Today, this guide provides an in-depth exploration of electrostatic potential, which is introduced in the second chapter of Physics Class 12. It’s a foundational topic that will later help you understand electric fields and circuits. It’s also part of the current CUET Physics Syllabus and the major engineering entrances. Here, you will learn why and how we calculate electrostatic potential, which is the electric potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in an electric field.
- What is Electrostatic Potential?
- Electrostatic Potential Meaning by NCERT
- Working Principle of Electrostatic Potential
- Electrostatic Potential Equations
- SI Unit of Electrostatic Potential
- Electric Potential due to various charge distributions
What is Electrostatic Potential?
Electrostatic potential is the work done by an external agent to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to a point without changing its kinetic energy.
When speaking of calculating electrostatic potential, it means we measure the amount of electric potential energy a unit charge would have at a point in the electric field.
Let’s understand two key terms here.
Electric Potential Energy - This is the energy a charge has due to its position in the electric field.
Referring to Physics basics, such as the difference between potential and kinetic energy, you will notice that this concept is like gravitational potential energy.
The fundamental behind it is the higher you lift an object from the centre of gravity, the more enery it will have. Likewise, when you move a charge against the electrical field, the more electric potential energy it will have.
Unit Charge - This simply refers to one coulomb of electric charge.
By the above electrostatic potential definition, we are imagining how much energy one coulomb of charge would have at a specific point. That makes the electrostatic potential a per-charge quantity.
Importance of Learning Electrostatic Potential for National Exams
- This is an essential concept covered in various exam syllabi - CUET, IAT, etc. In exams like JEE Main, its weightage is around 6%.
- Electrostatic potential is the building block to understanding electromagnetism, particularly the concept of charge distribution that discusses how electric charges are arranged in space. This is important to learn in electrical engineering.
Electrostatic Potential Meaning by NCERT
In your CBSE Physics textbook, this is the second section of the chapter. The definition of electrostatic potential is
“Work done by an external force in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to a point = electrostatic potential (V) at that point.”
Why Infinity? Infinity is a reference point where the electrostatic potential is considered zero.
Also, while preparing for CBSE Board exam, check out the free NCERT Solutions for the 2nd Chapter.
Working Principle of Electrostatic Potential
Let’s go a little deeper to see how energy moves in electric fields.
We established above, electrostatic potential is like gravity, which is a conservative force.
The work done by a conservative force in moving a charge between two points depends only on the initial and final positions. In that logic, the charge movement is independent of the path.
Because the force is conservative, we can define an electrostatic potential energy (U) associated with the position of a charge in an electric field.
If you move a charge against the electric field, or let’s say push a positive charge toward another positive charge, you’re doing positive work. This work is stored as potential energy.
We say it as
Electrostatic Potential Equations
Within an electrostatic field, the electric potential at a point is defined as the work done by an external agent in taking a unit point positive charge from a reference point (generally taken at infinity) to that point without changing its kinetic energy.
Let's see how we represent it mathematically.
If ext is the work required in moving a point charge from infinity to a point , the electric potential of the point is
Note:
- can also be called as the work done by external agent against the electric force on a unit positive charge due to the source charge.
- We write both W and q with proper sign.
If we know the potential at some point (in terms of numerical value or in terms of formula) then we can find out the work done by electric force when charge moves from point ' ' to by the formula
SI Unit of Electrostatic Potential
The S.I. Unit of Electrostatic Potential is Volt and its dimensional formula is .
Electric Potential due to various charge distributions
| Name / Type |
Formula |
Note |
Graph |
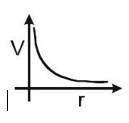
| Point charge |
kq/r | q is source charge. r is the distance of the point from the point charge. |
|
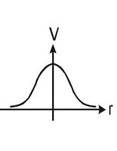
| Ring (uniform/nonuniform charge distribution) |
at centre: kq/r at the axis: s:KQ/√R2+x2 |
Q is source chage. x is the distance of the point on the axis from centre fring |
|
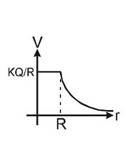
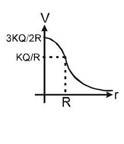
| Uniformly charged hollow conducting/nonconducting /solid conducting sphere |
for r >= R, V = kQ/r for r <= R, V =kQ/R |
R is radius of sphere r is the distance from centre of sphere to the point Q is total charge .= 4πR2 |
|
| Uniformly charged solid nonconducting sphere. |
For r >= R, V = KQ/r For r <= R V= KQ (3R2-R2)/2R3 = P/6ε₀(3R2-R2) |
* R is radius of sphere * r is distance from centre to the point vcenter = 3/2 V surface Q is total charge . = p 4/3πr3 * Inside the sphere potential varies parabolically * Outside the sphere potential varies hyperbolically. |
|
| Infinite line charge |
Not defined |
*Absolute potential is not defined. * Potential difference between two points is given by formula: |
|
| Infinite nonconducting thin sheet |
Not defined |
*Absolute potential is not defined. * Potential difference between two points is given by formula VB - VA = -2Kλln(rB/rA) |
|
| Infinite charged conducting thin sheet |
Not defined |
*Absolute potential is not defined. * Potential difference between two points is given by formula VB - VA = - σ/ε₀(rB-rA) |
|
Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Overview
- Combination of Capacitors
- Electrostatic Potential
- Electrostatics
- Potential Due to Point Charge
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Capacitors and Capacitance
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance
- Electrostatics of Conductors
- Potential Energy of a System of Charges
- Potential due to a System of Charges
- Potential Energy in an External Field
- Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Dielectrics and Polarisation
- Equipotential Surfaces
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter