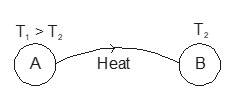
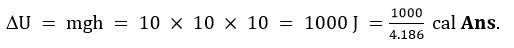Temperature and Heat are the most used terms in daily life. They are the fundamental concepts of thermodynamics and physical science. Students can understand how energy is transferred between two objects through this topic. Temperature and heat are fundamental for studying thermal expansion, change of state, heat transfer, Newton's law of cooling, calorimeter, and thermal expansion.
Also Read: Class 11 Physics NCERT Solutions | NCERT Solution for Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter
- Temperature and Heat Definition
- Understanding Temperature and Heat
- Mechanical Equivalent of Heat
- How does heat transfer?
- Source of Heat
- Comparision Between Heat and Temperature
Temperature and Heat Definition
The NCERT definition of Temperature and Heat is as follows:
- Temperature: Temperature is a relative measure, or indication of hotness or coldness.
- Heat: The energy transferred between two (or more) systems or a system and its surroundings by virtue of a temperature difference.
Read More: NCERT Solution
Understanding Temperature and Heat
Temperature indicates how hot or cold a body is, based on the average kinetic energy of particles of that material. When two objects at different temperatures come in contact, thermal energy flows from the warmer object towards the cooler object. This energy transfer continues until both objects attain the same temperature, the so-called thermal equilibrium.
Resources: Class 12 Physics Solutions
The energy that is transmitted due to the temperature difference is called heat. In short, heat is energy in transit because of the temperature difference. When this energy becomes absorbed by a body, it transforms into that body’s internal energy.
With regard to the term heat, it is confirmed that it applies only when energy is being transferred. It is, hence, wrong to say that a certain amount of heat is contained by a certain body, as once the transfer has taken place, the energy is no longer considered as heat; it is recognised as internal energy.
When an object is heated, it undergoes many changes such as a rise in temperature, expand or change the shape.
When we say that a body is heated it means that its molecules begin to move with greater kinetic energy. S.I. unit of heat energy is joule (J). Another common unit of heat energy is calorie (cal).
1 calorie = 4.18 joules.
1 calorie : The amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of 1 gm of water from 14.5 to 15.5 ºC at one atmospheric pressure is 1 calorie.
Mechanical Equivalent of Heat
In early days heat was not recognized as a form of energy. Heat was supposed to be something needed to raise the temperature of a body or to change its phase. Calorie was defined as the unit of heat. A number of experiments were performed to show that the temperature may also be increased by doing mechanical work on the system.
These experiments established that heat is equivalent to mechanical energy and measured how much mechanical energy is equivalent to a calorie.
If mechanical work W produces the same temperature change as heat H, we write,
W = JH
where J is called the mechanical equivalent of heat. J is expressed in joule/calorie. The value of J gives how many of joules of mechanical work needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C.
Example 1. What is the change in potential energy (in calories) of a 10 kg mass after 10 m fall?
Solution : Change in potential energy
How does heat transfer?
The transfer of heat can take place mainly in three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation
Conduction:
- Heat transfer from one molecule to another substance
- Example: touching hot metal
Convection:
- Heat transfer through the movement of fluid
- Example: water boiling on gas
Radiation:
- Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves
- Example: Fire, Sun
Source of Heat
There are various sources of heat, however, the most efficient sources are
- Chemical: burning coal, wood, gasoline and natural gas
- Nuclear: Nuclear reactor
- Electrical: Electric heater, ovens, water heater, electric stove, joule heating
- Sun
Comparision Between Heat and Temperature
Below is a comparison of heat and temperature on various aspects.
| Heat |
Temperature |
| Heat is an energy that is transferred from within two object |
Temperature is expressed as the degree of hot or cold |
| SI unit is the Joule |
SI unit is Kelvin, Degree Celsius |
| Denoted by the 'Q' symbol |
Denoted by the 'T' symbol |
Physics Thermal Properties of Matter Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion