
This guide details the equipotential surface definition. It will make your revision feel more intuitive and less like rote learning by letting you in on the ‘how’ and ‘why’.
Before exploring equipotential surfaces, pay heed to a few concepts you previously learnt about electrostatics, work done, and potential in Physics overall.
We will keep it byte-sized so that when you are preparing for the CBSE exam or for competitive tests, you don’t have to cram about equipotential surfaces from elsewhere.
- What You Must Know Before Learning Equipotential Surfaces
- What is Equipotential Surface Class 12?
- What is the Angle Between Electric Field and Equipotential Surface?
- Direction of Electric Field Relative to Electric Potential
- Properties of Equipotential Surfaces
- Illustrative Problem
- Class 12 Physics NCERT Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics Solutions
What You Must Know Before Learning Equipotential Surfaces
Test your knowledge on the following first.
- How do electric field lines behave?
- How is electrostatic potential a scalar while the electric field is a vector?
By convention, we are certain that electric field lines source out from positive charges and end on negative charges. Though abstract in their representation, these lines mathematically show the direction of force a positive charge in an electric field faces. These invisible lines are vectors, showing both the magnitude and direction of the field.
But we cannot directly find a scalar value like potential in the space or region where the electric field is created because of a single charge or a system of charges. To get the complete and correct picture of the whole electrostatic environment, we need to learn about equipotential surfaces.
So, think on this next question before moving further.
If you’ve a charged particle that’s moving between two points without any work required, what would be the potentials at those points? What surface will connect these points?
What is Equipotential Surface Class 12?
An equipotential surface is an imaginary three-dimensional surface with the same potential value (V) all across. The potential difference between any two points on it is always zero, ie., (ΔV = 0). This also gives a zero work done (W) result.
Shape of Equipotential Surface
The most common shape of an equipotential surface is spherical with the charge at the centre.
To know why this shape exists, we need to check some previously done concepts, especially, how you would figure out a Gaussian surface.
The equation previously derived for the potential due to a point charge is V (r) = kq/r, where k is the Coulomb constant.
Since V has a constant value, we rearrange the formula as
r = kq/V
What does this mean?
All points at the same distance r from the position or location of the charge will have the same value of V.
So the set of all points from the charge at the same distance of r will be creating a SPHERE with the charge at the centre. We can also safely assume now that the equipotential surface for a point charge will have concentric spheres.
For a complex configuration, like with multiple charges, we can come across different shapes of equipotential surfaces that reflect the cumulative influence. But the principle is the same, ie., points that have with the exact potential value will have a defined geometric shape.
How is Work Done ZERO?
Work done on an equipotential surface is always zero. No matter how much distance you are calculating the potential difference (ΔV) to be between two points, it will have the same separation.
Also, previously, when you learnt about the work done by an external force to move a charge from one point (let’s say A) to another (B, for now), you had this expression, W = qΔV
So,
W = q x 0 = 0
There are two implications to remember here. If the work done is zero on an equipotential surface, it means:
- Work is not required for a charge to move anywhere along the equipotential surface, as potential energy won’t change.
- Only the potential difference between two points on an equipotential surface is zero. It does not mean the potential is itself zero. The potential remains constant, so the difference between two points cancels out.
What is the Angle Between Electric Field and Equipotential Surface?
The angle between the electric field and the equipotential surface is 90 degrees, as the field lines are normal (n) to the surface.
To learn this mathematically, we must be sure about the relationship between two factors (and while excluding the external force acting on the charge to move on the surface):
- The force (which is related to the electric field)
- The direction of motion along the equipotential surface for the work done to be zero
From the main work equation, we know W = F dr.
This work done is the vector dot product of force and small movement which is creating a small distance.When introducing the electric field concept in this general work done equation, we need to use work to move a charge along an equipotential surface.
So, when the electrostatic force or Coulomb Force (F) is acting on the charge q, the electric field (E) acting per unit positive charge is E = F/q. And that gives us F = qE.
Now, we have W = qE dr cos θ
As we know that the work done is zero on an equipotential surface, think of what it’s actually telling us about the angle between the electric field and the surface.
There’s some charge. And there’s some distance from the charge. But work done is zero on an equipotential surface. So there must be some other factor that is making us know that there’s no work done.
That leaves us with one other term in the equation, W = qE dr cos θ, which could prove that the work done is zero. You guessed it by now, probably, and that it is cos θ which is 0 when the angle is 90 degrees.
So, it’s established right here. The electric field is perpendicular to the equipotential surface, where the electric field lines are at right angles when crossing such a surface.
But to understand the complete electrostatic ecosystem, can you now answer this:
What’s the direction of the electric field (E) relative to the electric potential (V)?
Direction of Electric Field Relative to Electric Potential
If you go back to Class 12 Electrostatics, the definition of the electric field at a specific point is the force per unit positive charge. It tells us that a positive test charge in an electric field experiences a force in the direction of the electric field.
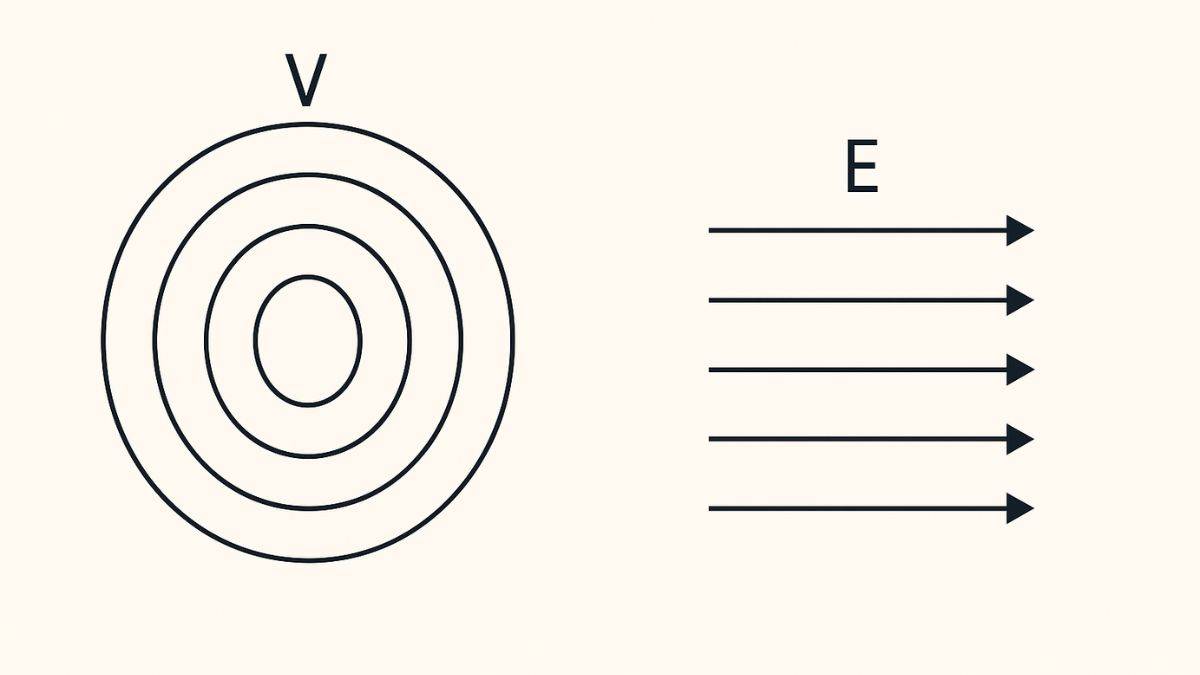
So, it is a convention that the potential at the source charge is at the highest, and it gradually decreases as it moves away from the charge.
The electric field puts a force on a positive charge where potential decreases.
So it’s like gravity acting on a ball rolling down a hill, where you can consider the force the field creates actually causes the charge to move from regions with higher potential to those in the lower potential.
And here too, there is no external work required when going down the gradient. There will be work if the movement is from lower potential to higher potential.
Deriving the Relation between Electric Field and Equipotential Surfaces
We know electric potential formula when there is a point charge
V (r) = kq/r
The inverse relationship with distance tells us the potential increases when there is less distance from the charge, and the more the distance there is from the charge, there will be lesser of a potential value.
Now, we should know or find out how much this potential value changes with distance. And there is a term for this rate of change, known as potential gradient.
The potential gradient is a way to define how fast the potential V changes when moving a small distance dr.
In maths, the potential gradient is dV/dr
So in the original equation of V = kq/r, we substitute to get
dV/dr = d (kq/r)/dr
When we use the power rule in differentiation for d (kq/r) or d (kqr^-1), we simply have to rewrite r^-1 as a power function. After that, we take the derivative and multiply by -1 to reduce the power by one and get - kqr^-2 or - kq/r^2
This negative sign comes from the power rule (-1 x r^-2).
So,
dV/dr = - kq/r^2
Now, if we look at the electric field equation E=F/q with force from a unit positive charge and combining that with the Coulomb’s Law formula F = kq_1q_2/r^2, we get
E = kq/r^2
So that equates to
dV/dr = - E
Or,
E = -dV/dr
Now we can safely and accurately draw these conclusions about the relationship between electric field and electric potential.
- The electric field points in the direction of decreasing potential.
- The negative sign tells us the electric field points opposite when the electric potential increases.
This is the general equation of the potential gradient when we are dealing with one dimensional surface. But if we are looking at a 3D surface, we will have to include a del operator, ie., vector differential operator E = -∇V. The gradient here shows the change in direction across three coordinates.
Properties of Equipotential Surfaces
Here are some properties of equipotential surfaces to remember.
- Constant Potential:
- Electric potential is the same at all points.
- The potential difference is zero at any point.
- Zero Work Done:
- No work is required to move a charge on an equipotential surface.
- Perpendicular to Electric Field:
- The electric field intersects the equipotential surface at a right angle.
- This prevents any component of the electric field along the surface.
- Shape Depends on Charge Distribution:
- The surface is a concentric sphere for a point charge.
- Parallel equipotential surface for a uniform electric field.
- For the line of charge, it is cylindrical.
- Closer Surface:
- The electric field is stronger when the equipotential surfaces.
- A larger gap means a weaker field.
Illustrative Problem
.
.
Class 12 Physics NCERT Notes
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
Chapter 13: Nuclei |
| 14 |
Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
NCERT Class 12 Physics Solutions
Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Overview
- Combination of Capacitors
- Electrostatic Potential
- Electrostatics
- Potential Due to Point Charge
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Capacitors and Capacitance
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance
- Electrostatics of Conductors
- Potential Energy of a System of Charges
- Potential due to a System of Charges
- Potential Energy in an External Field
- Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Dielectrics and Polarisation
- Equipotential Surfaces
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter
