The word nomenclature is derived from the latin word nomen meaning name. This technique is used to allocate a unique name to every compound in chemistry. earlier, the newly discovered compounds were mostly named after the scientist who discovered them or the place where they were discovered. But this technique had it's own shortcomings which led to the introduction of a new concept for naming organic compounds.
In this article, you will learn some key details related to nomenclature such as principles, importance, rules and regulations, etc.
- IUPAC Nomenclature: Rules
- Nomenclature of Common Functional Groups
- Common Names vs. IUPAC Names
IUPAC Nomenclature: Rules
There are some certain set of rules and regulations to be followed while naming any organic compound. These are gas follows:
- First, check for the carbon chain having the longest length, which will become the parent chain.
- Then start numbering the carbon chain. Keep in mind to assign the lowest possible number to the functional group or substituents.
- Now identify the functional group, such as aldehyde, alcohol, alkyl group etc. and allot them their required suffix.
- Last step is combine the name of both carbon chain and substituent in the defined order.
Nomenclature of Common Functional Groups
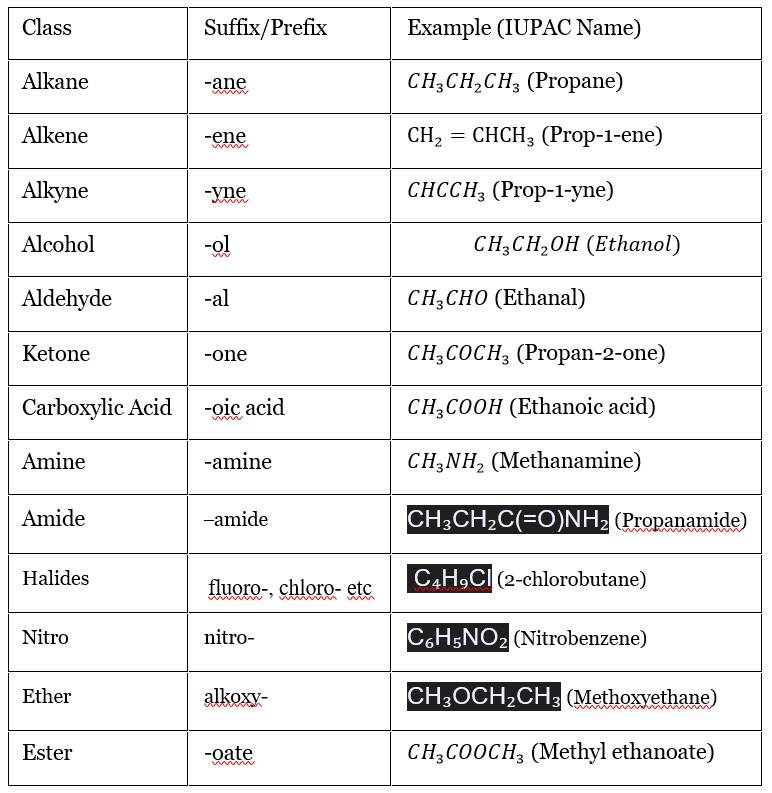
Organic compounds are classified based on their functional groups, which dictate their IUPAC suffixes and prefixes. Below is a table summarizing key functional groups, adapted with JEE-relevant examples:
Table 1: Common Functional Groups and Their Nomenclature
Common Names vs. IUPAC Names
IUPAC set of rules differ from the traditional used technique of naming any compound, and here is how:
IUPAC Names:
- They follow a defined order of rules for identification of compounds.
- They can be globally used for communication.
- They are very complex to name.
- Examples: ethyne, acetic acid, etc.
Common Names:
- They are named based on properties of the compound.
- They can vary widely and cannot be relied upon for effective communication.
- They are comparatively easier to understand.
- Example: dihydrogen monoxide is simply known as water (H2O)
Chemistry Organic Chemistry Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Overview
- Classification of Organic Compounds
- Tetravalence of Carbon Shapes of Organic Compounds
- Structural Representations of Organic Compounds
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- Isomerism
- Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism
- Methods of Purification of Organic Compounds
- Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds
- Quantitative Analysis
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics