- Concave and Convex mirrors
- Image formation by Spherical Mirrors
- Concave
- Convex
- Illustrative Examples
Concave and Convex mirrors
Plane Mirrors
This type of a mirror is a plane reflecting surface. The size of the image formed is almost equal to the size of the object.
Spherical Mirrors
These mirrors have curved surfaces. The spherical mirrors are of two types:
- Convex Mirrors
- Concave Mirrors
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
The concave mirror is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards (faces the centre of the sphere). On the other hand, a convex mirror has an outward-reflecting surface.
Image formation by Spherical Mirrors
The following ray diagrams show the various image formations for both the spherical mirrors.
Concave
1.
| Object Position |
Image Position |
Image Size |
Image Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
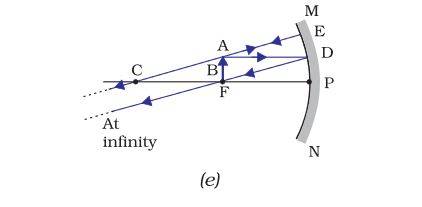
| At infinity |
At the focus F |
Highly diminished, point size |
Real and inverted |
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
2.
| Object Position |
Image Position |
Image Size |
Image Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
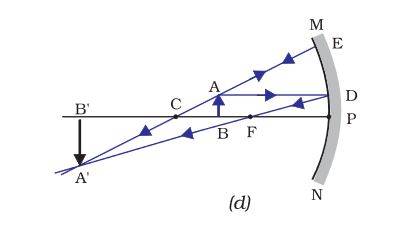
| Beyond C |
Between F and C |
Diminished |
Real and inverted |
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
3.
| Object Position |
Image Position |
Image Size |
Image Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
| At C |
At C |
Same size |
Real and inverted |
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
4.
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Size | Image Nature |
| Between C and F |
Beyond C |
Enlarged |
Real and inverted |
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
5.
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Size | Image Nature |
| At F |
At infinity |
Highly enlarged |
Real and inverted |
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
6.
| Object Position | Image Position | Image Size | Image Nature |
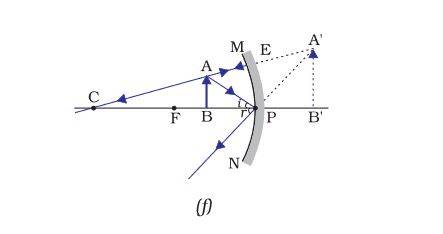
| Between P and F |
Behind the mirror |
Enlarged |
Virtual and erect |
(Image source:https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
Convex
| Object Position |
Image Position |
Image Size |
Image Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
| At infinity |
At F, behind the mirror. |
Highly diminished, point size |
Virtual and erect |
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
2.
| Object Position |
Image Position |
Image Size |
Image Nature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Between infinity and P |
Between P and F, behind the mirror. |
Diminished. |
Virtual and erect |
(Image source: https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/jesc110.pdf)
‘Convex and Concave Mirrors’ is a topic from the chapter ‘ Light- Reflection and Refraction’, taught in Class X Science (NCERT). 4 questions for 8 marks are asked in the exam from this chapter.
Illustrative Examples
Example 1: A convex mirror has a radius of curvature of 6.00m. If a tree is at 10.00m from this convex mirror, find the nature, position, and size of the image of the tree.
Solution: Radius of curvature, R=+6.00m;
Object-distance, u=–10.00m;
Image-distance, v=?
Height of the image, h′=?
Focal length, f=R/2=+6.00m/2=+3.00m
Since 1/u+1/v=1/f,
Thus, v=uf/(f-u)=30/13=+2.31 m
And, m=h'/h=-v/u=2.31/10.00=0.23.
Therefore, the image is virtual, erect, and smaller in size by a factor of 0.23.
Example 2: Given h=4cm, u=-25cm, f=-15cm. Find v and h'?
Solution: Since 1/u+1/v=1/f,
1/v=1/25-1/15
v=-37.5cm
m=h'/h=-v/u
h'=-vh/u.
h'=-6cm.
Example 3: h=4cm, h’=16cm, u=-10cm, v=?
Solution: h'/h=-v/u
16/4=v/10
v=40cm.
FAQs
Q: What is reflection?
A: The phenomenon of light when it bounces off shiny and polished surfaces is called reflection.
Q: What are the types of mirrors?
A: Plane mirrors and spherical mirrors.
Q: What are the types of spherical mirrors?
A: Concave and convex.
Q: Define Concave and Convex mirrors.
A: The concave mirror is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards. The reflecting surface of the convex mirror is curved outwards.
Q: What is the mirror formula?
A: 1/u+1/v=1/f; where u=object distance, v=image distance, f=focal length.
Explore exams which ask questions on Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Select your preferred stream
Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Reflection of Light by Spherical Mirrors
- Optical Instruments
- Refraction through a Prism
- Refraction at Spherical Surface and by Lenses
- Total Internal Reflection
- Refraction
- Raman Scattering
- Concave and Convex Mirrors
- Spherical Mirror
- Derivation of Lens Formula
- Beer Lambert law
- Lamberts Cosine law
- Derivation of Prism Formula
- Scattering of Light definition
- Fiber Optic Cable diagram
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test