
Thermodynamics Class 11 Chapter 11 Physics is the right place for all your doubts related to heat, work, and energy in Thermodynamics. The step-by-step solutions of this chapter are designed by the subject matter experts. Students can depend on these solutions for their CBSE Board and entrance exam preparations. The NCERT solutions are aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus and cover all textbook questions.
These important topics covered in this chapter are:
- Internal Energy, Heat, and Work
- Specific Heat Capacities (Cp and Cv)
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Carnot Engine and Efficiency
Related Links
| NCERT Class 11 Notes | NCERT Notes for Class 11 & 12 |
| NCERT Solutions Physics Class 11th | NCERT Solutions Class 11 and 12 |
- Chapter 11 Thermodynamics Important Formulas & Concepts
- NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 Thermodynamics: Key Topics, Weightage, and Important Formulas
- NCERT Physics Class11th Solution PDF for Thermodynamics
- NCERT Solutions for Physics Class 11 Thermodynamics
Chapter 11 Thermodynamics Important Formulas & Concepts
Following are the important concepts and formulas of the thermodynamics class 11 physics NCERT solutions:
Important Formulae of Thermodynamics for CBSE & Competitive Exams
-
-
First Law of Thermodynamics:
where : Heat added, : Change in internal energy, : Work done -
Work Done in Isothermal Process:
-
Work Done in Adiabatic Process:
-
Relation between and (Mayer’s Relation):
-
Adiabatic Relation:
where -
Efficiency of Heat Engine:
-
Efficiency of Carnot Engine:
(Temperatures in Kelvin)
-
NCERT Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 Thermodynamics: Key Topics, Weightage, and Important Formulas
Thermodynamics is a high-weightage chapter in Class 11 Physics and is extremely important for both CBSE Board Exams and competitive exams like JEE, NEET, and MHT CET.
The following are the topics covered in Chapter 11, Thermodynamics
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 11.1 | Introduction |
| 11.2 | Thermal Equilibrium |
| 11.3 | Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics |
| 11.4 | Heat, Internal Energy and Work |
| 11.5 | First Law of Thermodynamics |
| 11.6 | Specific Heat Capacity |
| 11.7 | Thermodynamic State Variables and Equation of State |
| 11.8 | Thermodynamic Processes |
| 11.9 | Second Law of Thermodynamics |
| 11.10 | Reversible and Irreversible Processes |
| 11.11 | Carnot Engine |
Class 11 Thermodynamics Weightage in NEET, JEE Main Exam
| Exam Name | Number of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| NEET | 1-2 questions | 4-7% |
| JEE Main | 4-5 questions | 10-15% |
NCERT Physics Class11th Solution PDF for Thermodynamics
To master the concepts, students must download the Thermodynamics Physics Class 11 NCERT PDF given below. The solutions help students to approach the complex questions with the right attitude and solve them accurately. It will help them improve their problem-solving skills and accuracy, which is going to boost their exam confidence.
Download Here: NCERT Solution for Class XI Physics Chapter Thermodynamics PDF
NCERT Solutions for Physics Class 11 Thermodynamics
| Here, we have offered the NCERT books solutions for all the questions of the Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 Thermodynamics. There are step-by-step solutions. Q.12.1 A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3.0 liters per minute from 27 °C to 77 °C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, what is the rate of consumption of the fuel if its heat of combustion is 4.0 × J/g? |
| Ans.12.1 Initial temperature, = 27 °C Final temperature, = 77 °C Rise in temperature, Heat of combustion = 4.0 × J/g Specific heat of water, c = 4.21 J/g/ Mass of flowing water, m = 3 lit/min = 3000 g/min Total heat used, = 3000 = 6.315 J/min Rate of consumption = g/min = 15.79 g/min |
| Q.12.2 What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 × kg of nitrogen (at room temperature) to raise its temperature by 45 °C at constant pressure? (Molecular mass of N2 = 28; R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1.) |
| Ans.12.2 Mass of Nitrogen, m = 2.0 × kg = 20 g Rise in temperature, = 45 °C Molecular mass of . M = 28 Universal gas constant, R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1 Number of moles, n = = = 0.714 Molar specific heat at constant pressure for nitrogen, = R = 29.05 J/mol/K The total amount of heat to be supplied is given by the relation Q = n = 0.714 = 933.38 J |
| Q.12.3 Explain why (a) Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2 if brought in thermal contact do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2 )/2.
