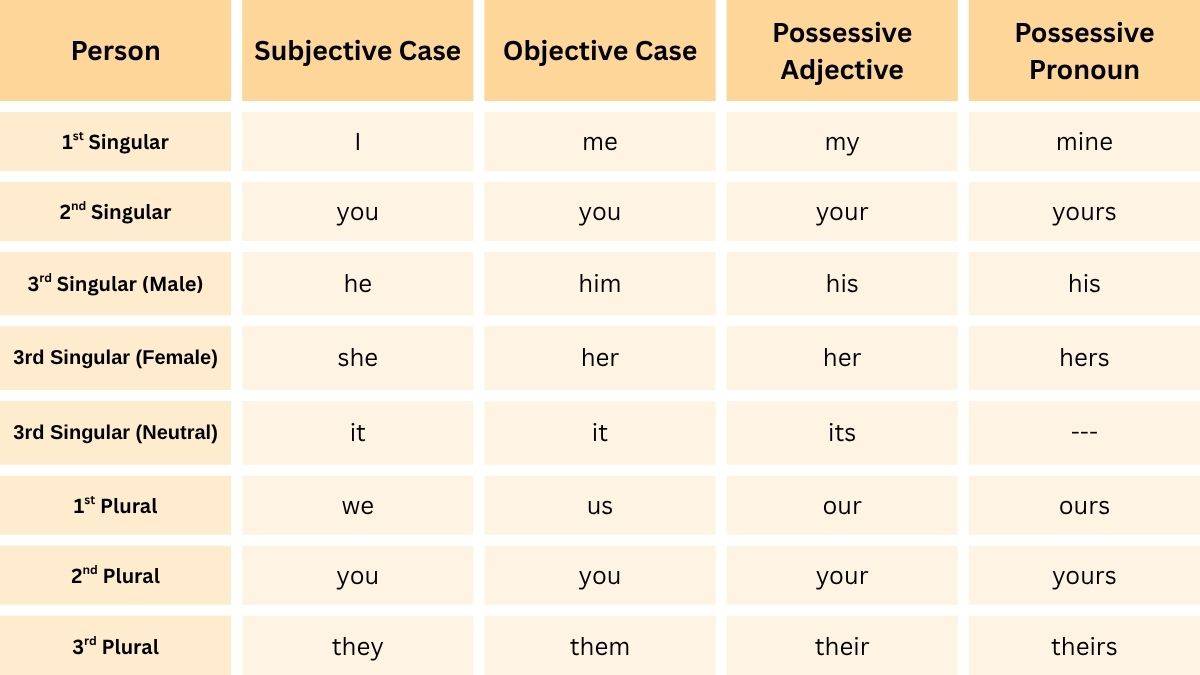
A personal pronoun is a type of pronoun that replaces nouns that usually refer to people or things. A personal pronoun can be in one of three ‘persons’. A first-person pronoun refers to the speaker, a second-person pronoun refers to the person being spoken to, and a third-person pronoun refers to the person being spoken of. These include: I, we, you, he, she, it, we, they etc.
Examples of personal pronouns in sentences:
- I love chocolates.
- She called me last night.
- Can you help us?
- What is Personal Pronoun in English?
- Definition of Personal Pronoun
- Types of Personal Pronoun in English Grammar
- Rules of Personal Pronoun in English
- Special Cases and Exceptions in Personal Pronoun used in English
- Personal Pronoun vs Other Pronoun Types
- Preparation Tips to Master English Personal Pronoun
- Common Errors to Avoid While Using Personal Pronoun
- Importance of Personal Pronoun in Competitive Exams
- Best Books for Personal Pronouns in English
- Examples of Personal Pronoun
- Personal Pronouns Practice Exercises with Answers
- FAQs on Personal Pronouns
What is Personal Pronoun in English?
Personal pronouns are words that are simple substitutes for proper nouns that get repeated in a particular context. A personal pronoun indicates the grammatical person, gender, number, and case of the corresponding noun.
Examples of personal pronouns in English:
- They are going to the party.
- You should try the new restaurant.
- The cat is sleeping on its bed.
Also Read:
| Tenses: Types, Structure, Examples and Exercises with Answers |
Definition of Personal Pronoun
According to the Cambridge dictionary, “A word that is used to refer to a person in speech or in writing. For example, the words 'I', 'you', and 'they' are personal pronouns.”
As per Collinsdictionary.com, “A personal pronoun is a pronoun such as 'I', 'you', 'she', or 'they' which is used to refer to the speaker or the person spoken to, or to a person or thing whose identity is clear, usually because they have already been mentioned.”
Examples include:
- The cookies are for us.
- The decision is yours.
- Me and my friend went to the movies.
- She talked to him about the project.
Also read:
Types of Personal Pronoun in English Grammar
Personal pronouns are used to replace specific nouns, usually to avoid repetition. They refer to people or things and change form based on person, number, gender, and case. Personal pronouns can be classified into three main types-
1. Subjective Case (used as the subject of a sentence)
The subjective case refers to the form of a pronoun or noun that is used when the word is functioning as the subject of a sentence or clause- that is, the person or thing doing the action. The subjective case is used when a noun or pronoun is the subject of a verb – the one acting.
| Person |
Singular |
Plural |
|---|---|---|
| First |
I |
We |
| Second |
You |
You |
| Third |
He. She, It |
They |
Examples:
- I like coffee.
- She is learning to make coffee.
- They are playing tennis.
2. Objective case (used as the object of a verb or preposition)
The objective case is used when a noun or pronoun functions as the object in a sentence. That means it receives the action of the verb or comes after a preposition.
| Person |
Singular |
Plural |
| First |
Me |
Us |
| Second |
You |
You |
| Third |
Him, her, it |
them |
Examples:
The doctor called me.
He will invite you and them.
He gave the phone to her.
3. Possessive case (shows ownership)
Possessive case personal pronouns show ownership or possession and are used to replace nouns. Unlike possessive adjectives, they are not followed by a noun. These are of two forms:
A. Possessive adjectives
These adjectives show ownership or possession and are placed before a noun. They describe whose things we are talking about like my, your, his, her. Its etc.
List of possessive adjective pronouns:
| Person |
Singular |
Plural |
|---|---|---|
| First |
My |
Our |
| Second |
Your |
Your |
| Third |
His, her, its |
their |
Examples:
- This is my toy.
- Their house is new.
- Your shoes are under the table.
B. Possessive pronouns
These pronouns show ownership and are used in place of a noun. They help avoid repeating the noun already mentioned like mine, yours, his, hers etc.
| Person |
Singular |
Plural |
| First |
Mine |
Ours |
| Second |
Yours |
Yours |
| Third |
His, hers, its (rare) |
Theirs |
For example:
- This toy is mine.
- The house is theirs.
- That book is yours.
Also Read:
Rules of Personal Pronoun in English
Personal pronouns replace specific nouns (people, animals, or things) and must agree with person, number, gender, and case in a sentence. Here are certain rules to follow:
1. Pronouns must match the noun in number and gender.
- Use singular pronouns for singular nouns and plural for plural nouns.
- Match the gender correctly when required.
Examples:
- Maya is a teacher. She teaches Biology.
- My teachers are kind. They always help me.
2. Usage of correct case (Subjective, Objective, Possessive)
Personal pronouns change form based on their role in the sentence. Check the table below for more details:
| Role |
Examples |
Pronouns |
|---|---|---|
| Subject |
He dances. |
I, you, he, she, it, we, they |
| Object |
I like her. |
Me, you, him, her, it, us, them |
| Possession |
This is mine. |
Mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs |
For example:
- I am learning English.
- We saw him at the store.
- Where is your car?
3. Use reflexive pronouns when the subject and object are the same
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same person or thing. They end in –self (singular) or –selves (plural).
Examples:
- I taught myself to play the piano.
- We enjoyed ourselves at the party.
- The dog cleaned itself after eating.
(Here, the subject and object are the same animal/person(s))
4. Use correct pronoun case after ‘than’ or ‘as'
When using ‘than’ or ‘as’, it is important to choose the correct pronoun (subjective or objective) based on what’s implied in the sentence. Use subjective case when the pronoun is the subject of a verb. Use objective case when the pronoun is the object of a verb or preposition.
Examples:
- He is taller than I.
- She likes him more than me.
- You are as smart as she.
5. Make pronoun reference clear. Avoid ambiguity.
Clear pronoun is essential to avoid confusing or ambiguous sentences. If a pronoun doesn’t clearly refer to one specific noun, the meaning of the sentence can become unclear or misleading.
For example:
- When Rita spoke to Gita, she seemed upset. (Who is upset- Rita or Gita?)
- Elvis told David that he had won the prize. (Who won – Elvis or David?)
- The book was lying on the sofa, but it was gone later. (What was gone- the book or the sofa?)
Correct usage:
- When Rita spoke to Gita, Gita seemed upset.
- Elvis told David that Elvis had won the prize.
- The book was lying on the sofa, but the book was gone later.
6. Use ‘it’ for things, animals (when gender is unknown), weather, time, distance
For example:
- I bought a phone. It was expensive. (Thing)
- There’s a dog in the garden. It looks hungry. (Animal)
- It is raining heavily today. (Weather)
- It is 9 o’clock. (Time)
- It is 10 km to the nearest market. (Distance)
7. Use ‘they/them’ as a singular gender-neutral pronoun
‘They/them’ are commonly used as a singular gender neutral pronoun when:
- The gender of the person is unknown or irrelevant
- The person prefers ‘they/them’ pronouns
- You are referring to ‘someone’, ‘anyone’, ‘everyone’ etc.
For example:
- Each employee must submit their access card.
- If a student needs help, they should ask the teacher.
- Rita is my friend. They are a graphic designer.
Special Cases and Exceptions in Personal Pronoun used in English
While personal pronouns generally follow clear rules, certain cases and exceptions can make their usage tricky. Let us list these cases below:
1. Referring singular gender-neutral pronoun as ‘they’
Traditionally, ‘he/she’ was used for singular people, but now ‘they/them’ is accepted widely for unknown or unspecified genders.
For example:
• If anyone calls, tell them I’ll be late.
• Anant said they would call me later.
• Someone left their umbrella here.
2. Misuse of reflexive pronouns
Reflexive pronouns, like myself, yourself, ourselves etc., should only be used when subject and object are the same person or thing.
Incorrect: Myself will handle the meeting.
Correct: I will handle the meeting.
Incorrect: He invited myself to the party.
Correct: He invited me to the party.
Incorrect: Sandy and myself completed the report.
Correct: Sandy and I completed the report.
3. Confusion between Possessive Adjectives vs Possessive Pronouns
Many students get confused between Possessive Adjectives and Possessive Pronouns because they both show ownership. But they are used differently in a sentence. The difference can be clearly understood in the table below:
| Type |
Function |
Followed by noun? |
Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Possessive adjectives |
Describes a noun (comes before it) |
Yes |
My, your, his, her, its, our, their |
| Possessive Pronouns |
Replaces a noun (stands alone) |
No |
Mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs |
Examples:
Possessive Adjectives:
• This is my cat.
• That is her dress.
• It is our house.
Possessive Pronouns:
• This cat is mine.
• That dress is hers.
• The house is ours.
4. Formal vs Informal Pronoun Usage
In formal English, the subjective case is used more consistently. In the examples below, ‘whom’ is the object, used after verbs or prepositions in formal writing, though ‘who’ is more common in casual speech.
Examples:
- Who is at the door? (correct in both forms)
- Whom are you calling? (In casual speech, ‘who’ is often used in both cases)
- To whom did you give the book? (Formal)
Also Read: Punctuation in English Grammar; Usage, Type, Definition
Personal Pronoun vs Other Pronoun Types
Pronouns are words that replace nouns to avoid repetition. There are several types of pronouns with different purposes, personal pronoun being one. Let us compare personal pronouns with other types of pronouns below.
1. Personal pronouns vs Possessive pronouns
Personal pronouns and possessive pronouns are closely related as both of them refer to people or things, but they serve different grammatical functions in a sentence. Let us check out their differences below:
| Feature |
Personal pronoun |
Possessive pronoun |
|---|---|---|
| Shows |
Person (subject or object) |
Ownership |
| Examples |
I, you, he, she, it, we they |
Mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs |
| Usage |
· I like bananas. · She saw me. · We spoke to her. |
· This pen is mine. · The book is yours. · That house is theirs. |
2. Personal Pronouns vs Reflexive Pronouns
Personal and reflexive pronouns both refer to people or things, but they play different roles in a sentence. Let us break down the difference in the table below clearly:
| Feature |
Personal pronoun |
Reflexive pronoun |
|---|---|---|
| Role |
Subject or object |
Reflects the subject back to itself |
| Examples |
I, you, he, she, it, we they |
Myself, yourself, himself, herself, etc |
| Usage |
· They helped us. · She is my friend. · Sita helped me with my homework. |
· I hurt myself. · She looked at herself in the mirror. · They introduced themselves at the meeting. |
Read: Moods in English
Preparation Tips to Master English Personal Pronoun
Students can find here some effective preparation tips to master the English Personal Pronouns. These will help students especially those preparing for exams or working to improve their writing and speaking skills.
1. Learn the different types of personal pronouns and revise them regularly
Understand the four main nouns:
Subjective: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
Objective: me, you, him, her, it, us, them
Possessive adjectives: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
Possessive pronouns: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs
Reflexive: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, themselves, ourselves
2. Use real-life sentences
Practice using pronouns in your daily life, while writing and speaking, to make learning more relatable and clear.
Examples:
- I love to eat chocolates.
- She is my teacher.
- Their dog is very friendly.
3. Read books and practice worksheets and quizzes
Use grammar books to get a good hand on using personal pronouns. Get online worksheet, quizzes to practice fill-in-the-blank exercises, error correction tasks, sentence rewriting using correct pronouns etc. Try to practice a little bit every day. Consistency is the key to success.
4. Practice speaking and listening and focus on common mistakes
Practice talking about yourself or someone else using pronouns, listen to podcasts or watch English shows, and note how pronouns are used naturally. Focus on mistakes made by others and avoid them like mixing up possessive adjectives and possessive pronouns, using reflexive pronouns unnecessarily, using incorrect pronouns after ‘than’ or ‘as’ as explained above etc.
Also Read:
Common Errors to Avoid While Using Personal Pronoun
Importance of Personal Pronoun in Competitive Exams
Best Books for Personal Pronouns in English
Examples of Personal Pronoun
Personal Pronouns Practice Exercises with Answers
FAQs on Personal Pronouns
Commonly asked questions
Can a sentence start with a personal pronoun?
Yes, a sentence can start with a personal pronoun. Many sentences begin with personal pronouns like I, we, she, he, they etc., especially when the pronoun is acting as the subject of the sentence.
Examples:
- I went to the market.
- He is going to watch a movie.
- She is going for her dance lesson.
What is the role of personal pronouns in formal English?
Personal pronouns play a vital role in formal English as they:
- Help in usage of correct case (eg – He is taller than I -not me.)
- Avoid ambiguity and repetition
- Maintain consistency in number and person
How are personal pronouns different from possessive adjectives?
Personal pronouns and possessive adjectives are closely related, but they serve different grammatical roles in a sentence. Possessive pronouns replace a noun, for example: This book is mine, whereas possessive adjectives comes before a noun, example: This is my book.
Are personal pronouns asked in competitive exams?
Yes, personal pronouns are commonly asked questions in competitive exams, especially in English language and grammar sections. These pronouns test a candidate's understanding of subject-verb agreement, pronoun-antecedent agreement, and the correct use of subjective, objective, possessive pronouns and possessive adjectives cases.
The types of questions asked in the examinations may include fill-in-the-blanks, error detection, sentence correction, or identifying correct usage. Thus, when studying for competitive exams, students must go through personal pronouns thoroughly.
What is the significance of pronouns?
Pronoun is one of the important aspects of English grammar. It is one of the eight traditional parts of speech. The significance of pronoun lies in the fact that it provides an alternate or substitute for nouns. This helps in breaking the monotony and avoiding repetition, hence bringing variation in reading or conversation.
Can ‘they’ be used for a singular person?
Yes, they can be used for a singular person, and this usage is both grammatically correct and widely accepted in Modern English. Known as singular 'they', it is commonly used when the gender of a person is unknown, irrelevant, or when referring to someone who identifies as non-binary.
Singular 'they' has been used by well-known authors like Shakespeare and Jan Austen in their works. It helps avoid awkward or gendered language and has become a practical choice in both spoken and written English.
Example: Someone left their phone on the table.
What are the pronouns for non-living objects?
Pronouns for non-living objects in singular form are It and Its. In plural form, these pronouns are They, Them, These and Those. These pronouns are also applicable for living things whose gender cannot be determined such as animals, birds, etc.
How many types of pronouns are there?
There are over 10 types of pronouns. The major pronoun types are as follows:
- Personal Pronoun
- Subject Pronoun
- Object Pronoun
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Intensive Pronoun
- Interrogative Pronoun
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Possessive Pronoun.
English Pronouns Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds