Have you ever said "She walk to the office everyday" to someone and immediately felt something was off with the sentence? Well, that's because you have ignored the most basic rule in English grammar; i.e., Subject-Verb Agreement. The rule forgotten in this sentence is that the subject (who ro what the sentence is about) and the verb (action being done) do not match in number. For this sentence to be grammatically correct, the rule to be followed is, a singular subject takes a singular verb and a plural subject takes plural verb.
Read this article to understand the 26 rules of subject-verb agreement, so you can avoid common grammatical mistakes in Subject Verb Concord and improve your English. You will also find helpful preparation tips and subject-verb agreement worksheets with answers, making it easy and fun to learn subject-verb agreement in grammar. Also, find examples of subject-verb agreement.
How do I know is a subject is 'singular' or 'plural'?
A subject in a sentence is singular, if it refers to one person, place, or thing. However, a subject is plural, if it refers to more than one person, place, or thing.
Another way to identify the subject as singular or plural, is by looking at the pronoun used. Singular nouns often do not end in '-s', while plural nouns usually do.
Examples:
- The child plays in the garden. (Singular)
- The children play in the garden. (Plural)
What happens when there are two subjects joined by 'and'?
When two subjects in a sentence are joined by 'and', usually the plural verb is used to make the sentence gramatically correct. However, if both nouns refer to a single idea, singular verb is used.
Examples:
- My brother and I are going on a trip.
- Fish and chips is a popular dish in the UK.
- What is Subject Verb Agreement?
- Definition of Subject-Verb Agreement
- Rules of Subject-Verb Agreement
- English Grammar Subject-Verb Agreement and Verb Tense
- How to Identify Subject-Verb Agreement in a sentence?
- Common Errors to Avoid in Subject-Verb Agreement in English
- Best Books to Prepare for Subject-Verb Agreement in Grammar
- Examples of Subject-Verb Agreement
- Subject-Verb Agreement Worksheet
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- Frequently Asked Questions on Subject-Verb Agreement
What is Subject Verb Agreement?
Subject-Verb Agreement, also known as subject-verb concord, is a rule in English grammar where the subject and verb in an English sentence must match in number. This means:
- If the subject is singular, the verb must also be singular.
- If the subject is plural, the verb must also be plural.
Here,
- Subject: The person or thing doing the action.
- Verb: The action or state of being.
With the help of subject-verb agreement, we can create gramatically correct sentences. Additionally, you must note that no matter whether the subject of a sentence is a name, pronoun, or noun, the verb must match it in number and tense.
Examples of Subject-Verb Agreement:
- Singular: Riya dances gracefully.
Here, the subject 'Riya' is singular, therefore, the verb 'dance' will also be in singular form; i.e., dances - Plural: Riya and Tanu dance gracefully.
Here, the subjects 'Riya and Tanu' are plural, therefore, the verb 'dance' will also be plural; i.e., dance
Commonly asked questions
What if the subjects in a sentence are joined by 'or' or 'nor'?
In a sentence, when two subjects are joined by 'or' or 'nor', the verb should agree with the nearest subject. The rule followed here is the proximity rule.
Examples:
- Either the teacher or the students have the answer.
- Either the students or the teacher has made a mistake.
Do titles of books or movies take singular or plural verbs?
Titles of books, plays, movies, etc., may appear plural but are treated as singular. It is because these books, plays, or movies refer to a single entity.
Examples:
- "The Great Gatsby" is a wonderful movie.
- "Pride and Prejudice" is a classic novel by Jane Austen.
Should we use singular or plural verbs with measurements and time?
If you are discussing a specific amount of time, money, weight, distance, or volumne, which is considered as one unit or a total quantity, use singular verb. It is because measurements are treated as a single idea, instead of individual parts.
Examples:
- Ten miles is too far to walk.
- Five hundred rupees is not enough for the Rakhi gift.
- Two liters of water is enough for the recipe.
- Three hours is a long time to wait.
Definition of Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-Verb Agreement Definition: Oxford Dictionary
According to Oxford Dictionary, subject-verb agreement refers to "the grammatical rule that a subject must agree with its verb in number and person."
Pronunciation: /ˈsʌbdʒɪkt vɜːb əˈɡriːmənt/ (British) | /ˈsʌbdʒɪkt vɝːb əˈɡriːmənt/ (American)
Examples of Subject Verb Agreement:
- The dog barks loudly at night.
- The book on the table belongs to my sister.
- The children play in the park.
Subject-Verb Agreement Definition: Collins Dictionary
According to the Collins Dictionary, subject-verb agreement is “the rule in grammar that the subject of a sentence must match the verb in terms of number (singular or plural) and person (first, second, or third).”
Subject-Verb Agreement Definition: Cambridge Dictionary
As per the Cambridge Dictionary, “the person and number of the subject of the clause determine the person and number of the verb of the clause. This is called subject–verb agreement or concord.”
Also Read: What are Gerunds in English Grammar?
Rules of Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject and Verb Agreement in English Grammar helps us make a sentence that is clear to the reader or listener and is grammatically correct. It also creates a relationship between the subject and the verb of agreement to ensure they match in terms of number (singular or plural) and person (first, second, third). While creating sentences using subject-verb agreement, certain rules must be followed.
In this section, we will explore the 26 subject-verb agreement rules with examples.
Rule 1: Verbs in Present Simple Tense Act Differently From Nouns
The nouns and verbs in grammar loose 's' or add 's' when used in the simple present tense. That is;
- Nouns add 's' when they are plural.
- Verbs lose the 's' when the subject is plural.
- Exception: With "I" and "you," we don't use 's' on the verb.
Examples:
He likes mangoes. / They like mangoes.
The bird flies high. / Birds fly in the sky.
Rule 2: Phrases Between the Subject and Verb do not Change Agreement
- While deciding which verb form to use in the sentence, ignore any extra words or phrases between the subject and the verb.
Examples:
The players who practice every day are improving quickly. (Here, "Players" is the subject, not "who practice every day". So, as "players" is plural, the verb "are" is used.)
A group of students is attending the seminar. (Here, "Group" is the subject, not "students." Since "group" is singular, the verb "is" is used.)
Rule 3: Collective Nouns in Grammar Can Take Singular or Plural Verbs
- If the group is acting as one unit, use a singular verb.
- If individuals in the group are doing different things, use a plural verb.
Examples:
The committee decides on the policy tomorrow. (Here, the committee is acting as one unit. So, we will use the singular verb 'decides')
The committee have submitted their individual reports. (Here, each member of the committee is considered as an individual. So, we will use the plural verb 'have')
Also Read: English Paraphrasing: Rules and Examples
Rule 4: Subjects Connected by ‘And’ Are Usually Plural
- When two people or things are joined with "and", plural verb should be used.
Examples:
Tom and Jerry make a great team.
Bread and butter are on the table.
Rule 5: Two Nouns Referring to One Thing Take a Singular Verb
- If the two nouns refer to the same person or idea, use a singular verb.
Examples:
My teacher and mentor is retiring.
The poet and philosopher lives in Paris.
Rule 6: Ignore Words Like ‘Along With’ or ‘As Well As’
- Do not consider words like 'along with' or 'as well as' while selecting the verb form, as they do not change the number of the subject.
Examples:
The principal, as well as the staff, was present.
The captain, along with his team, is ready.
Rule 7: Words Inside Brackets Don’t Affect the Verb
- The information provided in parentheses doesn’t change subject-verb agreement.
Examples:
The child (and his toys) is sleeping.
My sister (with her kids) goes to the park.
Rule 8: Use Singular Verbs With Singular Subjects Joined by ‘Or’ or ‘Nor’
- When connecting singular subjects, the verb stays singular.
Examples:
Either Sarah or Emma has the keys.
Neither the phone nor the charger works.
Rule 9: Verb Agrees With the Subject Closest to It (Or/Nor)
- When using "or/nor," match the verb with the noun closer to it.
Examples:
Neither the cats nor the dog is here.
Either the manager or the workers are late.
Also Read: Articles: Exercises with answers
Rule 10: Indefinite Pronouns Like 'Each' or 'Everybody' Use Singular Verbs
- Even though they seem to refer to many people, these are singular in grammar.
Examples:
Each of the answers makes sense.
Everybody knows the rules.
Rule 11: Plural Indefinite Pronouns Use Plural Verbs
- Words like many, few, both always take plural verbs.
Examples:
Several have arrived.
Few know the truth.
Rule 12: Some Pronouns Change Based on What They're Referring To
- If the noun is uncountable, the verb is singular. If countable, the verb is plural.
Examples:
All of the rice is burnt.
All of the cookies are gone.
Rule 13: Some Nouns Look Plural But Are Actually Singular
- If a plural form subjects with a plural meaning, the verb is plural:
Examples:
The scissors are missing.
The pair of scissors is missing.
Rule 14: Time, Distance, and Money Act as Singular Units
- Use a singular verb when referring to a single idea or amount.
Examples:
Five hours is too long to wait.
One hundred dollars is enough.
Rule 15: ‘Everyone’, ‘Everybody’, and ‘Each’ Are Always Singular
- These words always take singular verbs.
Examples:
Everyone wants to win.
Each of the gifts has a tag.
Rule 16: Some Nouns Are Singular Even Though They Look Plural
- Words like civics, physics, news take singular verbs.
Examples:
Physics is my favorite subject.
The news is not good.
Note: If there is a countable noun, it may follow a plural verb. For example: Three hairs were in the food.
Also Read: Conjunction in English
Rule 17: Words That Can Be Both Singular and Plural Depending on Meaning
- Use a singular or plural verb depending on whether you mean one idea or many.
Examples:
Economics is a complex subject. (one subject)
The economics of the deal were confusing. (many aspects)
Rule 18: In Sentences Beginning With ‘There Is/There Are’ — Look at the Real Subject
- Match the verb with the noun that comes after it.
Examples:
There is a cat on the roof.
There are stars in the sky.
Rule 19: “None” Can Be Singular or Plural Based on Context
- Use a singular verb with uncountable nouns and plural verb with countable nouns.
Examples:
None of the water is left.
None of the books are left in the library.
Rule 20: Fractions Agree With the Noun They Describe
- Place the verb after checking the singularity and plurality of the noun.
Examples:
Half of the cake has been eaten.
One-third of the fans are cheering.
Rule 21: “More Than One” Takes a Singular Verb
- Even though 'more than one' sounds plural, it is treated as singular. So, in this case, use a singular verb.
Examples:
More than one person is needed.
More than one bird has flown away.
Rule 22: Titles of Works or Entities Use Singular Verbs
- Even if the title of some work or entity seems plural, it is one unit. Therefore, use singular verbs in these cases.
Examples:
"Stranger Things" is a fantasy web series.
The United States is a big country.
Rule 23 (A): “One of Those Who…” Takes a Plural Verb
- When using "one of those", the verb must be plural.
Examples:
She is one of those players who train daily.
He is one of those students who participate in every competition.
Rule 23 (B): “The Only One of Those Who…” Takes a Singular Verb
- When using "the only one," the verb refers to that single person.
Examples:
He is the only one of those students who gets full marks.
She is the only one who knows the answer.
Rule 24 (A): “The Number Of…” Takes a Singular Verb
- 'The number of' means one amount. Therefore, it uses singular verb.
Examples:
The number of books has increased.
The number of calls is rising.
Rule 24 (B): “A Number Of…” Takes a Plural Verb
- 'A number of' means several or many. Therefore, it takes plural verb.
Examples:
A number of students have submitted the form.
A number of issues remain unresolved.
Rule 25: Sentences Starting With ‘Every’ Use Singular Verbs
- If a sentence is starting with 'every', use a singular verb. It does not matter whether there are more than one nouns in that sentence.
Examples:
Every pen, pencil, and notebook is missing.
Every athlete and coach attends the meeting.
Rule 26: Use ‘Were’ to Show a Wish or an Unreal Situation
- In imaginary statements, use ‘were’ even with singular subjects.
Examples:
If I were taller, I’d play basketball.
I wish it were Saturday.
Singular and Plural Verb
In English grammar, verbs change form depending on whether the subject is singular (one person or thing) or plural (more than one person or thing). This is called verb agreement.
Singular Verbs
A singular verb is used when the subject is one person, animal, or thing.
Examples:
- She writes neatly.
- The dog barks loudly.
Easy Trick: In the present tense, singular verbs often end in -s or -es.
Plural Verbs
A plural verb is used when the subject is more than one person or thing.
Examples:
- The dogs bark loudly.
- Rahul and Meena play cricket.
Easy Trick: In the present tense, plural verbs are usually in their base form (without -s or -es).
Singular Verb v/s Plural Verb
Here is a quick difference between singular and plural verb:
| Subject Type |
Verb |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Singular |
Verb + s/es |
The bird sings. |
| Plural |
Base verb |
The birds sing. |
This basic understanding of singular and plural verbs will help you apply subject-verb agreement rules more confidently.
Also Read:
| Rules of Suffix in English Grammar | Prefix Rules in English | English Punctuation Rules |
| List of Irregular Verbs | List of Transitive Verbs | List of Intransitive Verbs |
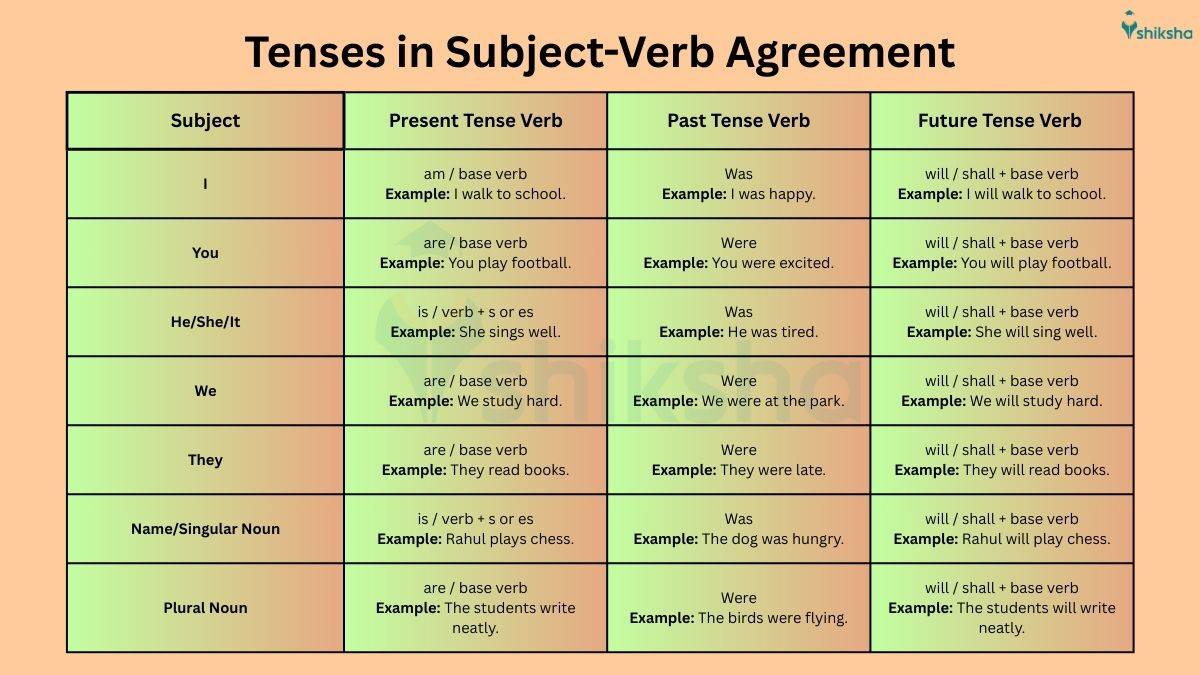
English Grammar Subject-Verb Agreement and Verb Tense
In subject-verb agreement, we not only have to match the subject and verb in number (singular or plural), but we also have to use the correct verb form. To write the accurate form of the verb, we have to consider the tense of the sentence.
A verb tense shows when something happens: present tense, past tense, or future tense.
Let’s look at how verbs agree with subjects in different tenses:
Present Tense:
In the present tense, the verb forms changes with singular or plural subjects.
| Subject Type |
Correct Verb Form |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Singular (he, she, it, name) |
verb + s/es |
She reads a book. |
| Plural (I, you, we, they) |
base verb |
They read books. |
Past Tense:
In the past tense, verb forms do not change with singular or plural subjects (except with was/were):
| Subject Type |
Verb Form |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Singular |
was / past form |
He was happy. She walked fast. |
| Plural |
were / past form |
They were late. We walked fast. |
Future Tense:
In future tense, the verb remains in its base form and is used with will/shall (or is going to, etc.)
| Subject Type |
Verb Form |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Any subject |
will/shall + base verb |
She will sing. They will sing. |
Easy Tricks:
- In present tense, the verb changes the most based on subject number.
- In past tense, the change is seen in helping verbs (was/were).
- In future tense, the base verb stays the same for all subjects.
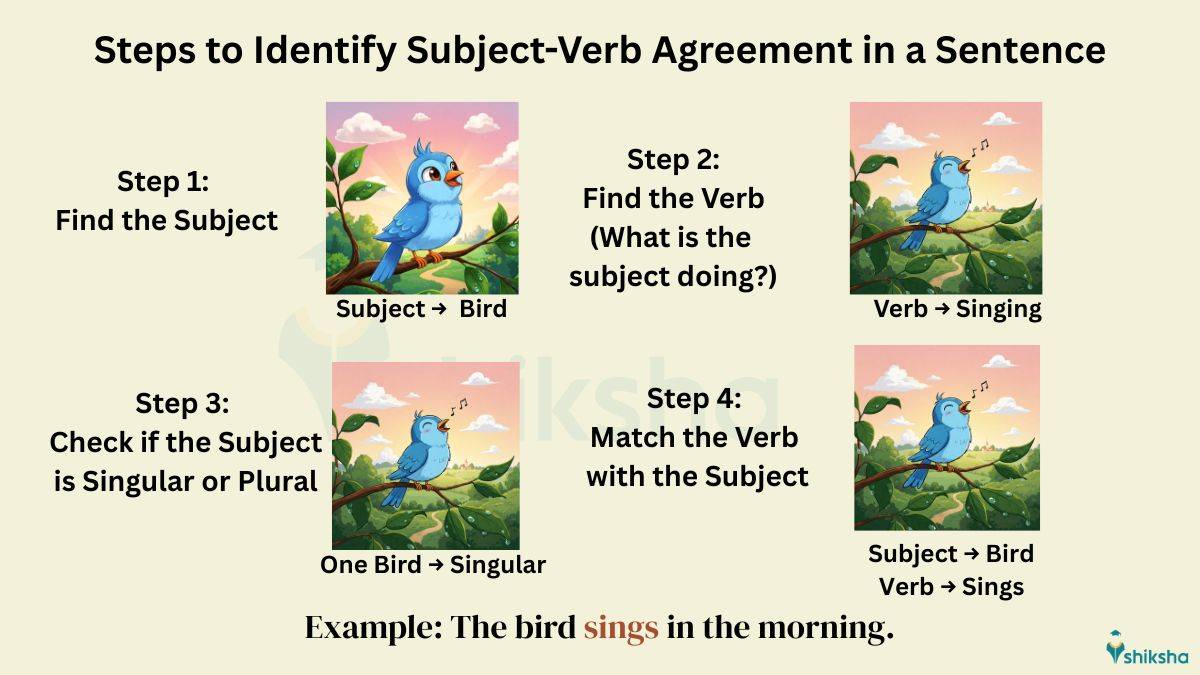
How to Identify Subject-Verb Agreement in a sentence?
1. Read the sentence and identify the subject.
- Example: A bird sings in the morning.
2. Find out the verb in the sentence.
- Example: A bird sings in the morning.
3. Once you have found out the subject and verb, check whether the subject is singular or plural.
- Examples:
The girl runs fast. (Singular)
The girls run fast. (Plural)
4. Make sure that the verb matches the subject of the sentence. Take example from the below table:
| Subject |
Correct Verb Form |
Incorrect |
|---|---|---|
| She |
is running. |
She are running. |
| They |
are playing. |
They is playing. |
| The child |
plays. |
The child play. |
| The cat |
sleeps. |
The cats sleeps. |
5. Do not get confused by the words between the subject and the verb (e.g., prepositional phrases). Be careful with subjects joined by "and" (usually plural). Lastly, watch for "either/or", "neither/nor"—verb agrees with the subject closest to it.
- The box of toys is on the floor. (Subject = box)
- Ram and Shyam are friends.
- Either the teacher or the students are coming.
Quick Tip: Read the sentence aloud. If it sounds wrong, it probably is. Your ear often catches mistakes your eyes might miss.
Common Errors to Avoid in Subject-Verb Agreement in English
Below are some of the most common facts or rules people forget about while using subject-verb agreement in a sentence:
1. People usually get confused by the words placed between the subject and the verb of the sentence.
- Incorrect: The bouquet of flowers smell nice.
- Correct: The bouquet of flowers smells nice.
Here, the subject is 'bouquet' , so the verb is singular.
2. Most of the times, people treat collective nouns as always singular or plural. However, there are certain collective nouns in English such as team, jury, or family, which can be singular or plural. The singularity and plurality of a collective noun depends on the context of the sentence or paragraph.
- Incorrect: The team are winning the match.
- Correct: The team is winning the match. (one unit)
3. There are certain indefinite pronouns like each, everyone, and neither, which may sound like plural, but always uses singular verb. People tend to forget this fact.
- Incorrect: Everyone have a copy.
- Correct: Everyone has a copy.
4. When subjects are joined by either/or or neither/nor, the verb is placed according to the subject closest to it.
- Incorrect: Neither the teacher nor the students is ready.
- Correct: Neither the teacher nor the students are ready.
5. Just like indefinite pronouns, there are some nouns like physics, news, politics, etc., which looks plural, but are singular.
- Incorrect: The news are shocking.
- Correct: The news is shocking.
6. Uncountable nouns (like information, advice, furniture) are singular and take singular verbs.
- Incorrect: The furniture are new.
- Correct: The furniture is new.
7. Words like cattle, police, and people look singular but are always plural.
- Incorrect: The police is coming.
- Correct: The police are coming.
Best Books to Prepare for Subject-Verb Agreement in Grammar
Check out these books to learn more about Subject-Verb Agreement:
| Book Title |
Author |
|---|---|
| High School English Grammar & Composition |
Wren & Martin |
| Objective General English |
S.P. Bakshi |
| English Grammar in Use |
Raymond Murphy |
| Plinth to Paramount |
Neetu Singh |
| A Mirror of Common Errors |
Dr. Ashok Kumar Singh |
| Common Errors in English Usage |
Paul Brians |
| Practical English Usage |
Michael Swan |
Also Read: Subject-Verb Agreement MBA preparation
Examples of Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-Verb Agreement Worksheet
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
Frequently Asked Questions on Subject-Verb Agreement
Commonly asked questions
There are 26 rules in subject-verb agreement. These cover a wide range of situations, such as rules for singular/plural subjects, compound subjects, collective nouns, indefinite pronouns, distances, time, money, and exceptions.
When using either/or neither/nor, the verb agrees with the subject the closest to it.
Example:
- Neither my friend nor her parents have arrived yet.
- Either my brothers or my sister is going to help you.
Here are some examples of subject-verb agreement:
- The girl is reading a book.
- The boys are playing football.
- Each of the books has a different topic.
- Each of the players has a unique skill.
- The children were playing in the park.
- Ten kilometers is a long distance to walk.
Subject-verb agreement means the verb in a sentence must match the subject in number. If the subject is singular, the verb should be singular. If the subject is plural, the verb should be plural.
Example:
- He runs fast. (singular subject + singular verb)
- They run fast. (plural subject + plural verb)
No. Some nouns like mathematics, news, and politics end in “s” but are singular and take a singular verb.
Example: Mathematics is difficult.
In case of group of people, the subject-verb agreement depends on whether the group is acting as one unit or as individuals:
- If the group acts as a single unit, use a singular verb.
Example: The group is planning a trip.
- If the group members are acting individually, use a plural verb.
Example: The group are arguing among themselves
English Subject Verb Agreement Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds