In the language of Thermodynamics, you know that a state is a condition of a system (whether it is in thermal equilibrium or not) determined by its macroscopic properties. These properties are variables, including temperature, pressure, and volume. If these properties remain unchanged, the state is in thermal equilibrium.
But what if they change?
That means the system is changing or moving from one state to another. This is where thermodynamic state variables come in. They help us describe the system’s current condition and even track how they respond to changes in energy, heat, and work.
Now, since you also know how energy lets a state transition from one to another through the First Law of Thermodynamics, you should also learn how to calculate the system’s behaviour when variables change, using the equation of state.
Today, we cover some key definitions, types of state variables, the ideal gas equation, applications, and a P-V diagram of isotherms that describe the equation of state.
- What are Thermodynamic State Variables?
- NCERT Definitions of Thermodynamic State Variables
- Types of Thermodynamic State Variables
- Key Concepts of Thermodynamics State Variables
- Ideal Gas Equation
- Applications of Thermodynamics State Variables
- Diagrams of Thermodynamic State Variables
- Key Points about Thermodynamic State Variables for JEE Main
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
What are Thermodynamic State Variables?
Generally, we define thermodynamic state variables as macroscopic properties (e.g., pressure, volume, temperature) that fully describe a system's equilibrium state. The equation of state is a mathematical relationship connecting these variables.
Importance of Learning Thermodynamic State Variables and Equation of State
From the CBSE syllabus standpoint, thermodynamic state variables in this Physics Class 11 chapter is quite brief. But knowing the applications of the state equation and its related concepts can help you score well in the engineering entrances, including JEE Mains.
Thermodynamic state variables and the equation of state also continue in undergraduate programmes. It’s part of the B.Sc. Physics syllabus in the third semester.
NCERT Definitions of Thermodynamic State Variables
Chapter 11 of Physics, in Class 11, provides this explanation of thermodynamic state variables and the equation of state.
“Thermodynamic state variables describe equilibrium states of systems. The various state variables are not necessarily independent. The connection between the state variables is called the equation of state. For example, for an ideal gas, the equation of state is the ideal gas relation PV=μRT."
In this equation, we have
P = Pressure
V = Volume
μ = Number of moles
R = Universal gas constant
T = Absolute temperature
Types of Thermodynamic State Variables
So, as you know, what state variables or properties are by now. But do remember that the state variables, including pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), internal energy (U), and mass (m) depend only on the system's state, not its history. Based on this condition, we have two major types of thermodynamic state variables.
- Extensive Variables: These primarily depend on system size (e.g., V,U,m). Dividing a system into two equal parts halves these values.
- Intensive Variables: These are independent of size (e.g., P,T, density ()). They remain unchanged when the system is divided.
Key Concepts of Thermodynamics State Variables
Here are a few aspects to remember. Find out the difference between state and path variables, what determines equilibrium states, and more.
- State vs. Path Variables: State variables (e.g., ) are path-independent, unlike heat and work , which depend on the process.
- Equation of State: For an ideal gas, , where is the number of moles, is the universal gas constant ( ). This relates , and , with only two being independent for fixed .
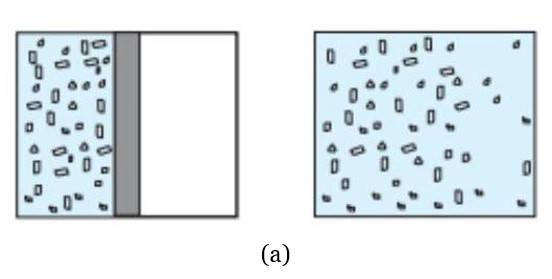
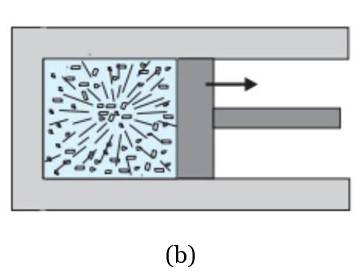
- Equilibrium States: State variables describe equilibrium states, where properties are uniform. Non-equilibrium states (e.g., free expansion, chemical reactions) lack welldefined state variables.
- Consistency Check: Thermodynamic equations (e.g., ) maintain consistency with extensive/intensive classifications, as (intensive extensive) is extensive.
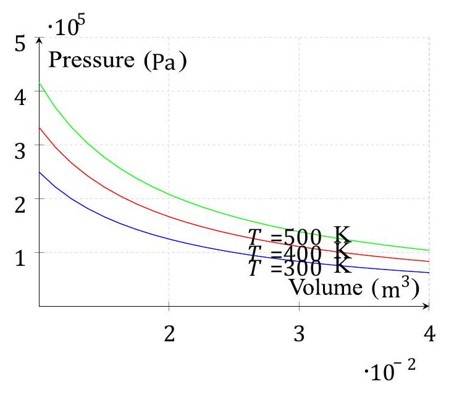
Ideal Gas Equation
The ideal gas equation, , is the simplest equation of state, assuming negligible intermolecular forces. For a fixed amount ( ), it defines relationships like:
Isotherms: At constant , yielding hyperbolic curves.
Dependent Variables: Only two of are independent, determining the third.
Real gases have more complex equations of state, but the ideal gas model suffices for JEE Main. Learn more about the ideal gas equation, explained simply for all types of exams.
Applications of Thermodynamics State Variables
The thermodynamic state variables and equation of state have applications in various scenarios.
- Gas Behaviour: The equation of state predicts how gases respond to changes in , or , guiding applications in engines and compressors. Consider air conditioners, gas cylinders, and other systems whose state behaviour can be calculated using this equation of state.
- Thermodynamic Analysis: State variables enable us to obtain a precise description of equilibrium states in processes such as isothermal or adiabatic changes. In isothermal processes, the temperature is constant, while pressure and volume change. On the other hand, in adiabatic processes, there is no heat exchange with the surroundings, but the temperature, volume, and pressure change together while conserving internal energy.
- Measurement Standards: Temperature and pressure scales rely on state variables for calibration in thermometry and manometry.
Diagrams of Thermodynamic State Variables
Key Points about Thermodynamic State Variables for JEE Main
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Physics Thermodynamics Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- What is Internal Energy
- Thermodynamic State Variables Equation of State
- Thermodynamic Process
- Thermal Equilibrium
- Reversible and Irreversible Process
- Overview
- Uses of Colorimeter
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Specific Heat
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Law of Conservation of Energy
- Van Der Waals Equation
- Third law of thermodynamics
- Boltzmann Equation
- Helmholtz Equation
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test