The Biot Savart Law is a basic concept in electromagnetism that deals with the magnetic field produced due to electric currents. This law describes the relationship between magnetic fields and electric current. Biot Savart law was given by French scientists Jean Baptiste Biot and Felix Savart in 1820.
With the help of Biot Savart law we can calculate the magnetic field around the conductor of any shape such as solenoid, spiral loop, circular, and straight wire. Ampere’s Law and Maxwell’s equations are based on Biot-Savart law. This law is an essential concept in Physics and engineering.
Also, the topics based on Biot-Savart law such as Biot - Savart law and its application to the current carrying circular loop, Ampere's law and its applications to infinitely long current carrying straight wire and solenoid is essential from the entrance exam point of view. These topics are covered in the JEE Main syllabus. Focusing on the topics will help to obtain a good mark in the Joint Entrance Examination Main.
Moreover, the Class 12 students can refer to Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism for Biot Savart law. We have provided NCERT Solution Class 12 Physics Ch 4 to help students prepare for the CBSE exam. It is advised to seek the subject experts' help to understand the topic in depth.
- What is Biot-Savart Law?
- Biot-Savart Law Formula Explanation
- Application of Biot-Savart Law
- Bio-Savart Law for Class XII
- Illustrative Examples
- FAQs
What is Biot-Savart Law?
We know that all magnetic fields are because of moving charges or currents and intrinsic magnetic moments of particles. Biot-Savart's law establishes the relation between the current and the magnetic field it produces
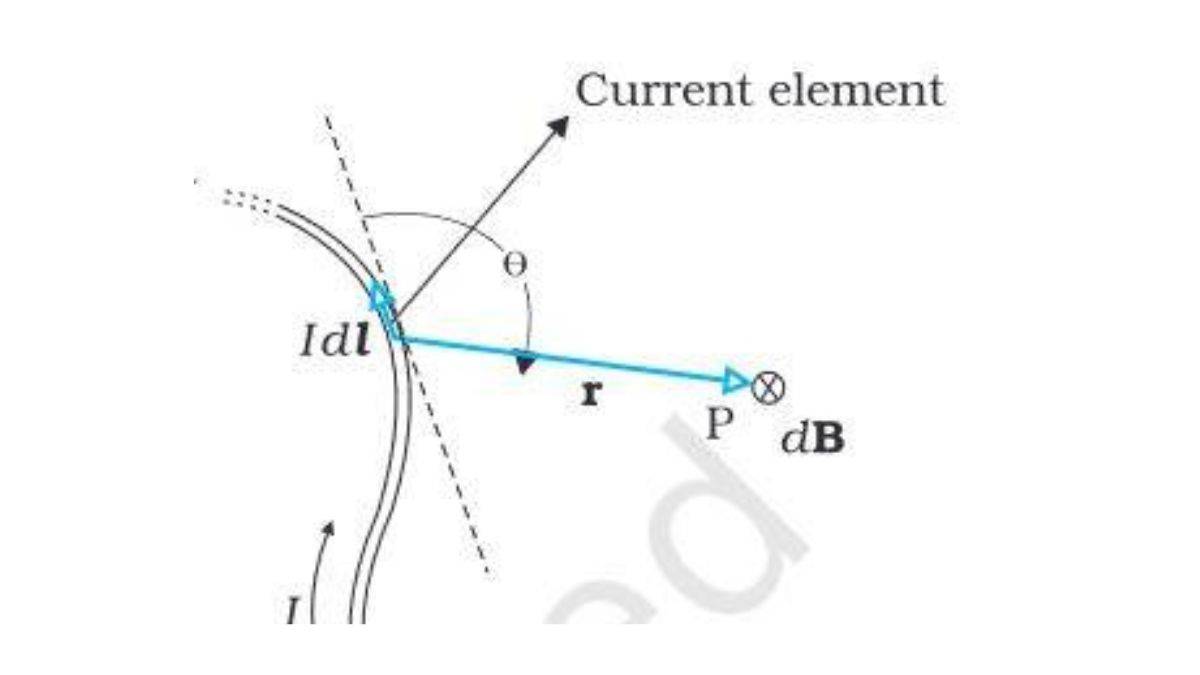
Diagrammatic Explanation of Bio-Savart Law
(Image Source: NCERT eBook)
Biot-Savart Law Formula Explanation
We have a conductor named XY carrying current I. Considering a minuscule element dl of the conductor, we have to find the magnetic field dB resulted by this element at a point p at a distance r from it. Assume Θ is the angle between dl and displacement vector r. Biot-Savart law says that the magnetic field dB size is directly proportional to the current I and the element length |dl|, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance r. Its direction is perpendicular to the plane of dl and r.
dB ∝ (Idl) x r/r³
= µ0/4π x (Idl) x r/r³
where µ0/4π is the proportionality constant. The above equation works only when the medium is the vacuum.
The magnitude of the magnetic field is
The constant of proportionality µ0/4π has the value 10-7 Tm/A. µ0 is the permeability of free space.
Application of Biot-Savart Law
The application of Biot-Savart law is mentioned below.
- Calculate the magnetic field in centre of a current-carrying arc, and indefinitely long straight wire owing to a constant current
- Calculate forces between lengthy and parallel current-carrying conductors.
Bio-Savart Law for Class XII
The topic 'Biot-Savart Law' is covered in the chapter 'Moving charges and Magnetism' of the third unit of class XII NCERT Physics. The other chapter is 'Magnetism and matter'. The fourth unit comprises the chapters 'Electromagnetic Induction' and 'Alternating Current'. These two units are combined in the exams for a total of 17 marks.
Illustrative Examples
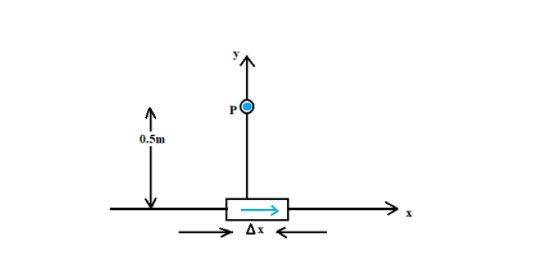
Example 1: An element dl = Δx is placed at origin and carries a current I = 10A. Find the magnetic field on the y-axis at a distance of 0.5m. Δx = 1cm.
Solution:
|dB| = µ0/4π x (IdlsinΘ)/r²
dl = Δx = 10-²m, I = 10A, r = 0.5, m = y, µ0/4π = 10-7 Tm/A.
Θ = 90°; sinΘ = 1.
|dB| = (10-7x10x10-²)/(25x10-²)=4x10-8T
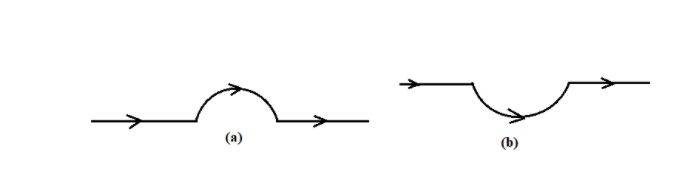
Example 2: A straight wire carrying 12A is bent into a semi-circular arc of radius 2cm. Considering the magnetic field B at the centre of the arc,
- a) calculate the magnetic field due to straight segments
- b) In which way does the contribution of B in the semi-circular arc differ from that of a circular loop?
- c) What if the semi-circular arc of the same radius was bent in the opposite direction as shown in the second figure?
Solution: a) dl and r for each element of the straight segments are parallel.
Therefore, dl x r = 0.
Thus straight segments do not contribute to |B|.
- b) For all segments of the semi-circular arc, dl x r are parallel to each other. All such add up in magnitude. The right-hand rule gives the direction of magnetic field B, and its magnitude is half that of a circular loop.
B = 1.9x10-4T.
- c) The same magnitude of B as that in b) but in the opposite direction.
Example 3: Consider a 100 turn coil of radius 10cm carrying a current of 1A. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field?
Solution: Given, radius R = 10cm = 0.1m
Number of turns N = 100
Current I = 1A
Thus,
B = µ0NI/2R
= 4πx10-7x10²x1/(0.2)
= 2πx10-4
= 6.28x10-4.
FAQs
Q: What is Biot-Savart Law?
Q: Write the Biot-Savart law equation.
Q: What is µ0?
Q: What is the condition for which Biot-Savart law holds?
Q: What is µ0/4π?
Physics Laws of Physics Concepts Exam
Student Forum
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test