Mensuration is a chapter in Mathematics that we all have studied in school. It forms an important section of test in various entrance exams for professional courses and competitive exams too. In MBA, Mensuration is an important chapter in Quantitative Aptitude section. It carries significant weightage in MBA entrance exams like CAT, XAT, CMAT, NMAT, SNAP, MAT, ATMA and others. Preparation for this topics starts with understanding concepts and is considered complete with practicing enough number of sample test papers. One needs to remember Geometry units and formulas by heart to be able to crack any question. Here's a comprehensive guide to Mensuration.
- What is Mensuration?
- Mensuration Formulas
- Illustrated Examples of Mensuration Formulas
- CAT Quantitative Aptitude Questions for Practice with Solutions
- FAQs Related to Mensuration and Mensuration Formulas
What is Mensuration?
Mensuration can be defined as the measurement of geometric figures such as quadrilaterals, their areas, perimeter, surface areas, and volumes. It is a very important topic in CAT and other MBA entrance exams. Mensuration questions are also asked in other competitive exams, so if you are preparing for any entrance or competitive exam, then you must prepare Mensuration thoroughly.
Mensuration Formulas
Given below are some key Mensuration formulas:
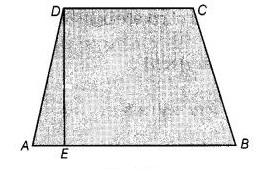
Trapezium:
A trapezium is outlined by a form that has 2 parallel sides and the other 2 are nonparallel. It has four sides and four vertices.
| Shape |
Area |
Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Trapezium |
Area= (1/2) H + (AB+CD) |
P= sum of all the sides i.e. AB+BC+CD+AD |
| 2. General quadrilateral |
Area= Area of △ABC + Area of △ADC |
The perimeter depends on the type of shape which is present |
| 3. Special quadrilateral (rhombus) |
½ × d1 × d2 |
P=4a |
Where, H= height, W= breadth, a,b,c,d= sides, d= diagonals.
Surface area: It is the the total area of all the surfaces of any form.
Volume: the degree is outlined by the number any third-dimensional form takes.
| Shape |
Surface area |
Volume |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Cube |
Area= 6a^2 |
V= a^3 |
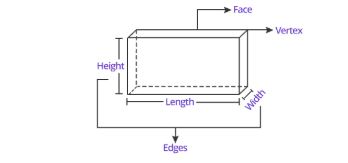
| 2. Cuboid |
Area= 2 [(l × b) + (l× h) + (b× h)] |
V= l*w*h |
| 3. Cylinder |
Ares= 2πr (r + h) |
V= πr2 × h |
Where, H= height, a= sides, r= radius, d= diameter, b= breadth, w= width
Also Read: MBA Preparation 2025: Tips to Prepare for MBA Entrance Exams
Illustrated Examples of Mensuration Formulas
Example 1: Calculate the area of a rhombus whose diagonals are 10 cm and 8.2 cm of length.
Ans: The formula for calculating area of a rhombus = ½ d1d2, (d1 and d2 are the lengths of the diagonal)
a= 2 × 10 × 8.2 cm2 = 41 cm2.
Example 2: A rhombus with an area of 240cm2 and whose one diagonal is of length 16 cm. Find the other diagonal.
Ans: We know d1 = 16 cm and let the other diagonal = d2
Thus the area of the rhombus = 2 d1 . d2 = 240
So, ½ 16 d2 = 240
Therefore, d2= 30cm
Diagonal 2 is 30 cm.
Also Read:
| VARC Preparation Tips for MBA Exams | DILR Preparation Tips for MBA Exams |
Example 3: A cuboid-shaped aquarium is a present whose external measurements are of 80 cm × 30 cm × 40 cm. The base, side faces and back face are to be covered with a coloured paper. Find the area of the paper needed?
Ans: The length of the aquarium = l = 80 cm
Width of the aquarium (b) = 30 cm
Height of the aquarium (h) = 40 cm
Thus the area of the base = 80 × 30 = 2400 cm2
Area of the side face = 30 × 40 = 1200 cm2 &
Area of the back face = 80 × 40 = 3200 cm2
Thus area required to be calculated = Area of the base + area of the back face + (2 × area of a side face)
= 2400 + 3200 + (2 × 1200) = 8000 cm2
Read More:
CAT Quantitative Aptitude Questions for Practice with Solutions
Get here sample questions and practice tests PDFs for CAT Quantitative Aptitude with solutions. Download these PDFs and practice Quants questions:
FAQs Related to Mensuration and Mensuration Formulas
Q: What is the formula of the area of a cube?
Q: What is the area of the quadrilateral?
Q: What is the height of a cylindrical structure?
Q: How many edges and faces will a cuboid have?
Q: What is the area of a cuboid?
Quantitative Aptitude Prep Tips for MBA Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Maths Chapters
- Quantitative Aptitude Prep Tips for MBA
- Maths Integrals
- Maths Differential Equations
- Maths Vector Algebra
- Maths Matrices
- Maths Determinants
- Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Maths Differentiation
- NCERT Class 12 Maths
- Maths Continuity and Differentiability
- Maths Applications of Derivatives
- Maths Application of Integrals
- Maths Linear Programming