The ideal gas equation in Physics shows how variables, including pressure, volume, and temperature of an ideal gas relate to each other. At the same time, absolute temperature defines the Kelvin scale, which is critical for analysing gas behaviour. These two concepts in physics are essential for preparing to gain mastery over thermodynamics, physical chemistry, and engineering-level sciences. This guide explains and simplifies definitions, derivations, and applications of the ideal gas equation. Clear your doubts with these and work confidently with the updated NCERT Solutions of Physics Chapter 10.
- What is Ideal Gas Equation?
- Ideal Gas Assumptions to Learn Ideal Gas Law
- Gas Laws for Ideal Gas Equation
- Absolute Temperature and Kinetic Theory
- Applications of Ideal Gas Equation
- Diagram
- JEE Main-Level Examples for Ideal Gas Equation
- Key Points for JEE Main
- Revision Notes NCERT Physics Class 11
- NCERT Solutions to Practice
What is Ideal Gas Equation?
The ideal gas equation describes the state of an ideal gas. It's a theoretical model where gas particles have negligible volume and no intermolecular forces except during elastic collisions. The equation is: where is pressure is volume is moles, is the universal gas constant, and is absolute temperature (K). Absolute temperature is measured on the Kelvin scale, where 0 K (absolute zero) is the point of zero molecular kinetic energy.
Why Should You Learn the Ideal Gas Equation and Absolute Temperature?
The ideal gas equation and absolute temperature are ideal scenarios or theoretical models, discussed in the "Thermal Properties of Matter" chapter, that help you progress to advanced concepts in Physics. You can say it's a simplification that becomes a springboard to more realistic models (like van der Waals). When you are dealing with thermodynamic state variables and equation of state, you need to know this aspect.
As this is an interrelated subject, you can expect it to be included in various entrance tests after your CBSE boards. For instance, it's in the IAT Physics syllabus where you can expect questions that combine all the gas laws (explained below) and concepts like their limitations. Have a look at the previous year's questions for the IISER Entrance exam.
Even while preparing for your upcoming NEET exam, you should look into these concepts, as earlier questions have tests the candidate's knowledge on interpreting graphs on the behaviour of gases in the ideal state, and comparing properties of gases, or similar.
Ideal Gas Assumptions to Learn Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas model typically assumes several key conditions.
- Molecules are point masses with negligible volume.
- No intermolecular forces except during elastic collisions.
- Molecules move randomly, obeying Newton's laws.
- Collisions with container walls cause pressure.
Real gases approximate ideal behaviour at low pressure and high temperature.
Gas Laws for Ideal Gas Equation
The ideal gas equation unifies empirical gas laws.
- Boyle's Law: constant (at constant ).
- Charles' Law: constant (at constant ).
- Gay-Lussac's Law: constant (at constant ).
These laws are derived from by holding variables constant.
Absolute Temperature and Kinetic Theory
Absolute temperature relates to molecular kinetic energy.
The average kinetic energy of a gas molecule is: where is Boltzmann's constant, and is Avogadro's number. At absolute zero ( ), molecular motion theoretically stops.
The ideal gas equation is derived from kinetic theory where is molecular mass, is number of molecules, and is mean square velocity. Equating kinetic energy to thermal energy yields:
Applications of Ideal Gas Equation
The ideal gas equation and absolute temperature are applied in several applications.
- Weather Forecasting: Balloon volume changes with temperature
- Engineering: Gas behaviour in engines and turbines.
- Chemistry: Calculating molar quantities in reactions.
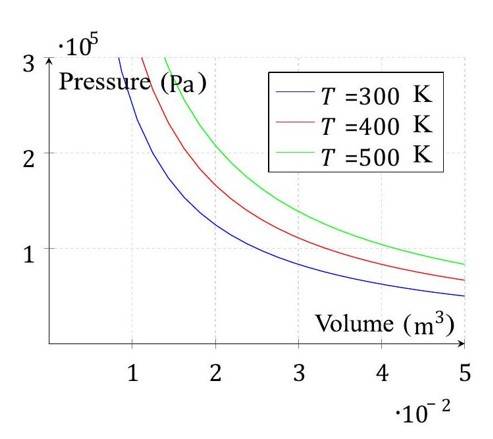
Diagram
JEE Main-Level Examples for Ideal Gas Equation
Based on previous year questions for JEE Main, here are some numerical problems to look at.
1. Problem: A gas occupies 2 L at and 1 atm . Find its volume at and 2 atm
2. Problem: Calculate the temperature when 1 mol of gas expands from to at constant pressure of 10 Pa
3. Problem: Find the number of moles in 11.2 L of gas at STP ( )
Key Points for JEE Main
Revision Notes NCERT Physics Class 11
NCERT Solutions to Practice
Commonly asked questions
What is an ideal gas?
An ideal gas is a theoretical or hypothetical gas that obeys the ideal gas law perfectly. That is, PV=nRT.
What are the limitations of the ideal gas equation?
The ideal gas equation fails at high pressures, low temperatures, and for gases with strong intermolecular forces or large molecular volumes.
Physics Thermal Properties of Matter Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion