Hydrocarbons Class 11th NCERT Solutions cover the compounds of carbon and hydrogen. The common fuels used, such as LPG and CNG are all part of the hydrocarbons. It is extremely useful in our daily lives. LPG, CNG, petrol, diesel, all these fuels contain a mixture of hydrocarbons. The applications of the hydrocarbons are also found in the manufacture of polymers like polypropene, polythene, polystyrene etc.
Hydrocarbons NCERT Solutions are given in a step-by-step format, and they cover all the NCERT textbook questions of this chapter. The key topics covered in this chapter include Alkanes, Alkenes, and Alkynes. Students should thoroughly read the main topics to get good marks in the school exam, CBSE Board, and other competitive exams like JEE Main and NEET. The NCERT solutions given here are accurate and reliable. After studying this chapter, the students will know how to write structures of isomers of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons, and also about various methods of preparation of hydrocarbons.
The chapter-wise chemistry NCERT notes of Class 11 are given here with solved examples, important topics, and free PDFs of all the chapters.
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrocarbons: Key Topics and Important Reactions
- Class 11 Hydrocarbons NCERT Solutions – Chapter 9 Chemistry PDF Free
- Topics Covered in Hydrocarbon Chapter
- Hydrocarbons Solutions
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrocarbons: Key Topics and Important Reactions
In the Hydrocarbons Class 11th NCERT solutions, students must focus on understanding the different types of hydrocarbons, isomerism, reactions, aromatic hydrocarbons, general methods of preparation, the petroleum refining, and environmental impact. Here are the topics covered in this chapter:
| Exercise | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| 9.1 | Classification |
| 9.2 | Alkanes |
| 9.3 | Alkenes |
| 9.4 | Alkynes |
| 9.5 | Aromatic Hydrocarbon |
| 9.6 | Carcinogenicity and toxicity |
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrocarbons Weightage in NEET and JEE Mains
| Exam | Number of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| NEET | 2-3 questions | 3-6% |
| JEE Main | 2 questions | 3.3% |
Important Reactions in Class 11 Chemistry Hydrocarbons
-
Important Reactions of Alkanes
-
- Halogenation; Free Radical Substitution (In the presence of sunlight)
- Wurtz Reaction; Preparation of Alkanes (Dry ether)
- 1.3 Decarboxylation Reaction; (Soda-lime formation)
-
Important Reactions of Alkenes
- Hydrogenation; Addition of H₂ (Ni, Pt, or Pd catalyst)
- Addition of Halogens; (Brown color of Br₂ disappears)
- Addition of HX; H⁺ adds to carbon with more H’s (Markovnikov’s Rule)
- Anti-Markovnikov’s Rule (Peroxide Effect)
- Oxidation; Cold alkaline KMnO₄, purple color disappears (Baeyer’s Test)
-
Important Reactions of Alkynes
- Hydrogenation; First alkene forms, then alkane
- Addition of Halogens
- Oxidation
- Important Reactions of Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Benzene)
- Halogenation; (AlCl₃ Catalyst)
- Nitration; (H₂SO₄ Catalyst)
- Friedel-Crafts Alkylation; (AlCl₃ Catalyst)
- Friedel-Crafts Acylation; (AlCl₃ Catalyst)
As per the CBSE 2025 syllabus, no topic has been added or deleted from this chapter.
Class 11 Hydrocarbons NCERT Solutions – Chapter 9 Chemistry PDF Free
The link to the free Hydrocarbons NCERT PDF is given below. It provides a reliable study material for Class 11 exams, CBSE Board, and entrance tests like NEET and JEE Mains. The study material is ideal for various exam preparations.
Class 11 Chapter 9 Hydrocarbon NCERT Solution PDF: Free Download PDF
For last-minute preparation, students can get the quick revision notes of Class 11 Physics, Chemistry, and Maths here.
Topics Covered in Hydrocarbon Chapter
Students can check below the list of all the topics that are covered in the Hydrocarbon chapter of NCERT class 11 Chemistry.
- Classification
- Alkanes
- Nomenclature and Isomerism
- Preparation
- Properties
- Conformations
- Alkenes
- Structure of Double Bond
- Nomenclature
- Isomerism
- Preparation
- Properties
- Alkynes
- Nomenclature and Isomerism
- Structure of Triple Bond
- Preparation
- Properties
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon
- Nomenclature and Isomerism
- Structure of Benzene
- Aromaticity
- Preparation of Benzene
- Properties
- Directive Influence of a Functional Group in Monosubstituted Benzene
- Carcinogenicity and Toxicity
Hydrocarbons Solutions
The Hydrocarbons class 11 NCERT solutions are provided below. Students can solve the question with answers for exam preparation.
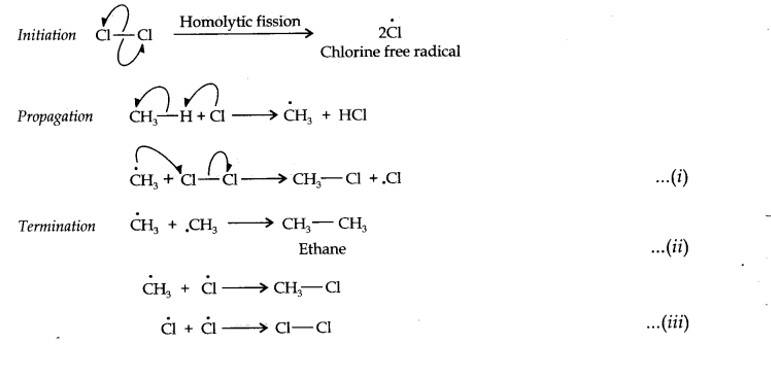
| 13.1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? |
| Answer: Chlorination of methane is a free radical reaction which occurs by the following mechanism involving initiation, propagation and termination steps: |
| 13.2. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
|
| Answer: (a) 2-Methykbuut-2-ene (b) Pent-1-ene-3-yne (c) But-1,3-diene (d) 4-Phenylbut-1-ene (e) 2-Methyl phenol (f) 5-(2-Methylpropyl)decane (g) 4-Ethyldeca-1,5,8-triene |
| 13.3. For the following compounds, write structural formulas and IUPAC names for all possible isomers having the number of double or triple bond as indicated: (a) C4H8 (one double bond) (b) C5H8 (one triple bond) |
| Answer: (a) Isomers of C4H8 having one double bond are: |
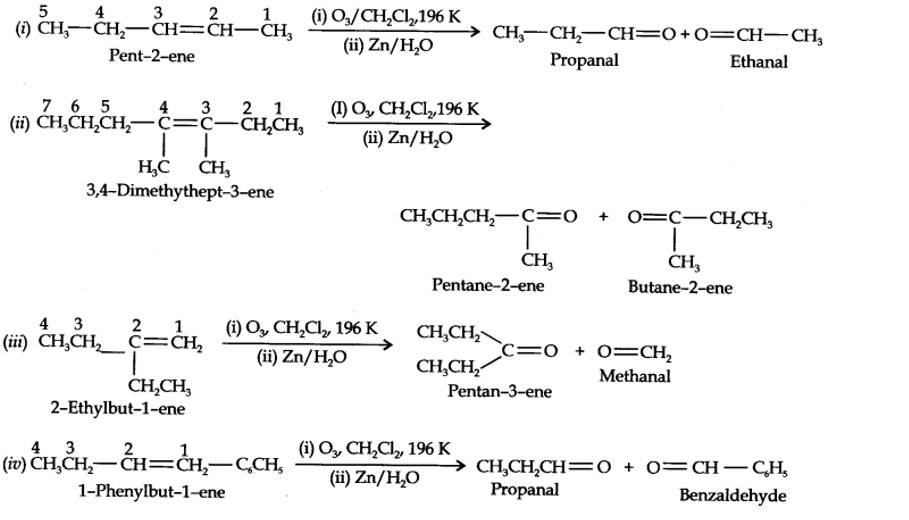
| 13.4. Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds: (i) Pent-2-ene (ii) 3, 4-Dimethylhept-3-ene (iii) 2-Ethylbut-l-ene (iv) 1-Phenylbut-l-ene. |
| Answer:
|
Commonly asked questions
14.40. Cite examples where green chemistry can be applied.
Green chemistry can be applied as mentioned in the following examples:
(i) In dry-cleaning, use of liquefied CO2 in place of tetrachloroethene.
(ii) In bleaching of paper using hydrogen peroxide instead of chlorine.
(iii) In the manufacture of chemicals like ethanal using environment-friendly chemicals and conditions.
13.15. What effect does branching of an alkane chain has on its boiling point?
Branching of carbon atom chain decreases the boiling point of alkane.
14.34. Read the following statements carefully. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) Besides carbon dioxide, other greenhouse gases are methane, water vapour, nitrous oxide, CFCs and ozone.
(b) Methane is produced naturally when vegetation is burnt, digested or rotted in the absence of oxygen.
(c) Large amounts of methane are released in paddy fields, coal mines, from rotting garbage dumps and by fossil fuels.
(d) Methane are man-made industrial chemicals used in air conditioning etc
(d) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are man-made industrial chemicals used in air conditioning etc.
13.6. An alkene ‘A’ contains three C – C, eight C – H σ bonds and one C – C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Write IUPAC name of ‘A’.
(i) An aldehyde with molar mass of 44 u is ethanal, CH3CH=0
(ii) Write two moles of ethanal side by side with their oxygen atoms pointing towards each other.
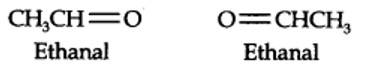
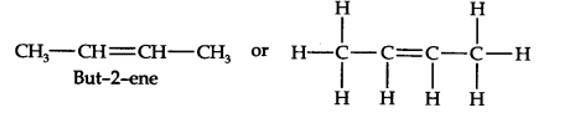
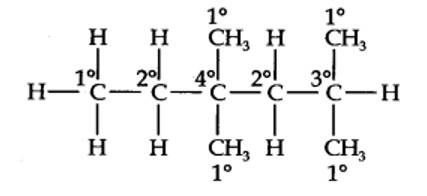
13.14. In the alkane, H3C—CH2—C(CH3)2—CH2—CH(CH3)2, identify 1°, 2°, 3° carbon atoms and give the number of H atoms bonded to each one of these.
The expanded formula of the given compound is
13.1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
Chlorination of methane is a free radical reaction which occurs by the following mechanism involving initiation, propagation and termination steps:
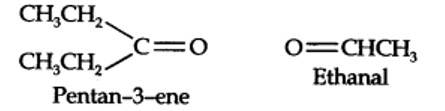
13.5. An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write structure and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Step 1. Write the structure of the products side by side with their oxygen atoms pointing towards each other.
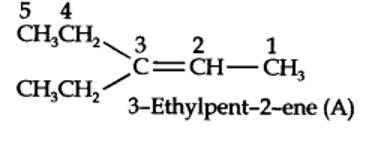
13.9. Draw the cis and trans structures for hex-2-ene. Which isomer will have higher b.p. and why?
The structures of cis- and trans-isomer of hex-2-ene are:
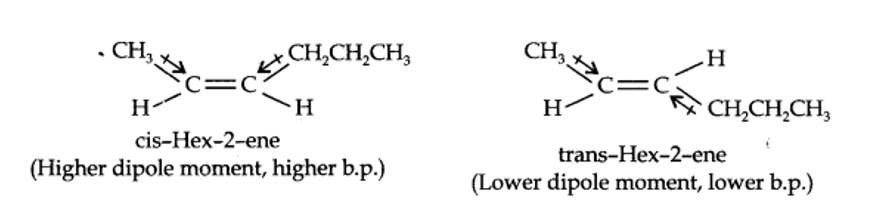
The boiling point of a molecule depends upon dipole-dipole interactions. Since cis-isomer has higher dipole moment, therefore, it has higher boiling point.
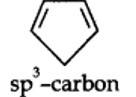
13.12. Explain why the following systems are not aromatic?
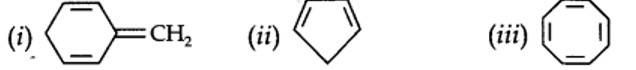
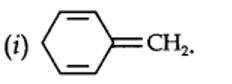
planar. It does contain six n-electrons but the system is not fully conjugated since all the six n-electrons do not form a single cyclic electron cloud which surrounds all the atoms of the ring. Therefore, it is not an aromatic compound.
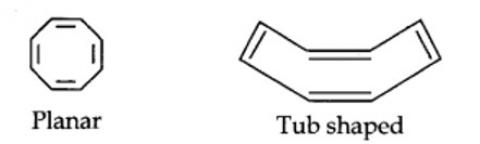
Cyclo-octatetraene is not planar but is tub shaped. It is, therefore, a non-planar system having 8 n-electrons.
Therefore, the molecule is not aromatic since it does not contain a planar cyclic cloud having (4n + 2) n-electrons.
13.17. Write down the products of ozonolysis ofl, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekule structure of benzene?
o-Xylene may be regarded as a resonance hybrid of the following two Kekule structures. Ozonolysis of each one of these gives two products as shown below:
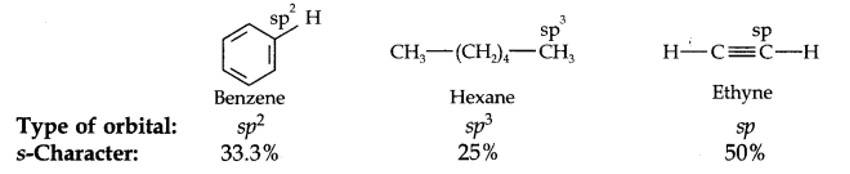
13.18. Arrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason for this behaviour.
The hybridization state of carbon in these three compounds is:
13.21. Write structures of all the alkenes which on hydrogeneration give 2-methylbutane.
The basic skeleton structure of 2-methylbutane is
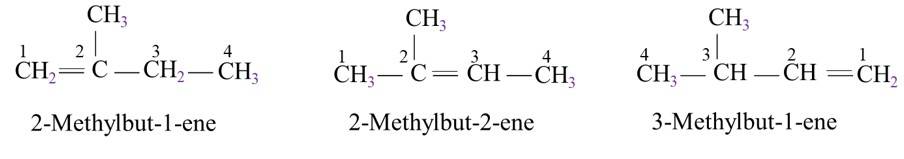
13.22. Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+.
(a) Chlorobenzene, 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene, p-nitrochlorobenzene
(b) Toluene,p—H3C—C6H4—NO2, p—O2N—C6H4—NO2.
(a) The typical reactions of benzene are electrophilic substitution reactions. Higher the electron-density in the benzene ring, more reactive is the compound towards thesereactions. Since NO2 is a more powerful electron-withdrawing group than Cl, therefore, more the number of nitro groups, less reactive is the compound. Thus, the overall reactivity decreases in the order:Chlorobenzene > p-nitrochlorobenzene > 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene
(b) Here, CH3 group is electron donating but NO2 group is electron-withdrawing. Therefore, the maximum electron-density will be in toluene, followed by p-nitrotoluene followed by p-dinitrobenzene. Thus, the overall reactivity decreases in the order:Toluene >p—H3C—C6H4—NO2>p—O2N—C6H4—NO2.
13.23. Out of benzene, m-dinitrobenzene and toluene which will undergo nitration most easily and why?
CH3 group is electron-donating while -NO2 group is electron-withdrawing. Therefore, maximum electron density will be in toluene, followed by benzene and least in m-dinitrobenzene. Therefore, the ease of nitration decreases in the order: toluene > benzene > m-dinitrobenzene.
MCQs
14.31 . Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) The atmosphere that surrounds the earth isnot of the same thickness at all heights.
(b) The lowest regionof atmosphere in which the human beingsalong with other organisms live is calledtroposphere.
(c) Below the troposphere,between 10 and 50 km above sea level lies stratosphere.
(d) Troposphere is a turbulent,
dusty zone containing air, much water vapour
and clouds.
(c) Stratosphere is above the troposphere.
14.42. List out the gases which are considered as major source of air pollution.
Carbon monoxide (CO), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and oxides of nitrogen (NO2).
14.44. What should be the tolerable limit of F ions in drinking water?
1 ppm or 1 mg dm-3.
14.45. Define (a) eutrophication (b) pneumoconiosis (c) Photochemical smog (d) Classical smog
(a) Eutrophication: When the growth of algae increases in the surface of water, dissolved oxygen in water is reduced. This phenomenon is known as eutrophication. (Due to this growth of fish gets inhibited). (b) Pneumoconiosis: It is a disease which irritates lungs. It causes scarring or fibrosis of the lung. (c) Photochemical smog: Photochemical smog is formed as a result of photochemical decomposition of nitrogen dioxide and chemical reactions involving hydrocarbons. It takes place during dry warm season in presence of sunlight. It is oxidising in nature. (d) Classical smog: Classical smog is formed due to condensation of SO, vapours on particles of carbon in cold climate. It is generally formed during winter when there is severe cold.It is reducing in nature. |
13.2. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
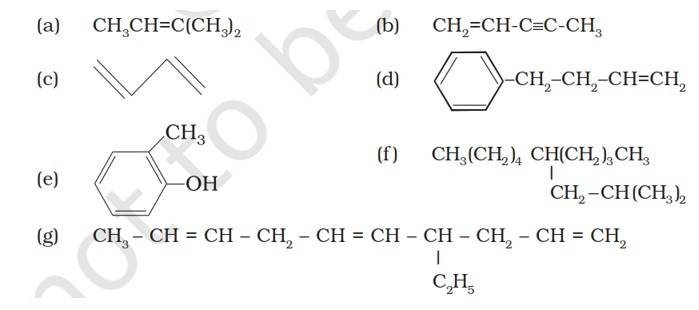
(a) 2-Methykbuut-2-ene
(b) Pent-1-ene-3-yne
(c) But-1,3-diene
(d) 4-Phenylbut-1-ene
(e) 2-Methyl phenol (f) 5- (2-Methylpropyl)decane
(g) 4-Ethyldeca-1,5,8-triene
13.3. For the following compounds, write structural formulas and IUPAC names for all possible isomers having the number of double or triple bond as indicated:
(a) C4H8 (one double bond) (b) C5H8 (one triple bond)
(a) Isomers of C4H8 having one double bond are:
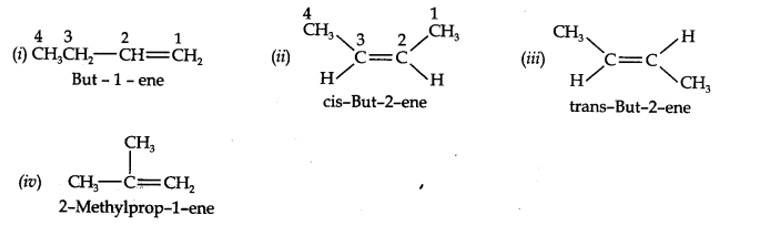
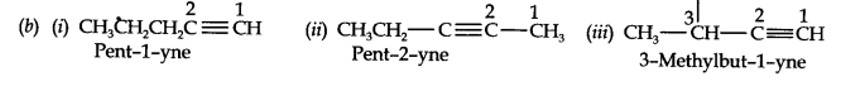
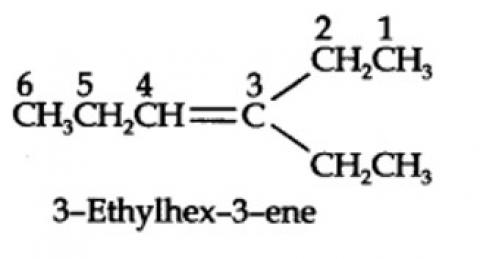
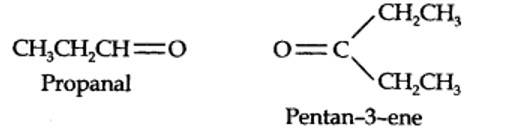
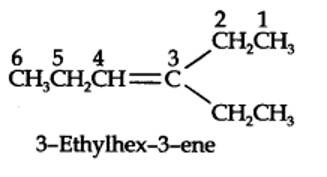
13.7. Propanal and pentan-3-one are the ozonolysis products of an alkene. What is the structural formula of the alkene?
The ozonolysis of 4-Ethylhex-3-ene gives propanal and pentan-3-one.
The structural formula of the alkene (4-Ethylhex-3-ene) is as shown.
13.8. Write chemical equations for the combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbons:
(i) Butane (ii) Pentene
(iii) Hexyne (iv) Toluene
A combustion reaction is a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas, there is a formation of carbon dioxide, water with the evolution of light and heat.
(i) 2C4H10 (g) +13 O2 (g)?8CO2 (g)+10H2O (g) + Heat
(ii) 2C5H10 (g) +15 O2 (g)?10CO2 (g)+10H2O (g) + Heat
(iii) 2C6H10 (g) +17 O2 (g)?12CO2 (g)+10H2O (g) + Heat
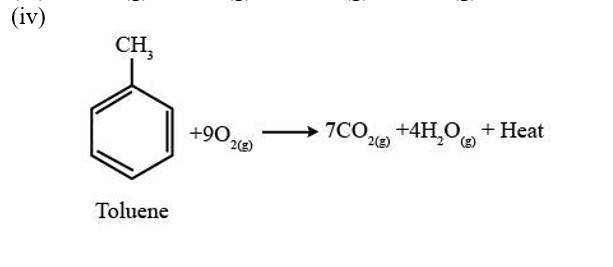
13.10. Why is benzene extraordinarily stable though it contains three double bonds?
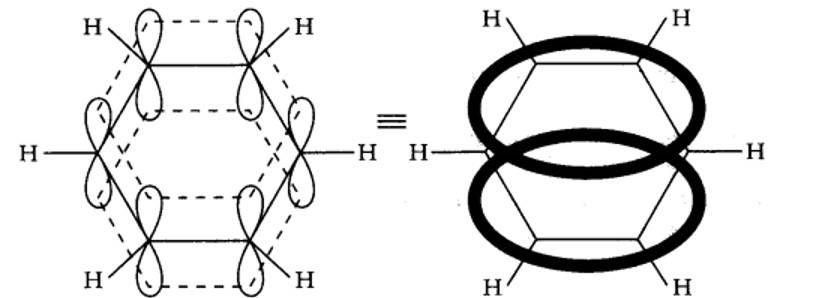
Benzene is a resonance hybrid of two canonical forms. In the resonance hybrid, all the six pi electrons are completely delocalized. This results in resonance stabilization.
13.11. What are the necessary conditions for any system to be aromatic?
The necessary conditions for a molecule to be aromatic are:
- It should have a single cyclic cloud of delocalised n-electrons above and below the plane of the molecule.
- It should be planar. This is because complete delocalization of n-electrons is possible only if the ring is planar to allow cyclic overlap of p-orbitals.
- It should contain Huckel number of electrons, i.e., (4n + 2) n-electrons where n = 0, 1, 2, 3 etc.
A molecule which does not satisfy any one or more of the above conditions is said to be non-aromatic.
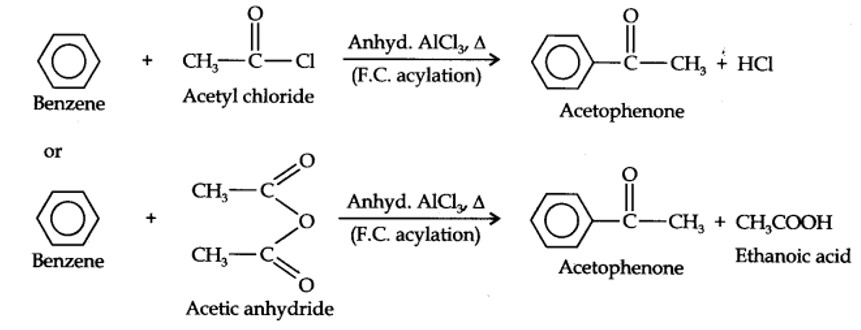
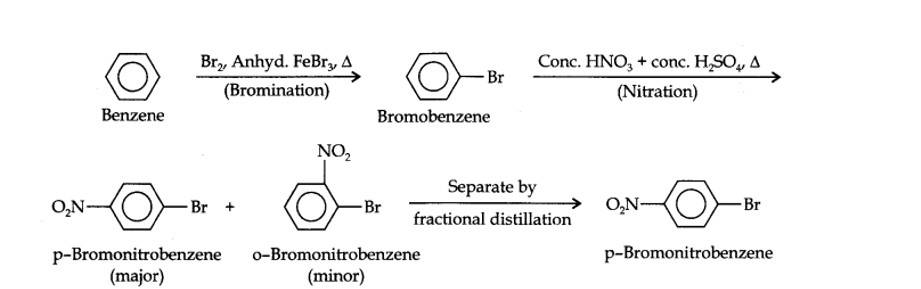
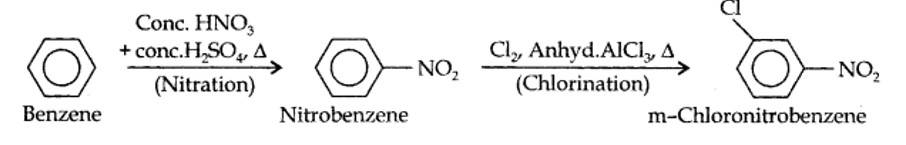
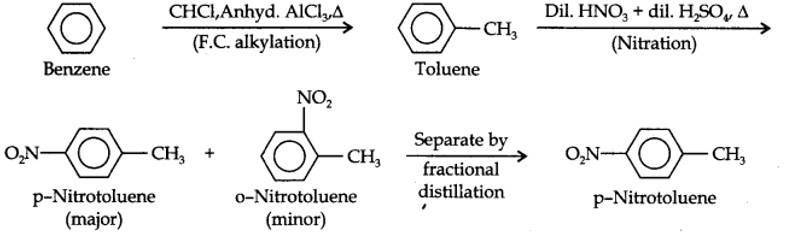
13.13. How will you convert benzene into (i)p-nitrobromobenzene (ii) m-nitrochlorobenzene (iii) p-nitrotoluene (iv) acetophenone?
(i) The two substituents in the benzene ring are present at p-positions. Therefore, the sequence of reactions should be such that first an o, p-directing group, i.e., Br atom should be introduced in the benzene ring and this should be followed by nitration. Thus,
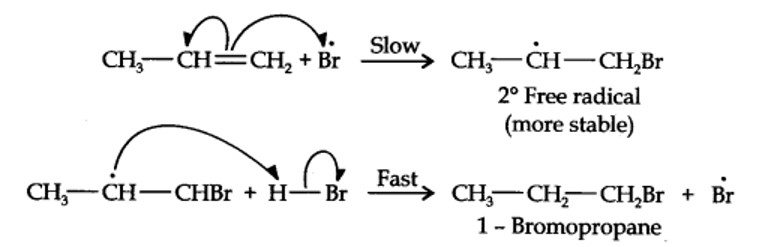
13.16. Addition of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane, while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanism.
Addition of HBr to propene is an ionic electrophilic addition reaction in which the electrophile, i.e., H+ first adds to give a more stable 2° carbocation. In the 2nd step, the carbocation is rapidly attacked by the nucleophile Br~ ion to give 2-bromopropane.
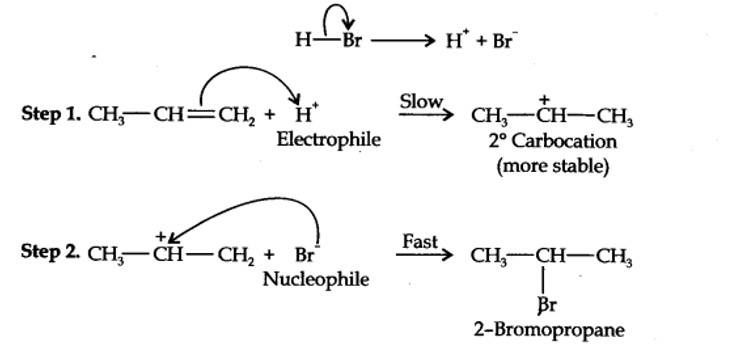
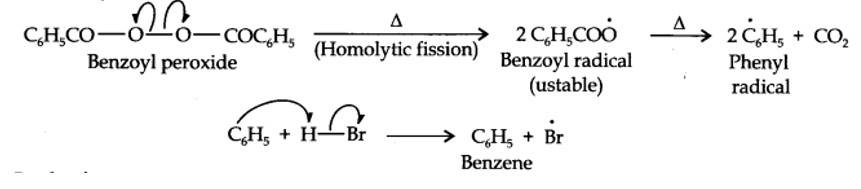
Even though both the reactions are electrophilic addition in nature, they yield different products because of different order of addition of H and Br atoms.
13.19. Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty?
Benzene is a rich source of electrons because of the presence of an electron cloud containing 6 n-electrons above and below the plane of the ring. Consequently, it attracts the electrophiles (electron-deficient) reagents towards it and repels nucleophiles (electron- rich) reagents. As a result, benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty.
13.24. Suggest the name of a Lewis acid other than anhydrous aluminium chloride which can be used during ethylation of benzene.
Anhydrous Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) is another Lewis acid which can be used during ethylation of benzene.
13.25. Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer by taking one example.
Alkyl halides on treatment with sodium metal in dry ethereal (free from moisture) solution give higher alkanes. This reaction is known as Wurtz reaction and is used for the preparation of higher alkanes containing even number of carbon atoms.
For preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms, a mixture of two alkyl halides has to be used. Since two alkyl halides can react in three different ways, therefore, a mixture of three alkanes instead of the desired alkane would be formed. For example, Wurtz reaction between 1-bromopropane and 1-bromobutane gives a mixture of three alkanes i.e., hexane, heptane and octane as shown below:
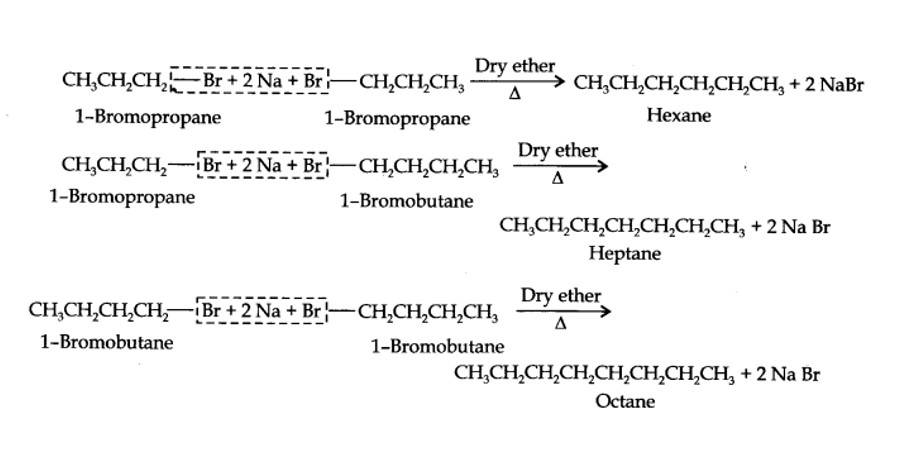
14.27 Assertion: CO is a colourless and odourless gas, highly poisonous to living beings.
Reason: It is produced as a result of incomplete combustion of carbon and is mainly released into the air by automobile exhaust.
(b) CO is highly poisonous to living beings because of its ability to block the delivery of oxygen to the organs and tissues.
14.28 Assertion: Tetra chlroroethene was earlier used as solvent for dry cleaning, which now a days are discontinued.
Reason: Chlorine gas was used earlier for bleaching
(b) The compound contaminates the ground water and is also a suspected carcinogen.
14.32 The main constituents of air are
(a) N2 and O2 (b) SO2 and CO2 (c) CO and CO2 (d) none of the above
(a) N2 and O2
14.33 The pollutant responsible for Bhopal gas tragedy was
(a) Ammonia (b) Methyl isocyanate (c) Nitrous oxide (d) Mustard gas
(b) Methyl isocyanate
14.35. Photochemical smog occurs in
(a) Warm, dry and sunny climate (b) cool (c) humid (d) none of the above.
(a) warm, dry and sunny climate.
14.37. BOD is a measure of
Organic pollutants in water
14.39. What is the full form of PCBs and what are they?
PCBs are polychlorinated biphenyls. They are contaminants of water. They are used as fluids in transformers and capacitors
14.41. What is siltation?
Mixing of soil or rock particles in water is called siltation.
14.43. What are insecticides? Give examples of insecticides.
Toxic substance that is used to kill insects are called insecticides. For example: DDT, BHC.
13.4. Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds:
(i) Pent-2-ene (ii) 3, 4-Dimethylhept-3-ene (iii) 2-Ethylbut-l-ene (iv) 1-Phenylbut-l-ene.
Kindly go through the solution
13.20. How would you convert the following compounds into benzene?
(i) Ethyne (ii) Ethene (iii) Hexane.
Kindly go through the solution
13.26. Assertion: Out of staggered and the eclipsed conformations of ethane, staggered conformation is more stable.
Reason: Hydrogen atoms are farthest apart in staggered conformation.
Kindly go through the solution
(a)
Explore exams which ask questions on Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 11th
Select your preferred stream
Chemistry Ncert Solutions Class 11th Exam
Student Forum
Other Similar chapters for you
- NCERT Chemistry 11th
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Structure of Atoms
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Prop
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- States of Matter
- Thermodynamics
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions
- Hydrogen
- The S-block Elements
- The p -Block Elements
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Tech
- Hydrocarbons
- Environmental chemistry
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test