To understand how capacitors behave, learn about the combination of capacitors. This becomes essential to solve numerical problems on circuits for your JEE Mains. Suppose you master how different capacitor combinations can be arranged for various purposes. In that case, you can analyse circuits better and learn how parts of daily electronic devices, from touchscreens to power supplies, work. Below, we simplify explanations for the major types of capacitors, as well as the formulas for deriving the capacitance of single and parallel capacitors.
- What is a Combination of Capacitors?
- Types of Combination of Capacitors
- Series Combination of Capacitors
- Derivation of Formulae: Meaning of equivalent capacitor
- Parallel Combination of Capacitors
- Formulae Derivation for Parallel Combination
- Mixed Combination
What is a Combination of Capacitors?
A combination of capacitors is a formation or arrangement of two or more capacitors in an electric circuit that collectively store charge.
Importance of the Combination of Capacitors for Exams
- In previous year JEE Mains or related exams like CUET, you will find questions on the combination of capacitors covering how charges are redistributed, how energy gets stored, and how complex combinations work.
- The combination of capacitors is interrelated to other topics in Class 11 and 12 physics. Some include current electricity, energy stored, and semiconductors.
Types of Combination of Capacitors
By combining capacitors in different ways, we can control how they store and share electric charge. In the world of physics, the combination of capacitors can create differences in charges and voltage.
So, what are the correct ways to combine them?
We can combine capacitors as
- Series Combination
- Parallel Combination
- Mixed Combination
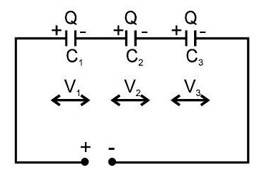
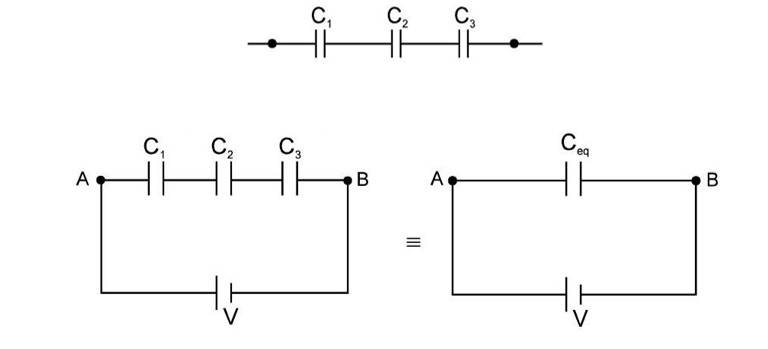
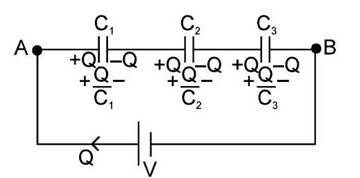
Series Combination of Capacitors
When we connect capacitors with the same charge but different potential differences across them, we have a series combination.
Characteristics of Series Combination
- We can say that
potential across
charge on positive plate of
capacitance of capacitor similarly
The potential difference across capacitor is inversely proportional to its capacitance in series combination.
Note : In series combination, the smallest capacitor gets maximum potential.
- Where
- Equivalent Capacitance : It’s the single capacitor value storing the same charge and energy as the entire combination when used in its place.
In series :
Note : In series combination, the equivalent capacitance is always less the smallest capacitor of the combination.
- Energy stored in the combination
Energy the battery supplies in charging the combination
Note : The battery supplies half of the energy and that is stored as electrostatic energy. The other half of the energy is converted into heat through resistance (if capacitors are initially uncharged).
Derivation of Formulae: Meaning of equivalent capacitor
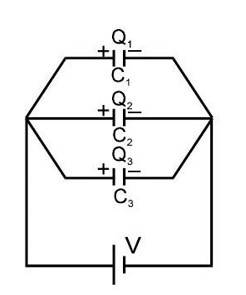
Parallel Combination of Capacitors
When one plate of each capacitor (more than one) is connected together and the other plate of each capacitor is connected together, such a combination is called a parallel combination.
Characteristics of Parallel Combination of Capacitors
- All capacitors have same potential difference but different charges.
- We can say that :
Charge on capacitor
Capacitance of capacitor
Potential across capacitor
The charge on the capacitor is proportional to its capacitance
-
Where
Note: The maximum charge will flow through the capacitor with the largest value. - Equivalent capacitance of a parallel combination
Note that equivalent capacitance is always greater than the largest capacitor of the combination.
- Energy stored in the combination :
Formulae Derivation for Parallel Combination
Here is a derivation for the parallel combination of capacitors.
Mixed Combination
The combination which contains the mixing of series parallel combinations or other complex combinations falls in the mixed category. There are two types of mixed combinations
(i) Simple
(ii) Complex.
Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Overview
- Combination of Capacitors
- Electrostatic Potential
- Electrostatics
- Potential Due to Point Charge
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Capacitors and Capacitance
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance
- Electrostatics of Conductors
- Potential Energy of a System of Charges
- Potential due to a System of Charges
- Potential Energy in an External Field
- Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Dielectrics and Polarisation
- Equipotential Surfaces
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter