Physics Class 11 Notes
Class 11th Physics seems tough?
Go through 11th Physics quickly.
Refraction is the bending of light when it travels from one medium to another, where the speed of light also changes. The phenomenon of refraction occurs because the speed of a light wave depends on the properties of the medium.
The content shared below has been reviewed for quality by Raghvendra Kumar, who is a subject matter expert with years of experience in teaching. We have referred to the NCERT and standard Physics books to maintain factual accuracy while creating the content.
In this lesson, we will be explaining the phenomenon of refraction, how it happens, refraction in different media and its important applications. Once you have completed this lesson, you can practice Ray optics and Optical instruments NCERT excercise.
As stated in the NCERT book:
“Light does not travel in the same direction in all media. It appears that when travelling obliquely from one medium to another, the direction of propagation of light in the second medium changes. This phenomenon is known as refraction of light.”
Refraction is the bending of light as it travels from one medium to another. This phenomenon occurs because light changes its speed as it travels from one medium to second medium. The side of the wave that enters another medium will travel at a different speed compared to the end of the wave that is still travelling in the first medium.
Here is a simulation that shows how light refraction causes image creation through lenses:
Physics Class 11 Notes
Class 11th Physics seems tough?
Go through 11th Physics quickly.Physics Class 12 Notes
Need to complete Physics chapters before exams?
Revise 12th Physics Notes.What is the unit of refractive index?
Refractive index (n) is a dimensionless quantity that has no units. Since both numerator and denominator are in meters per seconds (m/s), both units cancel each other. This makes refractive index simply a number.
There are two fundamental laws of refraction, which are mentioned below:
1. Incident Ray, Refracted Ray and Normal: The first law of refraction states that the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal all lie in the same plane. When light hits the boundary between 2 media, the incident ray (incoming light), the refracted ray and the normal (which is the imaginary line perpendicular to the surface) will all lie in the same plane.
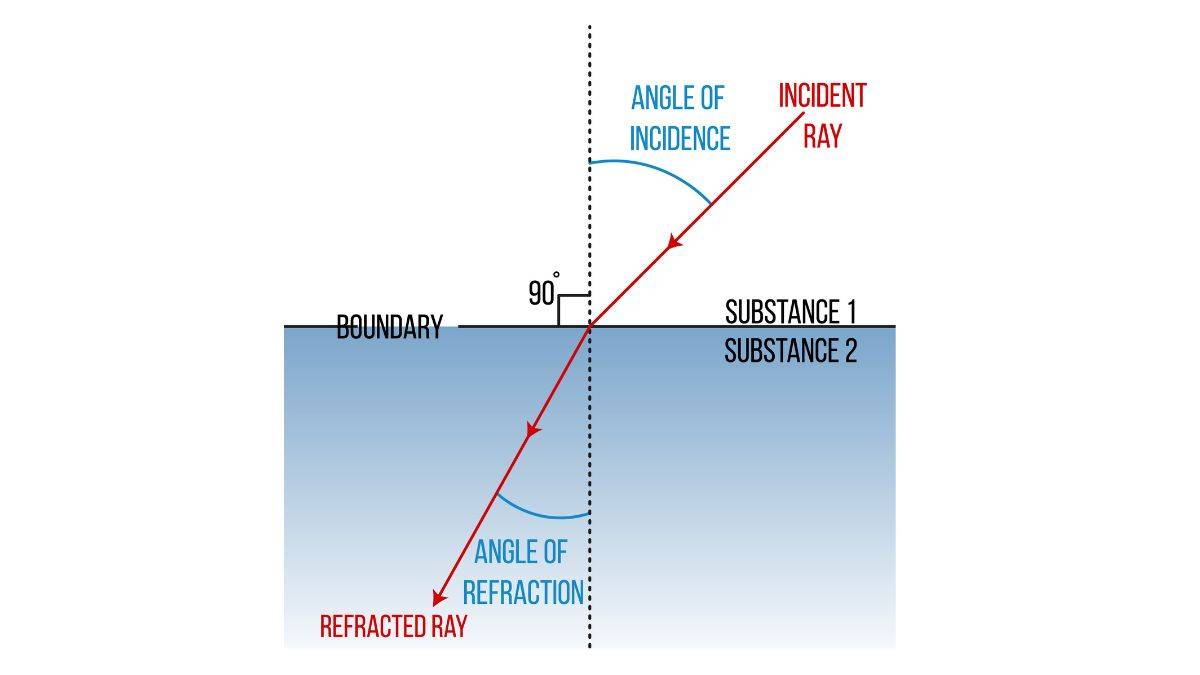
2. Snell's Law: The second law describes how light bends, whereas mathematically it describes how much the light bends.
and denote the refractive index of the first and second medium, respectively, is the angle of incidence and is the angle of refraction.
Class 12 CBSE Notes
Worried about the pending board syllabus?
Revise 12th Class Notes.11th CBSE Notes
Class 11th topics left before exams?
Revise 11th CBSE notes.Do remember that the speed of light is not the same in every medium. The speed of light is the maximum in vacuum since there are no particles that can interfere with light. However, it slows down in other media. Also, the speed of light changes with the refractive index of the material. The refractive index (n) measures how much the medium will slow down light as compared to a vacuum.
In short, the refractive index is inversely proportional to the speed of light. The higher the speed of light, the slower the speed of light will be.
The following table lists the speed of light in different media.
| Medium | Speed of Light (m/s) | Refractive Index (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum | 299,792,458 | 1.0000 |
| Air | 299,702,547 | 1.0003 |
| Water | 225,000,000 | 1.33 |
| Ethanol | 220,000,000 | 1.36 |
| Glass (typical) | 200,000,000 | 1.50 |
| Diamond | 124,000,000 | 2.42 |
Let us understand the applications of refraction.
Also known as the Fermat's principle, this is a fundamental concept in Optics that states that "light will follow the path that requires the least time when travelling between two distances". It is not necessary that the distance is also the shortest. This concept is expressed using concept of optical path length which is the product of distance travelled and refractive index of the medium.
Mathematically, the optical path will be:
L=∫nds
Here,
When light bends, it will spend less time in a slower medium to optimize the total travel time. As you can see, whenever the light travels through a denser medium, its path becomes longer in distance but the time taken to travel will reduce.
This principle also applies to reflection since light reflects in a way that total time is minimized. This is why the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
What is Refractive Index?
The refractive index is an optical property of the material that describes how much does the light bend or refract while passing from one medium to another. It is the ratio of spee of light in vacuum (c) to speed of light in a material (v) Refractive index is the reason which causes refraction. When light travels from a rarer medium (low refractive index) to denser medium (higher refractive index), it will slow down and bend toward the normal. Refractive index also changes according to the wavelength of light. Air has 1.003 refractive index, water has 1.33 refractive index and glass has a refractive index of 1.5 to 1.9.
What is atmospheric refraction??
This type of refraction is the bending of light rays when they pass through the atmosphere of Earth because of the change in the air density. The density of air varies with pressure and temperature.
Due to the atmospheric refraction, celestial objects appear higher than they actually are. This leads to an advanced sunrise and a delayed sunset as well as the twinkling of stars.
When light from space enters the Earth's atmosphere, it slows down and changes direction as light moves from a rarer to a denser medium, which causes refraction.
What is absolute refractive index??
Absolute refractive index is the ratio of speed of light in air/vacuum to speed of light in any medium. It is closely related to refractive index, except that it is relative to vacuum and not to any other medium. This is different from relative refractive index because it is the ratio of speed of light in one medium compared to the speed of light in another medium.
Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Exam
Exams accepted
CA Foundation
Exams accepted
ICSI Exam
Exams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka Test
Bachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBE
Exams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance Exam
Bachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance Exam
BA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT India
Bachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test