To define capacitors and capacitance is to know the reasons why even modern electronic gadgets exist. Known for their store-and-release mechanism, they can temporarily store electrostatic energy and even act as a temporary power source or stabilise electrical signals. Different devices have storage capacities, and that's measurable per volt.
The camera’s flash is perhaps the most common example of a capacitor. The battery releases stored electrical energy to produce a flash of light in seconds! Such behaviour of how much charge was already there to release is measurable with capacitance.
All you have been learning in this Electrostatics and Capacitance chapter is how electric potential energy responds to fields and between multiple charges. Learning about capacitors and capacitance is the first step to seeing the real-world applications of these fascinating Physics concepts.
In this article, aligned with the latest NCERT Physics Class 12 textbook for 2025-2026, you’ll learn:
- How to define capacitor and capacitance with the necessary depth to use the formula, working principle, and SI Unit of capacitance to excel in conceptual and numerical problems, common in CBSE boards.
- To develop a ground-up approach to learn electrical circuits and possibly get into electrical or electronics engineering, after doing well in JEE Mains.
- What is a Capacitor?
- What is the Principle of a Capacitor?
- What is Capacitance in Physics?
- Capacitor Formula and Its Meaning
- Factors that Affect Capacitance
- Class 12 Physics NCERT Notes
- Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions
What is a Capacitor?
Capacitors are devices for storing energy until activated by some voltage that converts into charge temporarily. Gadgets we have daily use for, like our ceiling fans or the phones, need this very component that's able to use this energy and turn it into electricity to work or power various components.
Parts of a Capacitor
For this capacitor device to work, there are two parts:
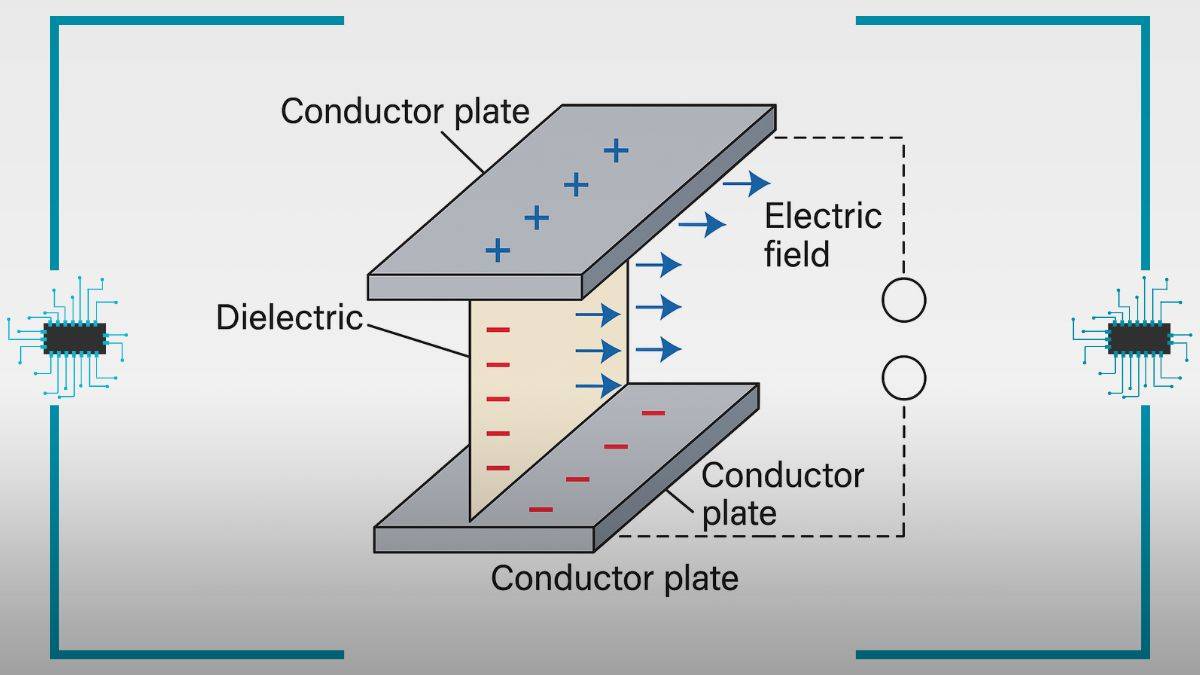
- There are two plates, which are conductors, and they allow electrons and overall electricity to flow, as we know from Class 12 electrostatics.
- These two conductor plates are separated by a dielectric - an insulating medium that blocks any charge to flow if in the natural state. And you can remember that the dielectric only temporarily creates polarisation when it enters an external field, ie, some voltage is applied to this dielectric that shifts the position of the bound charges and then the conductors start working.
What is the Principle of a Capacitor?
The principle of a capacitor is understood by the arrangement of the two plates with a dielectric in the middle and what is done to this system to respond in a specific way.
When there is voltage applied to the system, the conductor plates are able to collect equal and opposite charges. That ends up creating a uniform electric field between these plates. There's a condition to consider why this field is uniform, ie., the plates' sizes are way too large when you compare the distance.
With this logic, you need to remember a few points to connect the dots with the setup, detailed below.
- One plate has a positive charge (+Q); the other has a negative one (-Q).
- Current cannot flow freely, as there’s a dielectric that insulates or prevents the flow of current. This material only leads to the formation of the uniform electric field.
- The field lets the electrostatic potential energy to get stored which can be used up when charge is discharged.
Now comes the real question of the capacitor principle: How much charge can a capacitor have to work?
To learn that, we need to know how charge (Q), field (E), and the electrostatic potential, voltage, along with the size of and distance between the plates have interrelated roles to play in the capacitor.
How Voltage Creates a Potential Difference and an Electric Field Between the Two Plates
- The idea is that when you apply some voltage to the two plates connected, an electrostatic potential difference will occur between the two plates.
- The field created between the plates points from the positive plate to the negative one.
How Do Charges Balance the Electric Field and Voltage?
The field also exerts Coulomb’s force on the charges. That leads the positive charges to reside on or be pushed to one of the plates, while the negative ones are pulled to the other.
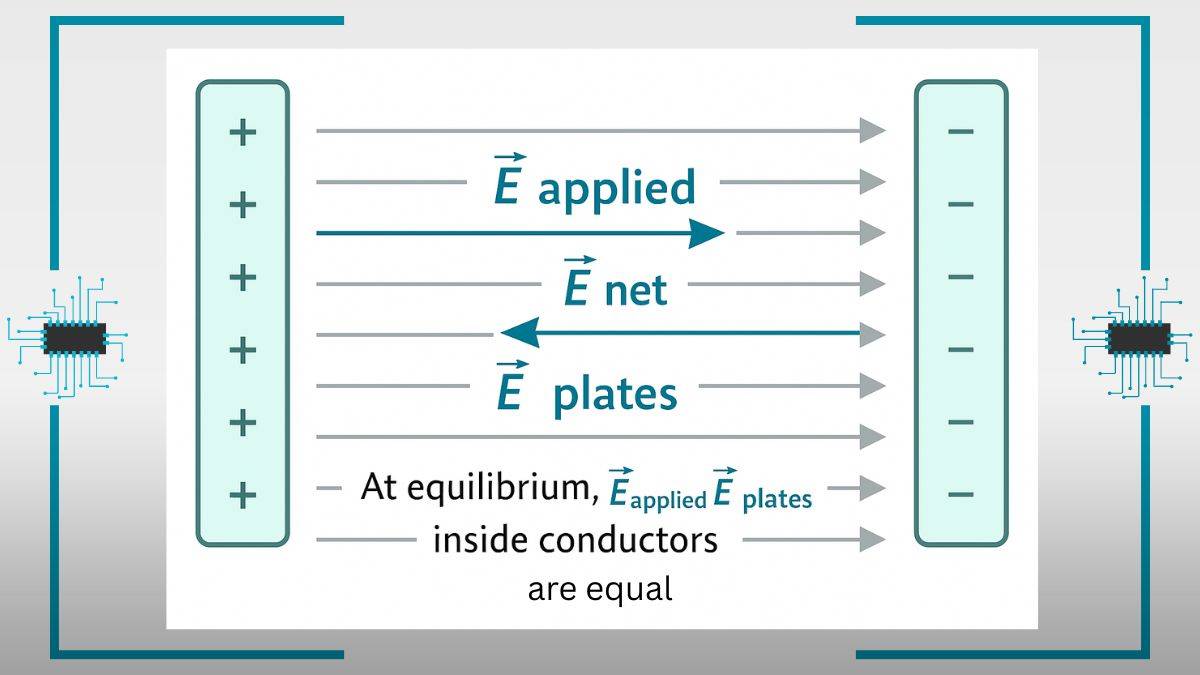
The two charges (+Q) and (-Q) create an opposing electric field to the voltage provided. Meaning, there is an applied electric field (E_applied) that directs from positive to negative plates.
After that, the charge on each of the plates will have its own electric field, which we can call E_plates.
From the positive charge plate, the field lines direct away or outward, and to the negative plate, the lines enter. Together, these fields add up between the plates and create a field moving from positive to negative.
Consider that the voltage comes from a battery pushing the charges onto the plates. But, the electric field from the plates tries to balance the opposing charges, and this keeps happening until the charge cannot flow.
So there can never be an infinite amount of charge buildup. There is only a finite amount of charge that can stay.
And this equilibrium is what limits the buildup of charge and defines what we know as capacitance.
This is why the capacitor does not have to run continuously.
Now, think, how should we measure this charge buildup on a capacitor?
It’s time to learn about capacitance below.
What is Capacitance in Physics?
Capacitance is basically the charge amount we calculate as and when the plates get some voltage to form an electric field in the capacitor.
The formula, C = Q/V, describes how much capacitance there is - the symbol C, then Q is the plate's charge, and V calculates voltage.
Now, we don’t really need to get confused with the voltage meaning when finding capacitance.
Voltage is the potential difference that's in between two points in a field. And in terms of a capacitor, we’re looking into this very difference between the two plates.
Capacitance of a Capacitor and its SI Unit
Farad (F) is the SI Unit of capacitance - derived from the equation of capacitance.
So, when talking about this unit, remember that one farad is achievable when one Coulomb of charge is applied per Volt.
1 farad = 1 Coulomb of charge per 1 Volt, and the dimensional formula for capacitance is [M^-1L^-2T^4A^2].
1 farad is, technically, too huge a value to hold. So, we use micro-units. μF for microfarad that’s 10^-6, picofarad as pF, holding a value of 10^-12, and so on.
Capacitor Formula and Its Meaning
What’s the capacitor formula? We take the capacitance formula above, C = Q/V, and just to know how much charge is required to find out the capacitance per unit volume, ie., Q = CV.
As we make a quick detour to touch on an important idea of the capacitance in the capacitor formula when the plates are in a parallel arrangement. You can look up our more detailed guide on the parallel plate capacitor, which derives the relation of capacitance.
C = ε_0 x A/d
A is the area of the plates, d is the distance between them, and epsilon naught is the permittivity of free space (vacuum).
We need to know this because the capacitance responds differently to the area of the plates and the distance between them. The next section details this interconnectedness.
Factors that Affect Capacitance
From the above capacitor formula, we find that the area of the plate and the distance can change the capacitance. There is one more aspect to find here, which is the medium between the plates.
Plate Area and Distance Between Plates
If the distance between the plates increases, the capacitance will decrease, which also means that capacitance is directly dependent on the plate’s area - any increase in the area will increase the capacitance.
Dielectric Medium
If you introduce a material containing a dielectric constant (k) between the plates, this will lead to an increased capacitance, too. This happens because the dielectric reduces the field more, and that allows for more storage of charge.
Board and JEE Tip: If you double the plate area and halve the distance from the original position between those plates, the capacitance increases four times. Try to develop such proportionality reasoning for the exams, as they get handy with quick numerical calculations.
Class 12 Physics NCERT Notes
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields |
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter |
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
Chapter 13: Nuclei |
| 14 |
Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Class 12 Physics NCERT Solutions
| Sl. No |
Name of Chapter |
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
| 12 |
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits |
Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Overview
- Combination of Capacitors
- Electrostatic Potential
- Electrostatics
- Potential Due to Point Charge
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Capacitors and Capacitance
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance
- Electrostatics of Conductors
- Potential Energy of a System of Charges
- Potential due to a System of Charges
- Potential Energy in an External Field
- Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Dielectrics and Polarisation
- Equipotential Surfaces
Other Class 12th Physics Chapters
- Physics Alternating Current
- Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Physics Electromagnetic Induction
- Physics Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Physics Semiconductor Devices
- Physics Wave Optics
- Physics Current Electricity
- Physics Nuclei
- Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Physics Atoms
- Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism
- NCERT Class 12 Notes
- NCERT Class 12 Physics
- Physics Electric Charge and Field
- Physics Electromagnetic Waves
- Physics Magnetism and Matter