
States of Matter is an important chapter in Class 11 NCERT chemistry. In this chapter students will learn about the three states of matter, Solid, Liquid and Gases. This chapter includes various properties of states of matter, the properties of changes when matter flows from one state to the other, type of bonding, melting and boiling points, role of gas laws in elucidating the concept of the molecule, intermolecular interactions.
Laws of matter combining forces like Boyle’s law, Charles’ law, Gay Lussac’s law, Avogadro’s law, ideal behavior, empirical derivation of gas equation, Avogadro’s number, ideal gas equation, deviation from ideal behavior, liquefaction of gases, critical temperature is also studied in the chapter, states of matter. We provide accurate solutions of NCERT Class 11 Chemistry chapters. Students can also refer to NCERT Solutions Chemistry class 12.
- Class 11 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Key Topics, and Weightage and Important Formulae
- State of Matter Solution
Class 11 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Key Topics, and Weightage and Important Formulae
Class 11 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Key Topics, and Weightage and Important Formulae
State of Matter Solution
| 5.1. What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 at 30°C? |
| Answer: Initial Pressure, P1 = 1 bar Final Pressure, P2 =? Initial Volume, V1= 500 dm3 Final Volume, V2=200 dm3 Or P2=500/200 bar =2.5 bar
= mRT/MV Replacing m/V by d (i.e. density), we get P = dRT/M P ∝ d Hence, at a given temperature, the density of a gas is directly proportional to its pressure. |
| 5.4. At 0°C, the density of a gaseous oxide at 2 bar is same as that of dinitrogen at 5 bar. What is the molecular mass of the oxide? |
| Answer: Using the expression, d =MP/RT, at 0°C Since, the same compound is under observation, so their densities will be same. Therefore, M1P1 = M2P2 Or P2 = 1.2 x 120 / 180 = 0.8 bar |
| 5.3. Using the equation of state PV= nRT, show that at a given temperature, density of a gas is proportional to the gas pressure P. |
| Answer: According to ideal gas equation Or P= nRT/V Replacing n by m/M, we get P M1 x 2 = 28 x 5(Molecular mass of N2 = 28 g/mol) |
Commonly asked questions
MCQs:
5.28. The average kinetic energy of the gas molecule is
(a) Inversely proportional to its absolute temperature
(b) Directly proportional to its absolute temperature
(c) Equal to the square of its absolute temperature
(d) All of the above
5.28. (b) directly proportional to its absolute temperature
5.29. At constant temperature, the pressure of the gas is reduced to one-third, the volume
(a) Reduce to one-third
(b) Increases by three times
(c) Remaining the same
(d) Cannot be predicted
5.29. (b) increases by three times
5.32. Which of the following gases will have the lowest rate of diffusion?
(a) H2
(b) N2
(c) F2
(d) O2
5.32. (c) F2
5.10. 34.05 mL of phosphorus vapour weighs 0.0625 g at 546°C and 1.0 bar pressure. What is the molar mass of phosphorus?
5.10. We know,
PV=nRT
n = PV/RT
n= (0.1 x34.05 x 10-3)/ (0.083 x 819)
= 5.01 x 10-5 mol
Hence, the atomic mass of phosphorus= 0.0625/ (5.01 x10-5)
= 1247.5 g/mol
5.30. With rise in temperature, the surface tension of a liquid
(a) Decreases
(b) Increases
(c) Remaining the same
(d) None of the above
5.30. (a) decreases
5.1. What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 at 30°C?
5.1. Initial Pressure, P1 = 1 bar Final Pressure, P2 =?
Initial Volume, V1= 500 dm3 Final Volume, V2=200 dm3
As the value of temperature constant (=30°C)
P1V1=P2V2
1 bar x 500 dm3 = P2 x 200 dm3
Or P2=500/200 bar
=2.5 bar
= mRT/MV
Replacing m/V by d (i.e. density), we get
P = dRT/M
P? d
Hence, at a given temperature, the density of a gas is directly proportional to its pressure.
5.42. State and explain Dalton’s law of partial pressures. Can we apply Dalton’s law of partial pressures to a mixture of carbon monoxide and oxygen?
5.42. Dalton's law of partial pressure: When two or more non-reacting gases are enclosed in a vessel, the total pressure of the gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures that each gas will exert when enclosed separately in the same vessel at constant temperature.
P= P1 + P2 + P3
Where, P is the total pressure of the three gases A, B, and C enclosed in a container. P1, P2 and P3 are the partial pressures of the three gases when enclosed separately in the same vessel at a given temperature one by one.
No, the law cannot be applied. Carbon monoxide and oxygen readily combine to form carbon dioxide. The law can be applied only to the non-reacting gases.
5.17. Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8 g of CO2 at 31.1 °C and 1 bar pressure. R = 0.083 bar LK-1 mol-1
5.17. No. of moles of CO2 = Given mass of CO2 / Molar mass
= 8.8g / 44g mol-1 = 0.2 mol
Pressure of CO2 = 1 bar
RR = 0.083 bar dm3 K–1 mol–1
T = 273 + 31.1 K = 304.1 K
According to ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
Therefore, V = nRT/P
= (0.2 x 0.083 x 304.1) / 1 bar = 5.048 L
5.13. Calculate the total number of electrons present in 1.4 g of dinitrogen gas.
5.13. Molecular mass of N2 = 28g
28 g of N2 has No. of molecules = 6.022 x 1023
1.4 g of N2 has No. of molecules = (6.022 x 1023 x 1.4 g)/28 g= 3.011 x 1022 molecules.
Atomic No. of Nitrogen (N) = 7
1 molecule of N2 has electrons = 7 x 2 = 14
3.011 x 1022 molecules of N2 have electrons= 14 x 3.011 x 1022= 4.215 x1023 electrons.
5.6. The drain cleaner, Drainex contains small bits of aluminium which react with caustic soda to produce dihydrogen. What volume of dihydrogen at 20 °C and one bar will be released when 0.15g of aluminium reacts?
5.6. The chemical equation for the reaction is
2 Al + 2 NaOH + H2O? 2 NaAlO2 + 3H2
i.e. 2 moles of Al give 3 moles of H2 gas.
Moles of aluminium = 270.15g = 5.56*10?3 moles
Moles of H2 produced= 23*5.56*10?3
= 8.33*10?3 moles
Volume of H2 = nRT / P
= 8.33*10?3 x 0.0831*293
= 0.203 litres
Therefore, volume of dihydrogen released is 0.203 litres.
5.37. What is the effect of temperature on (i) surface tension and (ii) Viscosity?
5.37. (i) Surface tension decreases with increase of temperature.
(ii) Viscosity decreases with increase of temperature.
5.39. Why liquids diffuse slowly as compared to gases?
5.39. In liquids, the molecules are more compact in comparison to gases.
5.40. (a) What do you mean by Surface Tension of a liquid?
(b) Explain the factors which can affect the surface tension of a liquid.
5.40. (a) Surface tension: It is defined as the force acting per unit length perpendicular to the line drawn on the surface.
(b) Surface tension of a liquid depends upon following factors.
(i) Temperature: Surface tension decreases with rise in temperature. As the temperature of the liquid increases the average kinetic energy of the molecules increases. Thus, there is a decrease in intermolecular force of attraction which decreases the surface tension.
(ii) Nature of the liquid: Greater the magnitude of intermolecular forces of attraction in the liquid, greater will be the value of surface tension.
5.18. 2.9 g of a gas at 95°C occupied the same volume as 0.184 g of hydrogen at 17°C at the same pressure. What is the molar mass of the gas?
5.18. Given, P1 = P2 and V1 = V2
We know that P1V1 = P2V2
Or, n1RT1 = n2RT2
i.e., n1T1 = n2T2
Substituting n = w/M, we get
(W1/M1) x T1 = (W2/M2) x T2
(2.9/M1) x (95 + 273) = (0.184/2) x (17 + 273)
M1 = (2.9 x 368 x 2) / (0.184 x 290) = 40 g mol-1
5.35. What is critical temperature?
5.35. When density of liquid and vapours becomes the same; the clear boundary between liquid and vapours disappears. This temperature is called critical temperature.
5.7. What will be the pressure exerted by a mixture of 3.2g of methane and 4.4g of carbon dioxide contained in a 9 dm3 flask at 27 °C?
5.7. Applying PV = nRT
We get P = nRT / V
Given: nCH4 = 3.2 / 16 mol = 0.2 mol
nCO2 = 4.4 /44 mol = 0.1 mol
So,
PCH4 = (0.2 mol) (0.0821 dm3atm K-1 mol-1) (300 K) / (9 dm3)
= 0.55 atm
PCO2= (0.1 mol) (0.0821 dm3atm K-1 mol-1) (300 K) / (9 dm3)
= 0.27 atm
Ptotal = PCH4 + PCO2 = 0.55 + 0.27
= 0.82 atm
= 8.314 x 104 Pa
Hence, the pressure exerted by a mixture is 8.314 x 104 Pa
5.12. Calculate the temperature of 4.0 moles of a gas occupying 5 dm3 at 3.32 bar (R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1).
5.12. Given,
P= 3.32 bar
V= 5 dm3
n= 4 mol
R= 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1
PV = nRT
Or T = PV / nR = 3.32 x 5 dm3 / (4.0 mol x 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1)
= 50 K
5.14. How much time would it take to distribute one Avogadro number of wheat grains if 1010 grains are distributed each second?
5.14. Time taken to distribute 1010 wheat grains = 1s
Time taken to distribute Avogadro number of wheat grains = (1s x 6.022 x 1023) / 1010
= 6.022 x 1013 s
= (6.022 x 1013 / 60 x 60 x 24 x 365) year
= 1.9 x 106 years
Assertion and Reason:
Directions:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
5.23. Assertion: The dipole-dipole interactionbetween two HCl moleculesis stronger than the London forces.
Reason: Only partial charges are involved
5.23. (a) The dipole-dipole interaction between two HCl molecules is stronger than the London forces but is weaker than ion-ion interaction because only partial charges are involved.
5.26. Assertion: Intermolecular interactions may hold the closely and slowly moving molecules together and thus the solid liquifies.
Reason: Compression brings the molecules in close vicinity and cooling slows down the movement of molecules.
5.26. (d) Compression brings the molecules in close vicinity and cooling slows down the movement of molecules therefore, intermolecular interactions may hold the closely and slowly moving molecules together and the gas liquifies.
5.19. A mixture of dihydrogen and dioxygen at one bar pressure contains 20% by weight of dihydrogen. Calculate the partial pressure of dihydrogen.
5.19. As the mixture H2 and O2 contains 20% by weight of dihydrogen, therefore,
If H2 = 20g, then O2 = 80g
No. of moles of H2 = 20/2 = 10 moles
No. of moles of O2 = 80/32 = 2.5 moles
Partial pressure of H2 = [No. of moles of H2/ (No. of moles of H2 + No. of moles of O2)] x
Ptotal= [10 (10 + 2.5)] x 1 = 0.8 bar
5.31. Viscosity of a liquid is a measure of
(a) Repulsive forces between the liquid molecules
(b) Frictional resistance
(c) Intermolecular forces between the molecules
(d) None of the above
5.31. (b) frictional resistance
5.15. Calculate the total pressure in a mixture of 8g of oxygen and 4g of hydrogen confined in a vessel of l dm3 at 27°C. R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1.
5.15. Molar mass of O2 = 32 g/mol
It means, 8 g of O2 has 8/32 mol = 0.25 mol
Molar mass of H2 = 2 g/mol
It means, 4 g of H2 has 4/2 mol = 2 mol
Therefore, total number of moles, n = 2 + 0.25 = 2.25 mol
Given, V = 1dm3, T = 27°C = 300 K, R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1
Applying PV = nRT,
P = nRT / V
= (2.25) (0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1) (300 K) / (1dm3)
= 56.025 bar
5.16. Pay load is defined as the difference between the mass of the displaced air and the mass of the balloon. Calculate the pay load when a balloon of radius 10 m, mass 100 kg is filled with helium at 1.66 bar at 27°C (Density of air = 1.2 kg m-3 and R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1).
5.16. Radius of the balloon = 10 m
Therefore, volume of the balloon = (4/3)? r3 = (4/3) x (22/7) x (10 m)3
= 4190.5 m3
Volume of He filled at 1.66 bar and 27 °C = 4290.5 m3
To calculate the mass of He,
PV = nRT = (w/M) RT, where M is molar mass of He i.e. 4 g per mole or 4 x 10-3 kg mol-1
=> w = [ (4 x 10-3 kg mol-1) (1.66 bar) (4190.5 m3)] / [ (0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1) (300K)]
= 1117.5 kg
Total mass of the balloon along with He = 100 + 1117.5 = 1217.5 kg
Maximum mass of the air that can be displaced by balloon to go up = volume x density
= 4190.5 m3 x 1.2 kg m-3 = 5028.6 kg
Hence, pay load = 5028.6 – 1217.5 kg = 3811.1 kg
5.3. Using the equation of state PV= nRT, show that at a given temperature, density of a gas is proportional to the gas pressure P.
Answer: According to ideal gas equation
PV = nRT
Or P= nRT/V
Replacing n by m/M, we get
P M1 x 2 = 28 x 5 (Molecular mass of N2 = 28 g/mol)
or M1 = 70 g/mol
5.8. What will be the pressure of the gas mixture when 0.5 L of H2 at 0.8 bar and 2.0 L of dioxygen at 0.7 bar are introduced in all vessel at 27 °C?
5.8. Calculation of partial pressure of H2 in 1L vessel:
P1= 0.8 bar, P2=? V1= 0.5 L, V2 = 1.0 L
As temperature remains constant, P1V1 = P2V2
=> (0.8 bar) (0.5 L) = P2 (1.0 L)
=>P2 = 0.40 bar, i.e., PH2 = 0.40 bar
Calculation of partial pressure of O2 in 1 L vessel
P1V1 = P2V2
(0.7 bar) (2.0 L) = P2 (1L)
=>P2 = 1.4 bar
=>Po2= 1.4 bar
Total pressure =PH2 + PQ2 = 0.4 bar + 1.4 bar = 1.8 bar
5.36. Define Avogadro law, Dalton’s law, Boyle’s law and Charles’ law.
5.36. Avogadro law states that equal volumes of all gases under same conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules.
Dalton's law of partial pressure states that total pressure exerted by a mixture of non-reacting gases is equal to the sum of partial pressures exerted by them.
Boyle's law states that under isothermal condition, pressure of a fixed amount of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
Charles' law is a relationship between volume and absolute temperature under isobaric condition. Itstates that volume of a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (V? T).
5.22. Critical temperature for CO2 and CH4 are 31.1°C and -81.9°C respectively. Which of these has stronger intermolecular forces and why?
5.22. Higher the critical temperature, more easily the gas can be liquefied, i.e., greater are the intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, CO2 has stronger intermolecular forces than CH4.
5.27. Assertion: At high altitudes, liquids boil at lower temperatures in comparison to that at sea level.
Reason: At high altitudes atmospheric pressure is high.
5.27. (c) At high altitudes atmospheric pressure is low. Therefore, liquids at high altitudes boil at lower temperatures in comparison to that at sea level. Since water boils at low temperature on hills, the pressure cooker is used for cooking food. In hospitals surgical instruments are sterilized in autoclaves in which boiling point of water is increased by increasing the pressure above the atmospheric pressure by using a weight covering the vent.
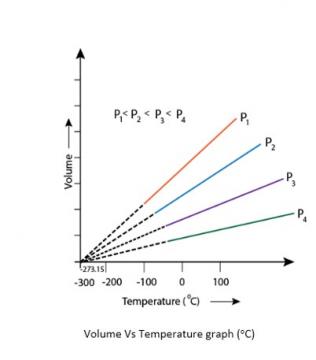
5.21. In terms of Charles’ law explain why -273°C is the lowest possible temperature.
5.21. At -273°C, volume of the gas becomes equal to zero, i.e., the gas ceases to exist.
5.24. Assertion: Viscosity of liquids decreases as the temperature rises.
Reason: Molecules of liquids are held together by attractive intermolecular forces.
5.24. (b) Viscosity of liquids decreases as the temperature rises because at high temperature molecules have high kinetic energy and can overcome the intermolecular forces to slip past one another between the layers.
5.25. Assertion: Liquids and solids are hard to compress.
Reason: Magnitude of the repulsion rises very rapidly as the distance separating the molecules decreases.
5.25. (a) Other than attractive forces, molecules also exert repulsive forces on one another. When two molecules are brought into close contact with each other, the repulsion between the electron clouds and that between the nuclei of two molecules comes into play. Magnitude of the repulsion rises very rapidly as the distance separating the molecules decreases. This is the reason that liquids and solids are hard to compress. In these states molecules are already in close contact; therefore, they resist further compression; as that would result in the increase of repulsive interactions.
5.34. Define boiling point of a liquid.
5.34. The temperature at which the vapour pressure of a liquid is equal to external pressure is called boiling point of liquid.
5.33. Liquids can assume the shape of the container. Explain how?
5.33. Molecules of liquids are held together byattractive intermolecular forces. Liquids havedefinite volume because molecules do notseparate from each other. However, moleculesof liquids can move past one another freely, therefore, liquids can flow, can be poured andcan assume the shape of the container in whichthese are stored.
5.38. What is Boyle Temperature?
5.38. The temperature at which a real gas obeys ideal gas law over an appreciable range of pressure, is called Boyle temperature or Boyle point.
5.41. What are ideal and real gases? Out of CO2 and NH3 gases, which is expected to show more deviation from the ideal gas behaviour.
5.41. Ideal Gas: A gas that follows Boyle's law, Charles' law and Avogadro law strictly, is called an ideal gas. It is assumed that intermolecular forces are not present between the molecules of an ideal gas.
Real Gases: Gases which deviate from ideal gas behaviour are known as real gases. NH3 is expected to show more deviation. Since NH3 is polar in nature and it can be liquified easily.
5.20. What would be the SI unit for the quantity PV2T2/n?
5.20. SI unit of pressure, P = Nm-2
SI unit of volume = m3
Si unit of temperature, T = K
SI unit of number of moles, n = mol
Thus, SI unit of pV2T2/n = (Nm-2) (m3)2 (K) 2mol = Nm4K2mol-1
5.5. Pressure of l g of an ideal gas A at 27°C is found to be 2 bar. When 2 g of another ideal gas B is introduced in the same flask at same temperature, the pressure becomes 3 bar. Find the relationship between their molecular masses.
5.5. Suppose molecular masses of A and B are MA and MB respectively. Then their number of moles will be
nA= 1/MA nB = 2/MB
Given: PA = 2 bar and PA + PB = 3 bar
=> PB = 1bar
Since, PV = nRT
PA= nART and PBV= nBRT
Therefore, (PA / PB) = (nA / nB)= (MB / 2MA)
=> MB / MA = 2 x PA / PB = 2 x 2 /1 = 4
=> MB = 4 MA
Explore exams which ask questions on Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 11th
Select your preferred stream
Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 11th Exam
Student Forum
Other Similar chapters for you
- NCERT Chemistry 11th
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Structure of Atoms
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Prop
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- States of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions
- Hydrogen
- The S-block Elements
- The p -Block Elements
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Tech
- Hydrocarbons
- Environmental chemistry
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test