(b) The coolant in a chemical or a nuclear plant (i.e., the liquid used to prevent the different parts of a plant from getting too hot) should have high specific heat.
(c) Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
(d) The climate of a harbor town is more temperate than that of a town in a desert at the same latitude. |
| Ans.12.3 (a) When the two bodies at different temperatures brought in contact, heat flows from the body of higher temperature to the body with lower temperature till the thermal equilibrium is achieved and both the body attains the temperature of (T1 + T2 )/2. But only when the thermal capacities of both the bodies are equal.
(b) The coolant used in Chemical or in Nuclear plant should have high specific heat. Higher specific heat allows coolant to absorb more heat.
(c) In motion, the air temperature inside the tyre increases due to the motion of the air molecules. According to Charles’s law, temperature is directly proportional to pressure. Hence, the air pressure inside the tyre also increases.
(d) A harbor town has a temperate climate ( without extreme heat or cold) than a town located in a desert at the same latitude. This is because the relative humidity in a harbor town is more than it is in a desert town. |
| Q.12.4 A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at standard temperature and pressure. The walls of the cylinder are made of a heat insulator, and the piston is insulated by having a pile of sand on it. By what factor does the pressure of the gas increase if the gas is compressed to half its original volume ? |
| Ans.12.4 The cylinder is completely insulated from its surroundings. As a result, no heat is exchanged between the system (cylinder) and its surroundings. Thus the process is ‘Adiabatic’. Let the initial and final pressure inside the cylinder be & and volume be & . Ratio of specific heat, = 1.4 For an adiabatic process, we know = It is given Hence = or = ( ( = = = 2.639 Hence the pressure increases by a factor of 2.639 |
Commonly asked questions
12.6 Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following :
(a) What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B ?
(b) What is the change in internal energy of the gas ?
(c) What is the change in the temperature of the gas ?
(d) Do the intermediate states of the system (before settling to the final equilibrium state) lie on its P-V-T surface ?
(a) When the stopcock is opened, the volume became double between cylinders A and B. Since volume is inversely proportional to pressure, the pressure will become half. So the initial pressure of 1 atm in cylinder A will become ½ atm in cylinder A and B.
(b) The internal energy will change when there is work done by the gas. In absence of any work done, there will be no change in internal energy.
(c) In absence of any work done, there will be no change in the temperature.
(d) The given process is a case of free expansion. It is rapid and cannot be controlled. The intermediate states do not satisfy the gas equation and since they are non-equilibrium states, they do not lie on the P-V-T surface of the system.
12.1 A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3.0 liters per minute from 27 °C to 77 °C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, what is the rate of consumption of the fuel if its heat of combustion is 4.0 × J/g?
Initial temperature, = 27 °C
Final temperature, = 77 °C
Rise in temperature,
Heat of combustion = 4.0 × J/g
Specific heat of water, c = 4.21 J/g/
Mass of flowing water, m = 3 lit/min = 3000 g/min
Total heat used, = 3000 = 6.315 J/min
Rate of consumption = g/min = 15.79 g/min
12.8 An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If system performs work at a rate of 75 joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
Heat is supplied to the system at a rate of 100W
Hence, heat supplied, Q = 100 J/s
The system performs at the rate of 75 J/s
Hence, work done, W = 75 J/s
From the 1st law of Thermodynamics, we have Q = U + W, where U is the internal energy
U = Q – W = 100 – 75 = 25 J/s = 25 W
Therefore the internal energy of the given electric heater increases at a rate of 25 W.
12.10 A refrigerator is to maintain eatables kept inside at 9 . If room temperature is 36 , calculate the coefficient of performance.
Temperature inside the refrigerator, = 9 = 9 + 273 K = 282 K
Room temperature, = 36 = 36 + 273 = 309 K
Coefficient of performance = = = 10.44
Therefore, the coefficient of performance is 10.44
12.9 A thermodynamic system is taken from an original state to an intermediate state by the linear process shown in Fig. (12.13)
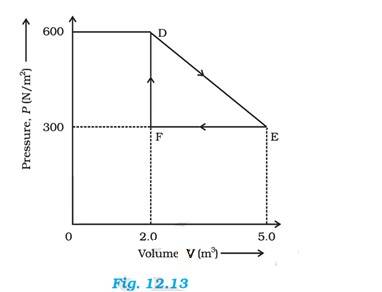
Its volume is then reduced to the original value from E to F by an isobaric process. Calculate the total work done by the gas from D to E to F
Total work done by the gas from D to E to F = Area of = EF
Where DF = Change in pressure = 600 – 300 = 300 N/
FE = change in volume = 5-2 = 3
Area of 3 = 450 J
Therefore work done by the gas from D to E to F is 450 J.
12.3 Explain why
(a) Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2 if brought in thermal contact do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2 )/2.
(b) The coolant in a chemical or a nuclear plant (i.e., the liquid used to prevent the different parts of a plant from getting too hot) should have high specific heat.
(c) Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
(d) The climate of a harbor town is more temperate than that of a town in a desert at the same latitude.
(a) When the two bodies at different temperatures brought in contact, heat flows from the body of higher temperature to the body with lower temperature till the thermal equilibrium is achieved and both the body attains the temperature of (T1 + T2 )/2. But only when the thermal capacities of both the bodies are equal.
(b) The coolant used in Chemical or in Nuclear plant should have high specific heat. Higher specific heat allows coolant to absorb more heat.
(c) In motion, the air temperature inside the tyre increases due to the motion of the air molecules. According to Charles's law, temperature is directly proportional to pressure. Hence, the air pressure inside the tyre also increases.
(d) A harbor town has a temperate climate ( without extreme heat or cold) than a town located in a desert at the same latitude. This is because the relative humidity in a harbor town is more than it is in a desert town.
12.5 In changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an equilibrium state A to another equilibrium state B, an amount of work equal to 22.3 J is done on the system. If the gas is taken from state A to B via a process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 9.35 cal, how much is the net work done by the system in the latter case ?
(Take 1 cal = 4.19 J)
The work done, W = 22.3 J
Being an adiabatic process, Q = 0
W = -22.3 J : since the work is done on the system
From the 1st law of thermodynamics, we know Q = W, where is the change of internal energy of the gas
U = 22.3 J
When the gas goes from state A to state B via a process, the net heat absorbed by the system is:
Q = 9.35 cal = 9.35 J = 39.1765 J
Heat absorbed Q = W
W = Q - = 39.1765 – 22.3 = 16.8765 J
Therefore, work done by the system is 16.8765 J
12.4 A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at standard temperature and pressure. The walls of the cylinder are made of a heat insulator, and the piston is insulated by having a pile of sand on it. By what factor does the pressure of the gas increase if the gas is compressed to half its original volume ?
The cylinder is completely insulated from its surroundings. As a result, no heat is exchanged between the system (cylinder) and its surroundings. Thus the process is ‘Adiabatic’.
Let the initial and final pressure inside the cylinder be & and volume be & .
Ratio of specific heat, = 1.4
For an adiabatic process, we know =
It is given
Hence = or = ( ( = = = 2.639
Hence the pressure increases by a factor of 2.639
12.2 What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 × kg of nitrogen (at room temperature) to raise its temperature by 45 °C at constant pressure? (Molecular mass of N2 = 28; R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1.)
Mass of Nitrogen, m = 2.0 × kg = 20 g
Rise in temperature, = 45 °C
Molecular mass of . M = 28
Universal gas constant, R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1
Number of moles, n = = = 0.714
Molar specific heat at constant pressure for nitrogen, = R = 29.05 J/mol/K
The total amount of heat to be supplied is given by the relation
Q = n = 0.714 = 933.38 J
12.7 A steam engine delivers 5.4×108J of work per minute and services 3.6 × 109J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the efficiency of the engine? How much heat is wasted per minute?
Work done by the steam engine per minute, W = 5.4 J
Heat supplied by the boiler, H = 3.6 J
Efficiency of the engine, = = = 0.15
Amount of heat wasted = Input energy – Output energy
= 3.6 5.4 J
Explore exams which ask questions on physics ncert solutions class 11th
Select your preferred stream
physics ncert solutions class 11th Exam
Student Forum
Other Similar chapters for you
- Physical World
- Units and Measurements
- Motion in a Straight Line
- Motion in a Plane
- Laws of Motion
- Work, Energy, and Power
- System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Gravitation
- Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Thermal Properties of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Kinetic Theory
- Oscillations
- Waves
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test
