Grammar is the backbone and the very foundation of any language. It’s not just about the rules, but the vast framework that envelopes the complexities of any language, including its structure. Such is the case for English grammar as well. In order to master the language, one must grasp the core itself. At a languag's centre is its grammar that makes any sentence more understandable.
Mastering English grammar is essential for both experienced writer or a novice tapping into the world of English,. In the following article, you’ll learn the following topics:
- Grammar rules
- Exceptions in English Grammar
- Common grammatical mistakes
- Examples of grammar in English.
- Best books for English grammar
What are the basic rules of grammar?
There are certain basic rules of grammar. Find below main rules of English grammar to not make any grammatical errors:
- Subject Verb agreement is a must.
- Correct verb tense must be followed
- Proper capitalisation of sentence needs to be done
- Punctuation
- Use proper pronoun agreement
- Adjective and Adverb placement
- Subject and a predicate must be there in each sentence
- Use the correct articles
- Avoid double negatives.
What are parts of speech in grammar?
Tere are 8 parts of speech. These play an important role in defining what purpose a word has in a sentence. The parts of speech are as follows:
| Part of Speech | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Nouns | Defines name, place, person, animal, idea, or thing |
| Pronouns | Words used in place of nouns |
| Verbs | Express an action, state of being, possession, condition, or occurences |
| Adjectives | Define noun & pronoun |
| Adverbs | Modify adjectives/ verbs/ other adverbs |
| Preposition | Join different parts of a sentence |
| Conjunctions | Words liking phrases/ clauses |
- What is English Grammar?
- Definition of Grammar
- Components of English Grammar
- English Grammar Rules
- Sentence Structure in English Grammar
- Sentence Pattern in English Grammar
- Understanding Clauses in English Grammar
- Grammar in Spoken and Written English
- Best Tips to Master English Grammar
- Best Books to Prepare for English Grammar
- Practice Questions for English Grammar with Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on English Grammar
What is English Grammar?
Grammar is a set of rules that support the structure and composition of the language. Imagine it as bricks that build a huge building, it is necessary that each brick is placed right to make the building stronger. Using English grammar can help one convey the message in a more comprehensible and meaningful way. Grammar confies rules which help sentences not sound unclear or hard to understand
Parts of Speech are building blocks of English grammar where each part of speech plays a significant role in structuring any sentence in a way that sounds sensible. Hence, mastering parts of speech can be a breakthrough in mastering grammar in English.
Also Read:
Definition of Grammar
As per the Oxford dictionary, grammar is defined as 'the rules in a language for changing the form of words and joining them into sentences.'
In Cambridge dictionary grammar is 'the study or use of the rules about how words change their form and combine with other words to express meaning.'
Word origin: Late Middle English: from Old French gramaire, via Latin from Greek grammatikē (tekhnē) ‘(art) of letters’, from gramma, grammat- ‘letter of the alphabet, thing written’.
Pronunciation: gra-muh
Components of English Grammar
Parts of Speech is at the centre of English grammar. There are eight parts of speech in English and you must know parts of speech and how to use them to help in categorising words based on their function within a sentence.
Each part of speech has a role to play to improve the sentence structure. Let us have a look at parts of speech in English grammar, with their general definition and examples for better understanding:
| Part of Speech |
Definition |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Defines the name of a person, place, animal, idea, or thing |
Janice, you’ve been awfully quiet these days. |
|
| Words used in place of a noun |
Joan was sipping her tea in the garden. She thought it was too sweet. |
|
| Words expressing an action, state of being, possession, condition or occurrences |
He ate the ice cream all by himself. |
|
| Words defining Noun and Pronoun |
Mirae looked beautiful in the blue dress. |
|
| Words which describe/ modify adjectives/verbs/ other adverbs/ clauses/ prepositions |
My friend and I often have sushi at a nearby restaurant. |
|
| Words linking different parts of a sentence |
I was waiting for the cab to arrive when I saw my friend. |
|
| Words linking phrases/ clauses/ words |
My mom was planning to go shopping regardless of the downpour outside. |
|
| Words used to convey strong emotions or reactions to showcase surprise/ joy/ astonishment |
Wow! The movie left me awestruck with its cinematography. |
Also Read:
English Grammar Rules
Are you someone who often looks at a sentence while thinking, “This sounds fine, it should be grammatically correct”, instead of checking whether the sentence is in fact grammatically correct?
If yes, then you can check out the following points to understand English grammar rules. By using the correct rule, you may realise that grammar can be quite easy. Learning this can also help you with questions on English grammar rules for competitive exams.
Subject - Verb Agreement
You must use a singular verb with a singular subject. Likewise, a plural subject needs a plural verb. See the example below to understand this better:
Example:
- Correct: Sunjae swims
- Incorrect: Sunjae swim
Also Read: Preparation Tips to Master Subject Verb Agreement
Usage of Article: A/An, The
It is essential to use articles wherever required. “A” needs to be used as a prefix for consonant sounds, “an” before vowel sounds, and “the” while referring to something specific.
Example:
- I met a man at the theatre yesterday.
- Rhea had an apple before leaving.
- The sun sets in the west.
Also Read: Articles in English grammar
Using the Correct Pronouns
One must not mix up pronouns. They must match the number/ gender of the noun in place of which the pronoun is used.
Example:
- Sarah is waiting and She is set on carrying her luggage all by herself.
- The kids were playing when they broke the window.
Using Tenses Correctly
While making a sentence, ensure to match the tense with the timeline of the action being talked about.
Examples:
- Shaun has watched Conjuring fifteen times. (Rule for Present Perfect Tense - Subject + has + V3 + Object).
- They have been working tirelessly on this project (Rule for Perfection Continuous Tense –Subject + has been + V1 + object)
- My friend bought a nice dress for herself after watching. (Subject + V2 + Object)
Also Read: Types of Tenses in English Grammar:
Adjectives v/s Adverbs
Use adjectives for nouns and adverbs for verbs/ adjectives or other adverbs. See the examples below to understand this:
Example:
- Harry’s a fast (adjective) swimmer.
- The plant is growing rapidly. (adverb)
Prepositions are a Game Changer
Using prepositions in a sentence can reflect time, place, and direction.
Example:
- Don’t worry, my friend, we’ll meet at the port.
- The dog is hiding under the table.
- He came to the bus stop in the heavy rain.
Capitalisation in English Grammar
Sentences might look all over the place and difficult to understand if the words aren’t capitalised in the right way. Some key points where it is essential that one capitalises correctly are as follows:
- Proper Nouns, such as names, places, brands
- Days, Months, and Holidays
- The first letter of the first word of a sentence needs to be capitalized in English
Punctuation Rules
Punctuation in English grammar is essential for sentence structure. Check out the points below to know about the common punctuation rules in English:
- Period (.) ends a statement
- Question mark (?) ends a question
- Exclamation mark (!) shows excitement
- Comma (,) separates items, clauses, and more
- Apostrophe (‘) shows possession or contractions
Avoid Using Double Negatives at All Costs
Just as two negatives cancel each other out in Mathematics, the same applies to English grammar. Don’t use double negatives in a sentence. Let’s take a look at some example to understand this better:
Example:
- Incorrect: I don’t need nobody.
- Correct: I don’t need anybody.
Note: This is acceptable in certain dialects and informal speech. For example, in AAVE (African-American Vernacular English) or Cockney English.
Example: I ain’t got no money, sweetie.
Standard English: I don’t have any money, sweetie.
Pro Tip: You can replace double negatives with positive or neutral words, such as any, ever, or anything.
Sentence Structure in English Grammar
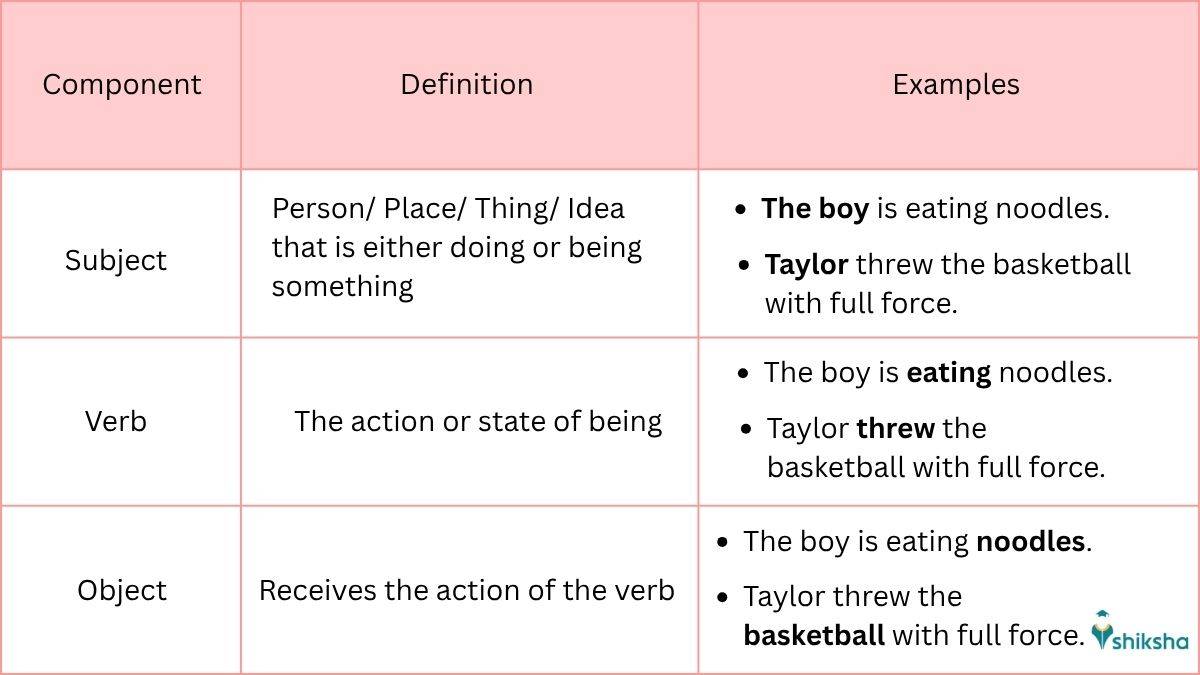
Sentence structure is used to arrange words/ phrases/ clauses, etc., in the correct order based on English grammar rules. A sentence is considered complete only when it has a Subject, a verb, and a thought that makes sense on its own. The main components of an English sentence are:
Subject: Person/ Place/ Thing/ Idea that is either doing or being something
E.g: 1: The boy is eating noodles.
E.g: 2: Taylor threw the basketball with full force.
Verb: The action or state of being
E.g: 1: The boy is eating noodles.
E.g: 2: Taylor threw the basketball with full force.
Object: Receives the action of the verb
E.g: 1: The boy is eating noodles.
E.g: 2: Taylor threw the basketball with full force.
A simple sentence can carry multiple components which in turn make the sentence coherent.
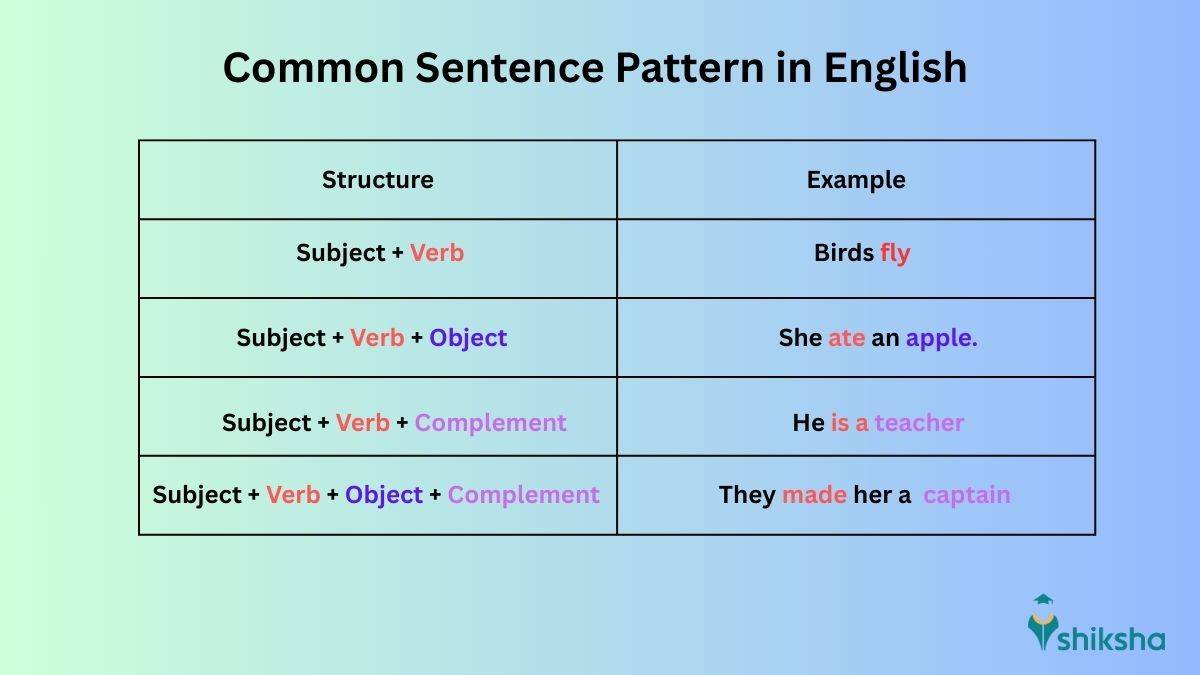
Sentence Pattern in English Grammar
A sentence has basic components, such as Subject, Object, Complement, Verb, etc. Check out the following image to learn about some common sentence pattern in English Grammar along with examples:
Types of Sentence Structure in English
From the image above, you may have gotten a general idea about the formation of a sentence. English sentences are often categorised by the complexity. The complexity is based on number and type of clauses. To understand it better, let’s have a look at the following points:
-
Simple Sentence
Simple sentences in English contain one independent clause and express a single complete idea.
Example: I hate milk.
-
Compound Sentence
Compound sentences contain two or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction, such as for, yet, so, and, but, etc.
Example: I love reading books, but I also enjoy watching movies.
-
Complex Sentence
Complex sentences in English grammar are when one independent clause is joined with at least one dependent clause. One must note that a dependent clause can’t stand alone.
Example: Although I was hungry, I skipped my meal to enjoy the sunset.
-
Compound-Complex Sentences
In English, compound-complex sentences are used when at least two independent clauses and one dependent clause are used.
Example: Although I was running late, I still went for a walk around the park and did some yoga.
Check out the following image to get a better idea about commonly used sentence pattern in English:
Understanding Clauses in English Grammar
Clauses in English grammar are words that contain a subject and a verb. Check out the following points to learn about the types of clauses in English:
- Independent Clause (aka Main Clause): Expresses a complete thought and can stand alone as a sentence.
Example: I enjoy star-gazing. (Subject- I; Verb- enjoy)
- Dependent Clause (Subordinate Clause): Neither expresses a complete thought nor can it stand alone as a sentence. It requires an independent clause to make sense.
Example: As I enjoy reading (The sentence is incomplete and leaves the listener/reader with questions, rather than getting the complete picture)
Types of Dependent Clauses in English Grammar
Check out the table below to learn all about dependent clauses in English grammar:
| Dependent Clause |
Words |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Adjective Clauses |
Usually begins with who, whom, whose, which, that |
The girl who made the pizza is from my hometown |
| Adverb Clauses |
Modifies verbs/ adverbs/ adjectives with time, cause, condition, contrast |
She looked to her side as someone called her name |
| Noun Clauses |
Act as a subject, object, or complement using that, what, who, whether, how, why |
That was the last time she called me before leaving. |
Tips to Identify Clauses
If you’re someone who finds it difficult to identify clauses in a sentence, then here are a few tips to might be of help in identifying clauses:
Tip 1: Look for a sentence and a verb in a sentence.
Tip 2: Check whether it can stand alone in a sentence and still make sense. If the answer is yes, then it is an independent clause. If the answer is no, then it is a dependent clause.
Tip 3: Ensure to see that a it starts with a subordinating word, such as if, when, that, etc.
Grammar in Spoken and Written English
Best Tips to Master English Grammar
Best Books to Prepare for English Grammar
Practice Questions for English Grammar with Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on English Grammar
Commonly asked questions
What are some tips to improve English grammar?
Here are some quick tips to master English grammar in an easy way so that you don't have to wing it, thinking “if it sounds right, it's probably correct”.
Tip #1: Understand the basics of grammar. Once you understand the rules, it'll be a piece of cake to master grammar.
Tip #2: Make a habit of reading frequently. Reading various books from different genres is one of the quickest and the easiest ways to notice the pattern of grammar. Once you realise the pattern, it'll be only a matter of time before you stop making grammatical errors.
Tip #3: Play online grammar quizzes.
Tip #4: Practice by answering English grammar workbooks.
What are some good books for English grammar?
Find below some popular books to prepare for English grammar:
Book | Author/ Publication |
|---|---|
Understanding and Using English Grammar | Betty Schrampfer Azar |
Practical English Usage | Michael Swan |
Fundamentals of English Grammar | Betty Schrampfer Azar |
Oxford Guide to English Grammar | John Eastwood |
The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language | Rodney Huddleston |
Basic English Grammar: With Answer Key | Betty Schrampfer Azar |
English Grammar Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds