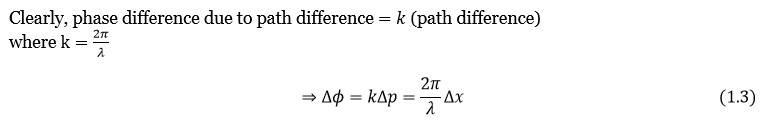Let us explain principle of superposition in Physics. When two waves arrive at the same spot at once, their effects just add together. On a stretched string, you see this as how far it moves up or down. In sound, it shows up as changes in air pressure. For light or radio waves, it’s the strength of the electric or magnetic fields. When two light waves travel almost side by side, they overlap and create a pattern of bright and dark areas. That pattern is called interference. Please note that this topic is important for JEE main exam and students must be thoroughly prepared to answer all conceptual questions.
Please note that this topic is important for JEE main exam and students must be thoroughly prepared to answer all conceptual questions.
- What is Superposition of Waves?
- What is the Principle of Superposition of Waves?
- Superposition of Waves Formula
- Example of Superposition Principle with Two Sinusoidal Waves
- What is the Principle of Superposition in Mathematical Terms?
- Types of Superposition of Waves
- Superposition of Waves: Path and Phase Differences in Wave Interference
- Conditions for Superposition in Waves
- Revise Physics Class 11 Notes
- Practice NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
What is Superposition of Waves?
Superposition of waves tells us what happens when two waves pass through the same medium at the same time. When the waves overlap, they combine to form a new, resultant wave. Now, this resultant wave has the displacement at every point to be the vector sum of the displacements of both waves at that specific point.
What is the Principle of Superposition of Waves?
Section 14.5 of Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 describes the principle of superposition like this
"When the pulses overlap, the resultant displacement is the algebraic sum of the displacement due to each pulse. This is known as the principle of superposition of waves. According to this principle, each pulse moves as if others are not present. The constituents of the medium, therefore, suffer displacements due to both and since the displacements can be positive and negative, the net displacement is an algebraic sum of the two."
Simple Explanation
The principle of superposition states that when two or more waves traverse the same medium at the same time, the total displacement at any point and time is the algebraic sum of the displacements caused by each wave alone.
Superposition of Waves Formula
Mathematically, for two waves with displacements, represented as y₁(x,t) and y₂(x,t), we get the sum as below. This is also known as the Superposition of waves Formula.
y(x,t) = y₁(x,t) + y₂(x,t)
Note that the superposition principle holds true if the dynamics remain linear. Otherwise, it will fail.
Example of Superposition Principle with Two Sinusoidal Waves
Consider superposition of two sinusoidal waves (having same frequency), at a particular point.
Let,
and,
represent the displacement produced by each of the disturbances. Here we are assuming the displacements to be in the same direction. Now according to superposition principle, the resultant displacement will be given by,
where
and
What is the Principle of Superposition in Mathematical Terms?
Let us explain the principle of superposition in mathematical terms. You can further go back to brush up on learning the displacement relation to understand this part better.
Step 1: Write down each wave’s equation
Pick two sinusoidal waves travelling in the same direction (same k and ω), but possibly different amplitudes and phases:
Step 2: Invoke linearity of the wave equation
also satisfies it exactly.
3. Interpret at a fixed point PPP
Imagine standing at a fixed x=P. At time t, the medium “would” be at
Since the medium doesn’t “care” which wave caused the displacement, but only the net force, it simply reaches the sum:
Types of Superposition of Waves
The following are the different types of superposition of waves.
- Constructive Interference: Whenever 2 waves are travelling in the same direction and are in phase with one another, the amplitude of those waves get added and a resultant wave is obtained. This is known as constructive interference.
- Destructive Interference: Destructive interference happens when two waves arrive out of sync so that a “hill” (crest) of one lines up with a “valley” (trough) of the other. At that moment, their pushes and pulls are opposite, and they cancel each other out which makes the combined wave smaller or even perfectly flat.
Superposition of Waves: Path and Phase Differences in Wave Interference
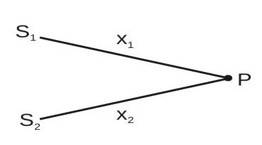
To advance with the superposition of waves principle, we need to dig a little deeper into interference patterns and differences in the paths the waves take.
Let
and
be two sources producing progressive waves (disturbance travelling in space given by
and
)
At point
,
Here, the phase difference,
where
Also, here is the path difference
In Figure 1.3, we can see this
Conditions for Superposition in Waves
Revise Physics Class 11 Notes
Practice NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
Physics Waves Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test