Pronouns are one of the essential chapters or topics of English grammar. It is one of the eight traditional parts of speech. Pronouns are not only a part of the basic English grammar curriculum but also find their usage in day-to-day conversation and written English communication. While we start a sentence with a noun, to avoid repetition of the same name or word, we replace nouns with pronouns such as he or him, she or her, they or them, etc.
Learning about pronouns is not just useful for regular English usage, but forms a part of the syllabus of any exam which tests English subject knowledge. This page of Shiksha.com brings you in-depth information about Pronouns, their types, practice questions, and examples, to name a few.
In which section of English grammar does Pronoun belong to?
Pronouns belong to the Parts of Speech section of English Grammar. Pronoun is one of the eight traditional types of Parts of Speech. The other seven types pf Parts of Speech include Noun, Verb, Adjective, Adverb, Preposition, Conjuntion and Interjection.
What are the primary types of Pronouns?
The primary types of Pronouns which are used in day to day lives are as follows:
- Personal Pronouns: This type of pronouns are used to indicate specific people or things. Examples: I, you, me, he, she, we, they, etc.
- Possessive Pronouns: These pronouns signify ownership or posession. Examples: Mine, your, our, their, his, her, etc.
- Reflexive Pronouns: This refers to the subject of the sentence such as myself, yourself, himself, herself, etc.
- Demonstrative Pronouns: These pronouns are used to point out specific things or objects like this, that, those, these, etc.
- Interrogative Pronouns: Used for asking questions such as who, whom, which, what, etc.
What is the right time to use Pronouns?
Pronouns are generally used after the first sentence, or after the first instance of Noun. Once the Noun is stated or the subject is introduced, Pronouns can be used as a substitute of the Noun. For example, Riya studies in Class 6. Her favourite subject is History. Here, the Pronoun 'Her' is used in the second sentence as a substitute to the Proper Noun, which is Riya.
- What is Pronouns
- Definition of Pronoun
- Types of Pronoun
- Grammar Rules of Pronouns
- Pronouns in English Grammar: Special Cases and Exceptions
- Pronoun Vs Noun
- Pronouns Vs Adjectives
- Preparation Tips to Master Pronouns in English
- Common Errors to Avoid in Pronouns
- Best Books for Pronoun Preparation
- Engaging Practice Exercises for Pronouns
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- FAQs Regarding Pronouns
What is Pronouns
Pronouns stand for words which are used in lieu of nouns to make a sentence or paragraph more concise. It is classified as a part of speech which plays a specific and identifiable role in sentence structure and formation. There are over 10 types of pronouns, and the usage varies from case to case.
The purpose of pronouns is to provide a context for the sentence, along with making the meanings clearer. The usage of pronouns also helps break the monotony in conversation or reading. Read the following lines to understand better.
Meet Rita, my sister. Rita is a medical student. Rita’s favourite colour is blue.
Isn’t it a monotonous read? Now, let us use pronouns to make it better.
Meet Rita, my sister. She is a medical student. Her favourite colour is blue.
Here, we have used the noun in the first instance, and pronouns in the second and third sentences.
Commonly asked questions
What are the benefits of Pronoun?
Using Pronouns in correct manner has the following benefits:
- Avoids repetition: Using pronouns appropriately can avoid repeating the nouns.
- Improves flow of sentence: Using pronouns help maintain the flow of the sentence and improves clarity.
- Supports sentence structure: Pronouns play important role in subject-verb agreement and sentence construction.
What are some gender neutral pronouns?
Some of the gender neutral pronouns include the following:
- It
- They
- Them
- Ze/zir
- Xe/xem
Which pronoun to use if I don't know the person's gender?
When you are not sure of a person's gender, then the most appropriate pronoun to be used is 'they/them'. Although 'they/them' is generally used as a plural pronoun, in case of gender ambiguity, 'they/them' is widely accepted, and can be considered gramaatically correct.
Definition of Pronoun
Pronouns can be defined in the simplest terms as substitutes for nouns.
According to the Oxford Dictionary, “A word that is used instead of a noun or noun phrase, for example he, it, hers, me, them, etc.”
Pronunciation: /ˈprəʊnaʊn/
Word Origin: late Middle English: from pro- ‘on behalf of’, + noun, suggested by French pronom, Latin pronomen (from pro- ‘for, in place of’ + nomen ‘name’).
Pronoun Definition as per Collins Dictionary
As per the Collin’s Dictionary, the definition of pronoun is, “A pronoun is a word that you use to refer to someone or something when you do not need to use a noun, often because the person or thing has been mentioned earlier. Examples are 'it', 'she', 'something', and 'myself'.”
Pronunciation: proʊnaʊn
Word Origin: from Latin prōnōmen, from pro-1 + nōmen noun
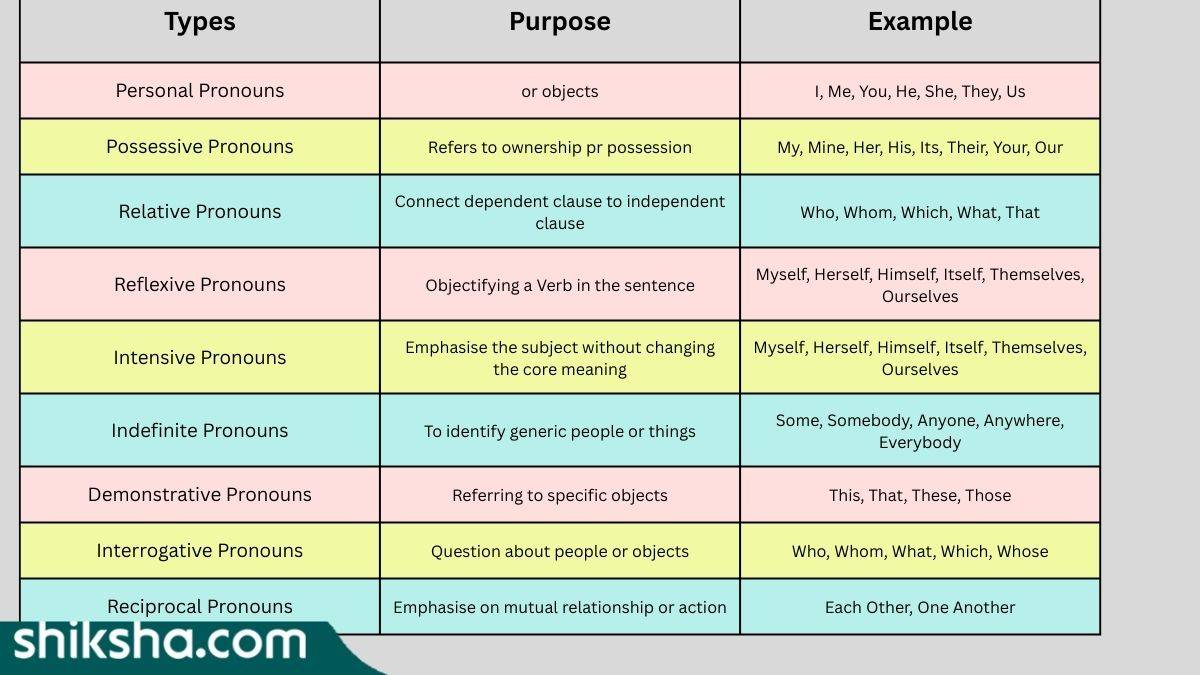
Types of Pronoun
Pronouns can be segregated into 10 broad types. Here is the list and explanation, along with examples given in this section.
-
Personal Pronouns:
Personal pronouns are those which are used to refer to people, animals or other living beings. The Personal Pronouns can be further segregated into First Person, Second Person and Third Person.
Types of Personal Pronouns:
- First Person Pronoun: I, Me, (Singular) and We, Us (Plural)
Example: I am reading a book.
Here ‘I’ is the pronoun used for first person.
- Second Person Pronoun: You, Your, Yours
Example: Will you be watching the match tonight?
Here ‘you’ is the second person pronoun which is used instead of using the proper noun while directly addressing the person concerned.
- Third Person Pronouns: He, Him, His, She, It (Singular) and They, Them (Plural)
Example: I saw him and the market today but he did not see me.
Here ‘him’ and ‘he’ are third-person pronouns which are used while referring a person to someone else.
-
Possessive Pronouns:
The Possessive Pronouns refer to those pronouns that signify possession or ownership of objects or relation with people or living beings. These pronouns include My, Mine, His, Her, Their, Its.
Example: This book is mine as my name is written on its cover.
Here ‘mine’ and ‘my’ are the possessive pronouns and ‘its’ is the possessive pronoun for book, which is an inanimate object.
-
Interrogative Pronoun:
This type of pronoun is used while asking questions about people or things. Interrogative pronouns include who, whom, whose, and which.
Examples:
- Whose pen is this?
- Which pizza do you want to have?
Whose and which are the subject of interrogation and no proper noun is used here to define the subject.
-
Indefinite Pronoun:
This type of pronoun does not specifically refer to any person or object in particular. The quantity of the subject may also vary. These pronouns are Anyone, Someone, Everybody, Everyone, etc.
Examples:
- Can anyone lend me an umbrella?
- Everybody must attend the meeting tomorrow.
The pronouns ‘Anyone’ and ‘Everybody’ are used to address multiple people or an indefinite number of people, and no specific person has been addressed here.
-
Demonstrative Pronouns:
These types of pronouns are used to point out a specific person or object, such as This, That, Those, These.
Examples:
- This is my favourite colour.
- These children are my students.
- That machine is making a lot of noise.
The pronouns ‘This’, ’These’ and ‘That’ are used to address specific people or things.
-
Relative Pronouns:
This type of pronoun connects the relative clauses to the independent clauses. In simple terms, Relative Pronouns act as a bridge between the subject and the related information. Such pronouns are That, Which, Whom, Where, Whose.
Examples:
- The boy who is playing the guitar is the lead singer of the music band.
- The book which I was reading last night is written by a Booker Prize winner.
- The woman with whom you were talking is my aunt.
The above-mentioned Relative Pronouns, Who, Which and Whom are connecting the relative clause to the independent clause.
-
Reflexive Pronouns:
These pronouns are used to refer to the same person or object, which is the subject of the sentence. This also acts the the object of the verb. These pronouns end with ‘self’ (singular) or ‘selves’ (plural). Such pronouns include Myself, Himself, Herself, Ourselves, Themselves.
Examples:
- Tina treated herself to a chocolate cake to celebrate her birthday.
- The car would not start itself unless you give it a push.
- We must introspect ourselves before criticising others.
The pronouns ‘Herself’, ‘Itself’ and ‘Ourselves’ are used to emphasise the main subject or the noun of the sentence which are ‘Tine’, ‘Car’ and ‘We’.
-
Reciprocal Pronouns:
These pronouns are used to refer to mutual relation or connection or action between two nouns or groups. These pronouns include Each Other, One Another.
Examples:
- Rohan and Riya take care of each other’s finances.
- The team members must support one another to complete the project on time.
Here ‘Each Other’ and ‘One Another’ are Reciprocal Pronouns which connect the nouns ‘Rohan’ and ‘Riya’ and ‘Team Members’.
-
Intensive Pronouns:
These are similar to Reflexive pronouns, which end with ‘self’ or ‘selves’. The Intensive Pronouns emphasise a noun or a pronoun. However, they are not essential or add value to the sentence, unlike the Reflexive Pronouns. These pronouns include Myself, Himself, Herself, and Themselves.
Examples:
- I have cooked this meal myself.
- Vihaan completed his homework all by himself.
As can be seen in the above sentences, the pronouns ‘Myself’ and ‘Himself’ are just emphasizing the noun or the subject of the sentence and the core meaning would not change if these are removed.
-
Distributive Pronouns:
This type of pronoun applies to a group of people or objects but refers to individuals separately. Distributive Pronouns include Each, Either, Neither, Any, None,
Examples:
- Roshni distributed chocolates to each of her classmates.
- None of the students received scholarships this year.
- I cannot find either of my glasses.
Here the distributive pronouns are used for the plural nouns or multiple people like ‘classmates’, ‘students’, and ‘glasses’.
-
Subject Pronouns:
These act as the primary subject of the sentence, and are used as the direct substitute of nouns. These pronouns include I, She, Him, We, and They.
Examples:
- She went to the bakery to buy a loaf of bread.
- He was declared the man of the match.
- They are playing football in the playground.
Here ‘She’, ‘He’ and ‘They’ are the subjects of the sentence.
-
Object Pronouns:
These pronouns act as the object of verbs or prepositions, which receive the action of the verb. Object pronouns include Me, Him, Her, Us, Them, You, It, Whom.
Examples:
- The garden is full of colourful flowers. The gardener tends to them every day.
- Sachin Tendulkar is my favourite cricketer. He is my inspiration for playing the game.
Here ‘Them’ and ‘He’ are Object Pronouns for flower and Sachin Tendulkar.
The following table brings the pronoun forms for different genders and persons along with their singular and plural versions.
| Gender/Person |
Types |
Pronouns |
|---|---|---|
| Male |
Singular |
He, Him, His |
| Female |
Sher, Her |
|
| Neutral |
It |
|
|
|
Plural |
They, Them |
| First Person |
Singular |
I, Me, Mine |
| Plural |
We, Us, Out |
|
| Second Person |
Singular |
You, Your |
| Plural |
|
|
| Third Person |
Singular |
She, He, Her, Him, His, It |
| Plural |
They, Them, Their |
Now that you are clear about the types of pronouns and how to appropriately use these according to genders, persons and numbers, let us now move on to the rules of pronouns along with their exceptions.
Grammar Rules of Pronouns
While grammar rules of pronouns are seemingly simple, there are certain factors which you must follow and maintain to avoid common mistakes.
- Subject pronouns can be used in the beginning of the sentence only when the preceding sentence mentions the noun.
Example:
Incorrect: She starts her day with a hot cup of coffee.
Correct: Sara is an early riser. She starts her day with a hot cup of coffee.
Ideally, the name of the person should be used first, before using the pronoun.
- Indefinite pronouns need not have antecedents. These pronouns can be used as stand-alone sentences.
Example:
Nobody likes to get stuck in a traffic jam.
Since this is a generic statement, it does not require an antecedent or a preceding sentence mentioning a proper or a common noun.
- Subject pronouns may be used to rename the subject.
Example:
It was she who decided to move to another country.
Here, ‘She’ is the subject, which is replacing the proper noun.
- Object pronouns can be used as direct or indirect objects, and objects of preposition.
Example:
Diya asked her to bring the book.
Here ‘her’ is the object pronoun is which objectifies the verb of ‘bring’.
Pronouns in English Grammar: Special Cases and Exceptions
As they say, every rule has an exception. The same is applicable for Pronouns as well. Some of the exceptions are in Pronouns as well. Some of the exceptions of Pronouns are as follows:
Rule 1: Pronouns should be at par with gender and number.
Indefinite pronouns such as Many, Few, and Both require plural pronouns.
Exception: Collective nouns are inferred as singular, and while using the pronoun, the singular pronoun should be used.
Example:
- The team participated in the hackathon. It has won the first prize.
- Many people send their children to summer camps during vacation.
Here, ‘many’ is the indefinite pronoun referring to multiple people; hence, ‘their’ is used instead of ‘him’ or ‘her’.
Rule 2: Antecedents should precede the pronouns.
Exception: In certain cases, pronouns should precede the antecedents.
Example:
After they exchanged vows, the couple was declared married.
Here, ‘they’ is the pronoun for the groom and bride, who are collectively referred to as ‘couple’. In this case, ‘couple’ is the antecedent. In this exception, the pronoun precedes the antecedent to add a dramatic effect to the sentence.
Rule 3: The pronouns for genders are fixed.
Exception: In case of gender neutrality or fluidity, the pronoun Zie or Zir is used.
Usage:
- ‘Zie’ is used instead of ‘he’ or ‘she’
- ‘Hir’ is used instead of ‘him’ or ‘her’
- ‘Zirs’ is used for ’his or ‘her’
- ‘Zirself’ or ‘Hiself’ is used for ‘himself’ or ‘herself’
Example:
- Zie bought zirself a cup of coffee.
- This book belongs to hir.
Pronoun Vs Noun
Pronouns are closely connected with Nouns as the former is a substitution of the latter. The following table brings a comprehensive comparison between Pronouns and Nouns.
| Parameter |
Pronoun |
Noun |
|---|---|---|
| Definition |
Pronouns are words used instead of nouns to avoid repetition. |
Nouns are names given to people, places or objects. |
| Function |
Pronouns can act as subjects, objects, possessives, or possessive adjectives. |
Nouns can be the subject or object of a verb, or can function as a noun phrase |
| Types |
Pronouns can be classified into personal, possessive, demonstrative, reflexive, etc. |
Nouns can be classified into proper, common, abstract, collective, and concrete |
| Examples |
I, Me, Him, Her, His, It, They, Them |
Raj, Rajasthan, Dog, Tree, Fleet |
Pronouns Vs Adjectives
While pronouns replace nouns, Adjectives emphasise or describe nouns. Let us take a closer look towards the comparison of pronouns and adjectives.
| Parameter |
Pronoun |
Adjective |
|---|---|---|
| Definition |
Pronouns are words used instead of nouns to avoid repetition. |
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns, adding details about their qualities or characteristics. |
| Function |
Pronouns can act as subjects, objects, possessives, or possessive adjectives. |
Adjectives enhance the noun by describing its aspects such as colour, size, etc. |
| Types |
Pronouns can be classified into personal, possessive, demonstrative, reflexive, etc. |
Adjectives can be descriptive, demonstrative, interrogative, possessive and compound |
| Examples |
I, Me, Him, Her, His, It, They, Them |
Red, tall, beautiful, big |
Preparation Tips to Master Pronouns in English
Common Errors to Avoid in Pronouns
Best Books for Pronoun Preparation
Engaging Practice Exercises for Pronouns
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
FAQs Regarding Pronouns
Commonly asked questions
What is the significance of pronouns?
Pronoun is one of the important aspects of English grammar. It is one of the eight traditional parts of speech. The significance of pronoun lies in the fact that it provides an alternate or substitute for nouns. This helps in breaking the monotony and avoiding repetition, hence bringing variation in reading or conversation.
What is the difference between Reflexive Pronoun and Intensive Pronoun?
Both Reflexive Pronoun and Intensive Pronoun end with 'Self' or 'Selves' such as 'Myself', 'Himself', 'Herself', etc. Reflexive pronouns are the object or indirect object of the main verb. On the other hand, the Intensive Pronouns emphasise a noun or a pronoun. Such sentences do not add value to the sentence.
What is the difference between Him and His in pronouns?
Both Him and His are pronouns for male people or living beings. His is a Possessive Pronoun. It indicates ownership or belonging. On the other hand, 'Him' is an objective case of pronoun. Him is at the receiving end and answers who is being acted upon. Example of His: This is his book. Example of Him: The book belongs to him. Example of usage of Him and His in the same sentence: The doctor called him to share his medical test reports.
How many types of pronouns are there?
There are over 10 types of pronouns. The major pronoun types are as follows:
- Personal Pronoun
- Subject Pronoun
- Object Pronoun
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Intensive Pronoun
- Interrogative Pronoun
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Possessive Pronoun.
What are the pronouns for non-living objects?
Pronouns for non-living objects in singular form are It and Its. In plural form, these pronouns are They, Them, These and Those. These pronouns are also applicable for living things whose gender cannot be determined such as animals, birds, etc.
English Pronouns Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds