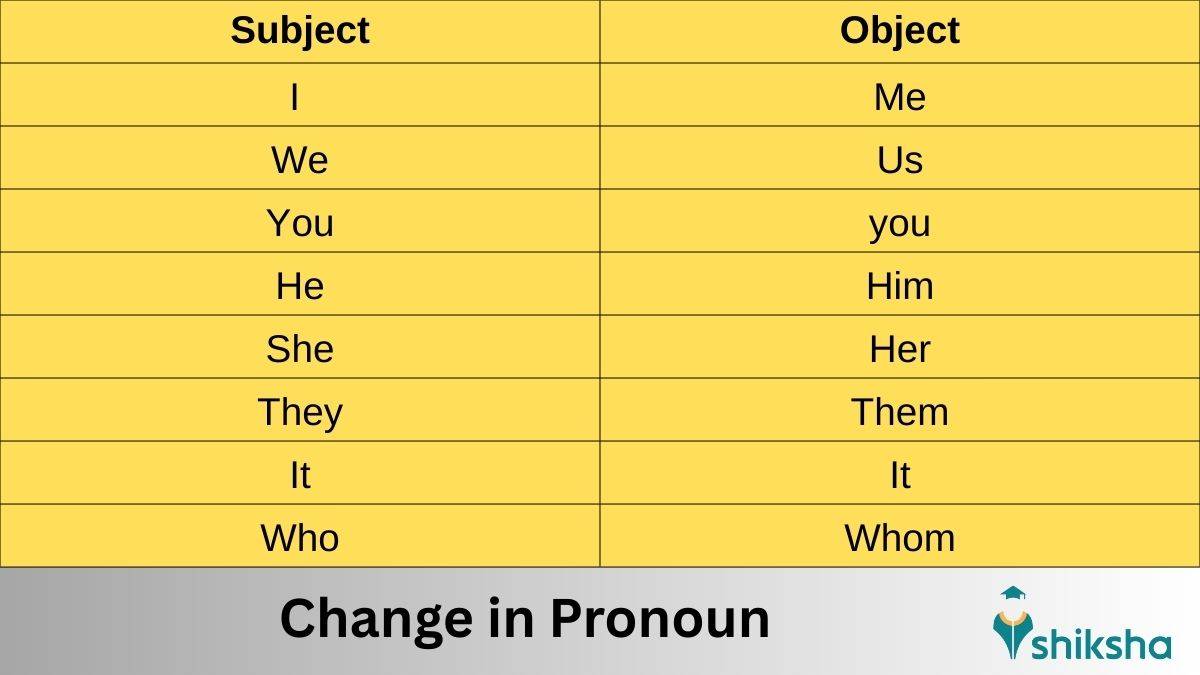
Passive Voice Rules: Change in Pronouns
While using the passive voice, we change the subject to the object. The table mentions the conversion of subject to object.
| Subject |
Object |
|---|---|
| I |
Me |
| We |
Us |
| You |
you |
| He |
Him |
| She |
Her |
| They |
Them |
| It |
It |
| Who |
Whom |
Active and Passive Voice Exceptions
Some of the common active voice and passive voice exceptions where the normal rules are not applicable. Hence, students are advised to be careful while solving such examples.
- Intransitive Verbs
These verbs cannot be converted to the passive voice because they do not accept a direct object. Hence, after recognising that the sentence has an intransitive verb, we can mention that there is no object being acted upon; hence, conversion is not possible.
Examples: Rain, go, sleep, come, die, arrive, exist
Active: Madhuri slept peacefully.
Passive: The passive voice can not be made.
- Reflexive Verbs
A reflexive verb is one in which the subject and object are the same. The passive voice can not be used for such sentences.
Example:
Active: Piyush hurt himself.
Passive: Not normally used, as "himself" refers back to the subject, hence passive voice can not be made.
- Verbs Followed by Infinitives
When an infinitive is used after a verb, some verbs do not naturally change to the passive.
Active: Ankur wants to eat a banana.
Passive (awkward): A banana wants to be eaten by Ankur. (Not natural). Hence, for such sentences, the passive voice can not be made.
How to learn active and passive voice
Students often search for the answer to how to learn active voice and passive voice. There is no shortcut or formula to master the active and passive voice quickly. Some of the tips and tricks to learn active and passive voice are listed below.
- Follow the standard books like Wren & Martin's High School & Objective General English.
- Learn and internalise the active and passive voice rules listed above.
- After this, solve and practise as many questions as we can.
- Solve previous year question papers of different competitive exams like SSC, SBI, and IBPS.
- We need to solve both types, one being how to convert active to passive voice and the other being how to change passive to active voice.
- It will help us to learn active and passive voice in the best possible way.
Also Know: Definition of Article in English
Should you write in the active voice or passive voice?
Active and Passive Voice Practise Questions & Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
FAQs on Active and Passive Voice
Commonly asked questions
Where can I get active and passive voice questions to practise?
Students who want to master the active and passive voice topics are advised to follow the questions mentioned on this page to practise. It will help them to develop an understanding about the active and passive topic.
How do I convert a sentence from active to passive voice?
To convert a sentence from active to passive voice, we first need to make the object of the active voice sentence the subject, then convert the sentence as per active-passive rules mentioned on the page above. There are some exceptions also which we need to keep in mind while converting a sentence from active to passive voice.
What will be the passive voice of the sentence "Whom have you called?"
For such kinds of sentences, Who will be converted to Whom and vice versa for making active to passive voice. Here, you is the subject and whom is the object.
Hence, the correct answer will be "Who has been called by you?"
English Active and Passive Voice Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds