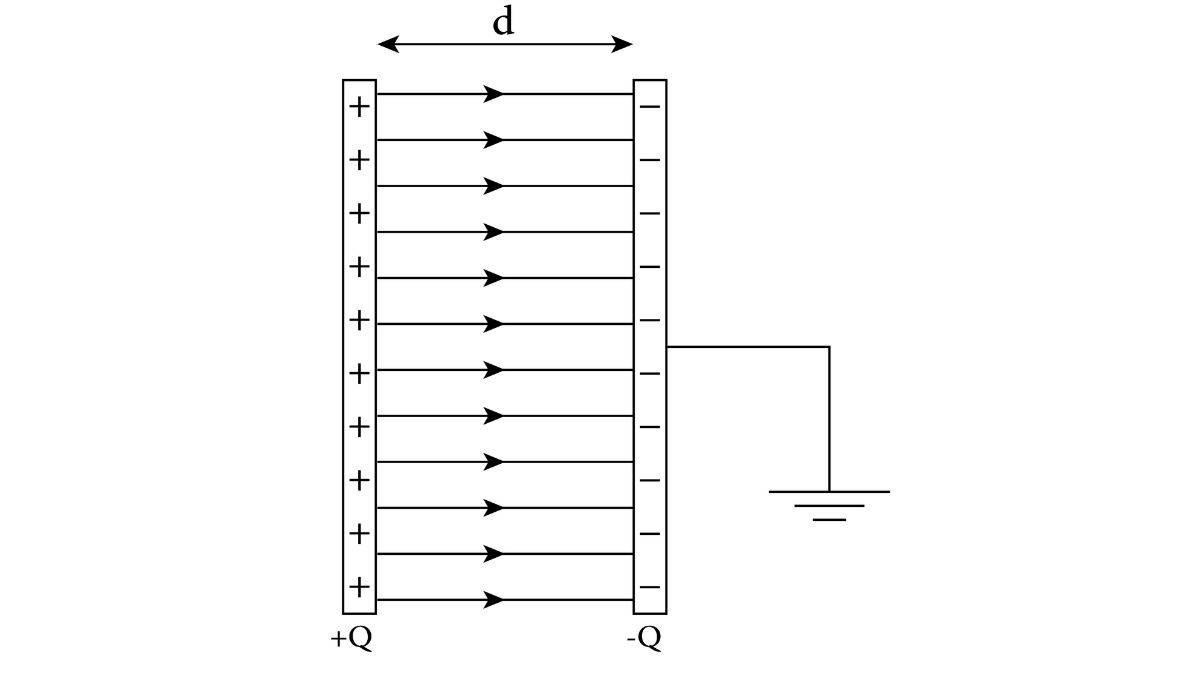
The energy stored in a capacitor is a concept in electrostatics that explains how a capacitor stores energy within its electric field. When we connect a capacitor to a voltage source, it moves the electrons from one plate to the other, and the work done to move the electrons is stored between the plates as electrical potential energy. Understanding this concept helps to analyze electric circuits in devices like flash cameras, filters, and energy storage systems. Check the article to know how energy is stored in a capacitor and the derivations.
- Define Energy Stored in Capacitor
- How is Energy Stored in a Capacitor?
- Derivation of Energy Density in an Electric Field ( from parallel plate capacitor)
- Energy Density in an Electric Field
- NCERT Physics Class 12 Chapters
- NCERT Solution for Class 12 Physics
Define Energy Stored in Capacitor
Energy stored in a capacitor is defined as the amount of work done by the applied voltage to move the electron from one plate to the other against the electric field. The energy is stored in the form of an electric field between the plates.
How is Energy Stored in a Capacitor?
A capacitor is an electronic component consisting of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When the current is applied to the capacitor, it moves the electrons from one plate to the other. The work done to move the electrons between the plates is stored as electrical potential energy. When the capacitor gets discharged, the stored energy is released.
Formula for Stored Energy in a Capacitor:
Where,
- C is capacitance
- U is energy stored
- V is the voltage across the capacitor
- Q charge on a capacitor
Derivation of Energy Density in an Electric Field ( from parallel plate capacitor)
Energy stored in the capacitor is given as:
- Capacitance (parallel plate capacitor):
- Electric Field:
- Substituting energy:
Volume (between plates): A ⋅ d
Energy density in the electric field:
Energy Density in an Electric Field
Energy stored per unit volume in the space where the electric field exists is known as energy density in an electric field.
Energy density u of an electric field is given as:
Where,
- represent the energy density (in J/m³)
- ε is the permittivity of the medium between the plates (for vacuum, )
- E is the electric field (in V/m)
NCERT Physics Class 12 Chapters
Here we have provided the link for NCERT Class 12 Physics notes. The notes are available for all chapters.
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
Chapter 13: Nuclei |
| 14 |
Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
NCERT Solution for Class 12 Physics
Here is the link for the complete NCERT solution for Class 12 Physics.
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Overview
- Combination of Capacitors
- Electrostatic Potential
- Electrostatics
- Potential Due to Point Charge
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Capacitors and Capacitance
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance
- Electrostatics of Conductors
- Potential Energy of a System of Charges
- Potential due to a System of Charges
- Potential Energy in an External Field
- Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Dielectrics and Polarisation
- Equipotential Surfaces
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter