
Among the 12 tenses in the English language, the most commonly used tense is the Present Tense. The Simple Present Tense is the type of present tense which is used to talk about what is currently happening or a current action that takes place regularly.
The simple present tense in English grammar is the verb tense describing the current event. It is the basic form of the ‘Present Tense’. The Simple Present Tense is also known as the Present Indefinite Tense. Read below to know all about the Simple Present Tense, including the rules of the simple present tense, usage of the present tense, simple present tense examples and exercises with solutions, etc.
What is the formula for the Simple Present Tense in English?
The formula for the Simple Present Tense is- Subject + Base form of the Verb (V1) + s/es + Object
Examples of Present Simple Tense:
1) Riya writes in her notebook.
Riya - Subject
Writes - V1 + s
Notebook- Object
2) The dog lick the bone.
Dog- Subject
Licks- V1 + s
Bone- Object
3) Mr. Simon teaches maths at a local school.
Subject- Mr. Simon
V1 (teach) + es- Teaches
Maths- Object
What are the four types of Present Tense?
In English, there are four types of Present Tenses. These are:
- Simple Present Tense- Subject + V1 + s/es + Object
- Present Continuous Tense - Subject + am/is/are + V1 + ing
- Present Perfect Tense- Subject + has/have + past participle
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense- Subject + has/have + been + V1 + ing
- What is Simple Present Tense?
- Simple Present Tense Definition
- How to Use Simple Present Tense and Examples
- Types of Simple Present Tense in English Grammar
- Rules For Simple Present Tense
- Special Cases and Exceptions for the Verb Tense- Simple Present Tense
- Irregular Verbs in Simple Present Tense
- Why is Simple Present Tense Important?
- Simple Present Tense vs Present Continuous Tense
- Best Books to Learn Simple Present Tense
- Simple Present Tense Worksheet with Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Simple Present Tense Preparation
- FAQs on Simple Present Tense
What is Simple Present Tense?
The Simple Present Tense is used to describe general truths or facts, habits, scheduled events, daily routines, permanent situations, etc. A tense is the form of the verb which expresses the time of action. And, the simple present tense is that verb tense in English Grammar which expresses the current action or situation.
There are three types of Present Simple Tense: Affirmative, Negative and Interrogative. Let's look at about 10 examples of the simple present tense:
Examples of Simple Present Tense:
- Ravi wakes up at 6 AM.
- I polish my shoes.
- My boss starts work on time.
- This ice cream tastes delicious.
- My daughter lives in London.
- Where do you play football?
- She helps her dad in the garden.
- They walk their dog every morning.
- We do not speak Spanish.
- Does Kelly write a story?
Also Read:
| Simple Past Tenses: Uses, Examples and Exercises with Answers | Past Perfect Tenses in English Grammar |
| English Past Perfect Continuous Tenses | Simple Future Tense: Rules, Types, Formula and Examples |
Commonly asked questions
How to form questions in Present Simple Tense?
To form questions in the Present Indefinite Tense, one can add 'do' or 'does' before the subject and the infinitive form of the verb. When asking a question using the wh-word, place the pronoun or adverb before 'do' or 'does'.
Examples:
- Why does Mayank never answers his phone?
- Where does Nisha work?
- Do you want to go to the park?
- Does Anjali work on Saturdays?
How to form passive voice in Simple Present Tense?
Passive sentences in the Simple Present Tense are the one which the subject is acted upon. In such sentences, the subject does not do the action but is being acted upon. The passive voice uses a conjugated form of the verb 'to be' along with past participle of the main verb.
Examples:
- Returned items are inspected by the shopkeeper.
- The stray dog is fed by everyone in the neighbourhood.
- The book is read.
- The meal is cooked by Rajni.
Simple Present Tense Definition
According to the Oxford dictionary, the simple present tense is “the form of a verb that expresses an action that is happening now or at the time of speaking.”
The Collins dictionary also has the same definition of the Present Simple Tense of English Grammar.
Pronunciation- /preznt ˈtens/
Examples of Simple Present Tense
Here are a few simple present tense examples:
| Helen talks very fast. | I love my new dress. |
| Does she talk a lot? | The King of England lives in Buckingham Palace. |
| Namrata enjoys cooking. | Sam brushes his teeth twice a day. |
| I like English and Geography. | My sister works at the museum. |
| Water boils at 100 degree celsius. | Mr. Clark does not teach maths. |
| Mary never lies. | Leila swims every morning before work. |
| It rains here even in summers. | We go to the cinemas every Sunday. |
| Ankit writes an email to his friends. | The dishes smell delicious. |
How to Use Simple Present Tense and Examples
The verb tense, Simple Present Tense is used to express the current event, as mentioned above. The root form of the verb is used for the Simple Present Tense in grammar.
For example, I ride a bike.
The present tense is used in the following cases:
General Truths
When talking about or stating general or universal truths, the simple present tense is used. General truths are statements depicting facts or situations which are permanently true. These statements are universally accepted and consistently held regardless of time or circumstances. These statements are not subject to change and also include scientific facts, such as 'the water freezes at 0 degree celcius',
Example:
- The kids go to school
- I run in the park.
- They work during the day.
Present Event/Time
The Present indefinite tense is also used to describe an event or activity that is ongoing.
Example:
- Rohan lives in Delhi
- I study in Class 10
Habits/Routines
The tense used to describe habits or usual routines is the simple present tense. Routine habits or activities are also described using the simple present tense or the present indefinite tense.
Example:
- I sleep at 11 PM.
- Children go to school.
- I play basketball.
Near Future Events
Events or activities that are to be performed in the near future are also described using the simple present tense. These cases are particularly seen when referring to things such as public transportation or fixed schedules or timetables.
Example:
- The movie starts at 10 PM.
- The train leaves at 6 AM.
- The bus goes at half past five.
Quotations and Headlines
The simple present tense is also used to quote famous sayings or things that are generally permanent. Simple tense is also used in live commentaries, sports, or news headlines to give a sense of immediacy.
Example:
- Honesty is the best policy.
- Rohit Sharma hits a six!
- Oscar Wilde said- “to live is the rarest thing in the world. Most people exist, that is all.”
A Past Event in a Narrative
The verb tense, simple present tense, is also used to express a past event in a narrative. Writers and speakers often use the simple present tense instead of the past tense to express a past event when narrating. This gives their story more depth, makes it vivid and dramatic, and immediate to give a sense to the listener or reader that the event is happening right now.
Example:
Past Tense: Neha walked into the room. Prateek looked up and smiled.
Narrative Present Tense: Neha walks into the room. Prateek looks up and smiles.
The second kind of narrative feels more alive, as in it is happening right now.
Also Read:
| Examples of Prefixes | Examples of Suffixes | Parts of Speech in English: Examples, Exercises with answers |
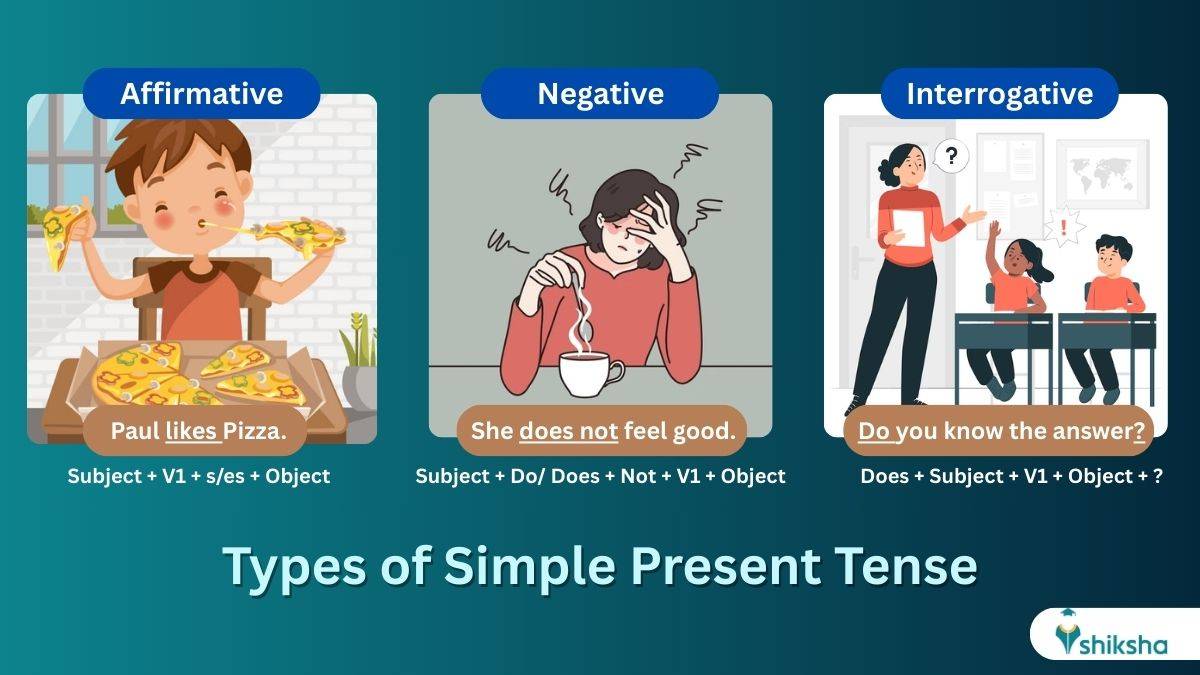
Types of Simple Present Tense in English Grammar
There are three types of simple present tense, i.e. Affirmative, Negative and Interrogative. Each type of simple present tense differs in structure and has a different grammar rule. Let’s understand each in detail.
Affirmative Simple Present Tense
In simple words, the affirmative simple present tense in grammar gives a sense of positive action or information. An affirmative simple present tense sentence tells what happens or what someone does.
Rule: Subject + V1 + s/es + Object
| Subject |
Form of the Verb |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| I/ You/ We/ They |
Base form of the verb (no changes) |
Example: We work hard. You dance beautifully. |
| She/ He/ It |
Base form of the verb (V1) + s/es |
Riya works hard. He sings beautifully. She goes to the gym. It barks loudly. |
Example:
- Rohan likes pizza.
- Tanya sings wonderfully.
- Janet and Anna exercise every morning.
Negative Simple Present Tense
The negative simple present tense is usually formed by adding ‘do not’ or ‘don’t’ between the verb and the subject. In simple words, this tense expresses of something that does not happen or someone does not do something.
To form such a sentence, always the base form of the verb is used.
Rule: Subject + Do/ Does + Not + V1 + Object
| Subject |
Verb |
|---|---|
| I/ You/ We/ They |
Do Not (Don’t) |
| He/ She/ It |
Does Not (Doesn’t) |
Example:
- We do not watch much television.
- He doesn’t like to dance.
- The remote doesn’t work properly.
Interrogative Simple Present Tense: How to Ask a Question
As the name suggests, a sentence in the interrogative simple present tense is a question.
Rule: Does + Subject + V1 + Object + ?
| Subject |
Verb |
|---|---|
| I/ You/ We/ They |
Do |
| He/ She/ It |
Does |
Example:
- Does it bother you?
- Does she go to school?
- Does he like pizza?
Take a look at the table below to understand the types of Simple Present Tense in English in Singular and Plural forms:
| Types of Simple Present Tense |
Singular |
Plural |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative |
Subject + V1 + S/es + Object |
Subject + V1 + Object |
| Negative |
Subject + Does/ Does Not + V1 + Object |
Subject + Do Not + V1 + Object |
| Interrogative |
Does + Subject + V1 + Object + ? |
Do + Subject + V1 + Object + ? |
Rules For Simple Present Tense
Mentioned below are some of the grammar rules for simple present tense. These rules explain the structure of the sentence where the simple present tense is used. The formulas for simple present tense are:
Rule 1: Base Form of Verb with He/ She/ It
Rule- Subject (He/She/It) + V1 + Object
The base form of the English verb is used in a simple present tense when the pronouns he, she or it are used.
Example:
He eats an apple.
It sits on the table.
She dresses up nicely.
Rule 2: Spelling Rules for Adding ‘s’ or ‘es’
The table below depicts some spelling rules in English when adding ‘s’ or ‘es’ to verbs in the third person singular:
| Verb Endings |
Rule |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| Ends in –ch, -sh, -x, -s, -o |
Add es |
Watches, patches |
| Ends in a constant + y |
Change y to ies |
Cry – Cries Fly- flies Dry- Dries |
| Ends in a vowel + y |
Add s |
Toy- Toys Tray- Trays Alley- Alleys |
| Most verb |
Add s |
Says, plays, thinks, reads |
Rule 3: Usage of ‘Do’ and ‘Does’ in Negative Sentences and Questions
The rule for the negative sentences where the simple present tense is used is as follows:
Rule: Subject + Do/ Does + Not + V1 + Object
Example:
- She does not like broccoli.
- Don’t you watch football on TV?
- Where does he go?
Rule 4: Time Expressions in Simple Present Tense
There are some common time expressions which can only be expressed by using the simple present tense. Such time expressions include, always, never, often, sometimes, usually, every day, every year, every week, in the morning, in the evening, etc.
Example:
- He wakes up at 5 in the morning.
- They never skip exercise after dinner.
- Reena goes to the gym every day.
Rule 5: Do not use –ing in Simple Present Tense
One of the stated rules of grammar while using the simple present tense is not to use –ing with verbs.
Example:
Incorrect: She is going to the market on Sunday.
Correct: She goes to the market on Sunday.
Incorrect: He is driving a taxi every evening.
Correct: He drives a taxi every evening.
Also Read:
Special Cases and Exceptions for the Verb Tense- Simple Present Tense
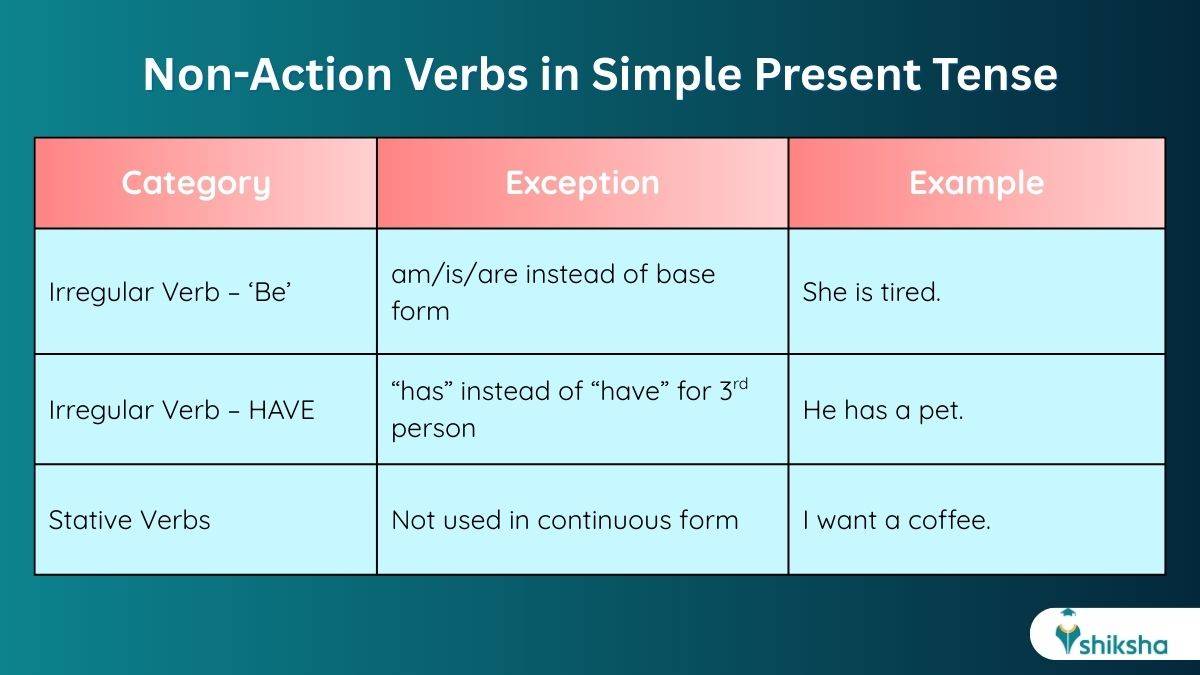
Although the Simple Present Tense follow a basic structure of the sentence, there are a few exceptions when using the simple present tense in the English language. These are:
Exception 1: Irregular Verbs
Some irregular verbs such as Be, Have and Do, do not follow the simple rule of adding ‘s’ or ‘es’ or using the base form. The word completely changes:
| Irregular Verb |
Subject |
Correct Form in Simple Present Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Be |
I |
Am |
| You/ We/ They |
Are |
|
| He/ She/ It |
Is |
|
| Have |
I/ You/ We/ They |
Have |
| She/ He/ It |
Has |
|
| Do |
I/You/ We/ They |
Do |
| She/ He/ It |
Does (In negative and interrogative sentences, do/does are used as auxiliary and the main verb stays in the base form. |
Exception 2: Sentence with Stative Verbs or Non-Action Verbs
Some verbs are known as non-action verbs or stative verbs, which describe states and not actions. These are usually not used in the continuous tense, even if the action is ongoing. Examples of such verbs are believe, think, know, love, own, like, need, want, etc.
Examples:
Incorrect: She knowing the answer.
Correct: She knows the answer.
Incorrect: He loving the music.
Correct: He loves the music.
Incorrect: Rohan is owning a bakery.
Correct: Rohan owns a bakery.
Irregular Verbs in Simple Present Tense
In the Simple Present Verb Tense of English grammar, the verbs usually follow the regular patterns, i.e. adding 's' or 'es'. However, there are some irregular verbs which do not follow the standard spelling rules of grammar or the structure. Such verbs behave differently in terms of verb structure, spellings and form, especially in the third-person singular. Read below to get a detailed explanation.
1. 'To Be': The irregular verb 'to be' changes to am/are/is depending on the pronoun used in the simple present sentence structure. 'To be' remains completely irregular in the present indefinite verb tense. The said verb also acts as a linking verb, which connects the subject to a descriptive phase or state of being.
| Subject | Verb Form |
|---|---|
| I | am |
| He/She/It | is |
| You/We/They | are |
Example:
- She is happy.
- I am a teacher.
- They are standing.
2. 'To Have': The verb 'to have' is an auxiliary verb in the present simple tense and is used to describe possessions, experiences and actions. Understanding the role of 'To Have' is crucial to prepare for the English language. The verb 'To Have' is slightly irregular in the English simple present tense and is used for describing habitual actions. It is also used to describe the present state or something that exists or is present in the current moment. It is also sometimes known as the foundational verb in the English language.
Example:
- She has a garden at her home.
- I have a meeting tomorrow.
- He has to go to the market today.
| Subject | Verb Form |
|---|---|
| I/You/We/They | have |
| He/She/It | has |
3. 'To Do': The 'to do' is an irregular verb in usage. The 'to do' verb is used in the simple present tense sentence structure to form questions and negative sentences. The verb also adds emphasis and force to the main verb. Usually, the 'do' verb is not used in the affirmative simple present tense, but can be used to put emphasis on something. Example: 'I do like this dress'. As per the Cambridge dictionary, the do/does is used "to give extra force to the main verb." In the negative and interrogative simple present tense, 'do' is used as the auxiliary verb.
Example:
- He does not eat non-vegetarian food.
- They do their work.
- Does Rohan work here?
| Subject | Verb Form |
|---|---|
| I/You/We/They | do |
| He/She/It | does |
Also Read:
Why is Simple Present Tense Important?
Simple Present Tense vs Present Continuous Tense
The Simple Present and Present Continuous Tense have various differences and similarities. Although both are used to depict present actions, they convey different meanings. Simple Present Tense is used to refer to habits, truths, states and facts, whereas the Present Continuous Tense describes temporary actions that are currently happening. The table below depicts the difference between the simple present tense and present continuous tense in English grammar:
| Features | Simple Present Tense | Present Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simple Present Tense is used to depict general truths or facts, habits, scheduled events, daily routines, and permanent situations | The type of Present Tense which describes an action happening right now or during a specific time period, or a planned future arrangement. Usually used for temporary actions happening in the present. |
| Usage |
|
|
| Structure | Subject + V1 + s/es + Object | Subject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + Object |
| Time Expressions | Always, Usually, Every Day, Often, Sometimes | Now, At the moment, Today, Currently |
| Examples |
|
|
Best Books to Learn Simple Present Tense
Simple Present Tense Worksheet with Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Simple Present Tense Preparation
FAQs on Simple Present Tense
Commonly asked questions
What are the common grammar mistakes in Simple Present Tense?
The following mistakes should be avoid when using the Simple Present Tense:
Forgetting the -s/-es in third-person singular
Example: She go to school. (Incorrect)
She goes to school. (Correct)
Using do/does in affirmative sentences
Example: She does eat the dinner. (Incorrect)
She eats dinner. (Correct)
Incorrect word order in questions
Example: He goes where? (Incorrect)
Where does he go? (correct)
Can the Simple Present Tense be used for Future events?
Yes, simple present tense cna be used when describing certain future events which are already scheduled, for example:
- The bus departs at 6 PM sharp.
- My Spanish classes begin next week.
In which scenarios can I use simple present tense?
Simple Present Tense is the kind of verb tense which is used in our everyday life. The scenarios where Simple Present Tense can be used are:
- To describe daily routine
- To describe facts or universal truths
- To describe scheduled events
- To describe feelings and state of being
- To describe directions and instructions
- To describe habits
What is the simple present tense structure?
There are three kinds of simple present tense in the English language. The structure for each is as follows:
Affirmative: Subject + base verb (add -s/-es for third-person singular)
Negative: Subject + do/does + not + base verb
Interrogative: Do/Does + subject + base verb +?
What is the difference between Simple Present Tense and Present Continuous Tense?
To understand the key differences between Simple Present Tense and Present Continuous Tense, look at the table below:
Aspect | Simple Present Tense | Present Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
Usage | Describes habitual actions, general truths, and facts | Describes actions happening now or around the present moment |
Structure (Affirmative) | Subject + base verb (+s/es for he/she/it) | Subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing |
Structure (Negative) | Subject + do/does + not + base verb | Subject + am/is/are + not + verb + -ing |
Structure (Interrogative) | Do/Does + subject + base verb? | Am/Is/Are + subject + verb + -ing? |
Time Indicators | Always, usually, often, never, every day/week | Now, right now, at the moment, currently |
Duration of Action | Regular or repeated over time | Temporary or happening at/around the present moment |
Verb Types | Often used with stative verbs (e.g., know, like) | Generally not used with stative verbs |
English Tenses Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds

What is the structure of Present Perfect Tense and its rules?