Auxiliaries are verbs that are used along with the main verb in sentences to express voice, tense, mood, aspect or modality in English. They are also known as auxiliary verbs or helping verbs. Auxiliaries help add grammatical meaning to a sentence. The commonly used auxiliary verbs are be, have and do. These are used to form continuous tenses, perfect tenses, and questions or negatives, respectively.
In addition to these, modal auxiliaries like can, may, must, shall, and will express possibility, necessity, and permission. Auxiliaries are very important in construction of sentences as they bring clarity, especially in forming questions, passives, negatives, and various verb tenses.
Examples of Auxiliaries:
- He is writing a poem.
- Did you call him?
- I do not like tea.
- The job was completed.
- I have finished his homework.
- What are Auxiliaries in English?
- Auxiliaries Definition
- Types of Auxiliaries with Examples in English Grammar
- Rules of Auxiliaries in English
- Auxiliaries used in English - Special Cases and Exceptions
- Auxiliaries vs Verbs?
- Preparation Tips to Master Auxiliaries
- Auxiliaries - Common Errors to Avoid
- Importance of Auxiliaries in Competitive Exams
- Best Books for Auxiliaries in English
- Examples of Auxiliaries
- Auxiliaries - Practice Exercises with Answers
- FAQs on Auxiliaries
What are Auxiliaries in English?
Auxiliaries are helping verbs that are used along with main verbs to form various moods, tenses, voices, or to express necessity, possibility, ability and more. They are essential for constructing questions, compound tenses, negatives, and passive forms. Auxiliaries are two types. Primary auxiliaries (be, have and do) that are used to form continuous and perfect tenses, questions and negatives and Modal auxiliaries such as can, should, must, may, and will express the speaker’s attitude and intention.
Auxiliaries are essential in shaping the grammatical structure of a sentence.
For example:
- She is reading a poem. (In this sentence, the auxiliary ‘is’ helps form the present continuous tense.)
- You should work hard. (Gives advice)
- He can slide. (Shows ability)
Also Read:
Auxiliaries Definition
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, an auxiliary verb is defined as, “A verb used in forming the tenses, moods and voices of other verbs.”
This means auxiliary verbs do not stand alone but assist the main verb to express different grammatical functions such as time (tense), possibility (mood), passive/active voice.
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, “A verb that is used with another verb to form tensions, questions, negatives and other grammatical structures.”
Here are a few examples of auxiliaries:
- She is working late today.
- You have finished your task.
- Can you drive?
- She is
Auxiliaries pronunciation: awg-zil-yuh-reez
Also read:
Types of Auxiliaries with Examples in English Grammar
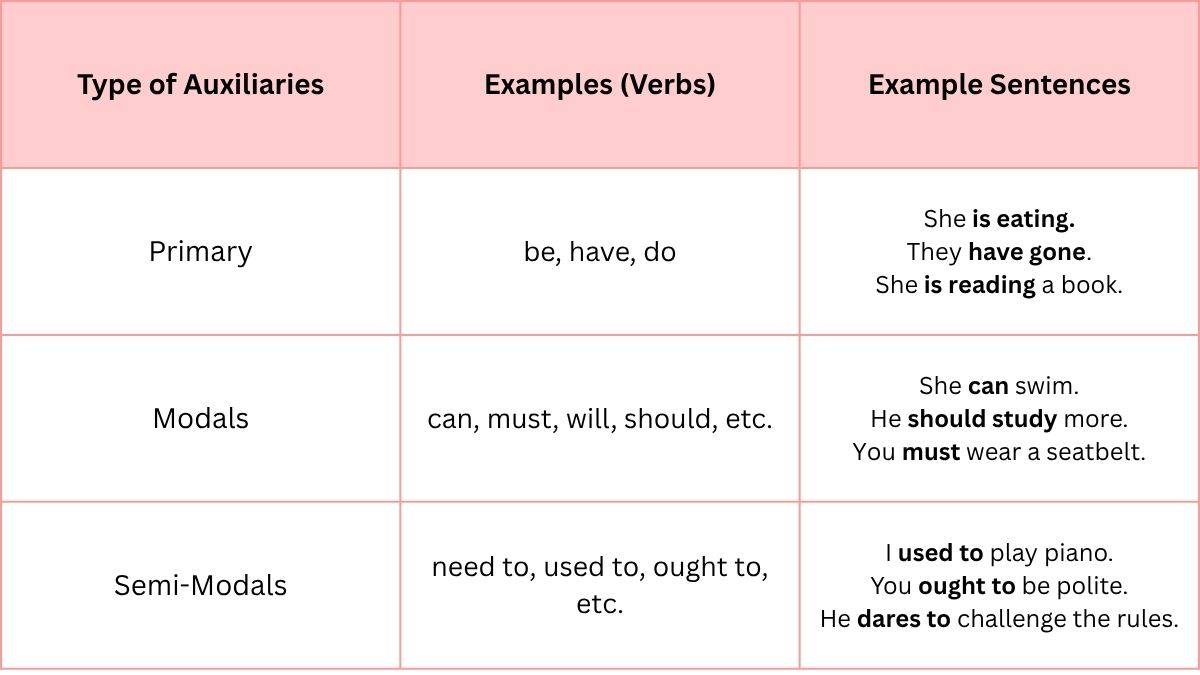
In English grammar, Auxiliaries are used to express mood, voice, tense, or aspect with main verb. There are three types of auxiliaries. Let’s know about them in detail below:
1. Primary Auxiliaries
Primary auxiliaries are the verbs such as be, have and do, which help form different tenses, voices and questions in English. They are known as the primary auxiliary because they perform the most basic grammatical functions in combination with main verbs.
These auxiliaries can also function as main verbs on their own such as in ‘I have a car.’ Or ‘He is a teacher.’
For example:
- Be (am, is, are, was, were, being, been)
- She is reading a book. (present continuous tense)
- The work was done by him. (passive voice)
- Have (have, has, had, having)
- They have finished their homework. (present perfect tense)
- I had seen that movie. (past perfect)
- Do (do, does, did)
- Do you like pizza? (question)
- I did not go to the party. (negative)
Also Read:
Interrogative Sentences
Exclamatory Sentences
2. Modal Auxiliaries
Modal auxiliaries, or modal verbs are helping verbs that express a speaker’s attitude or the necessity, possibility, possession, or ability related to the main verb. Common modals include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will and would. Modals are always followed by the base form of the main verb.
For example:
- It might rain tomorrow. (possibility)
- She must wear a seatbelt. (necessity)
- He can (ability)
3. Semi-Modals (Marginal Modals)
Semi-modals are verbs or phrases that work like modal auxiliaries but slightly differ in usage and form. They can sometimes take different forms and follow standard verb rules. Common semi-modals include need to, ought to, have to, used to and dare.
Examples:
- You ought to
- You need to finish your job.
- I used to play guitar.
- She dares to challenge the rules.
Also Read:
Rules of Auxiliaries in English
Auxiliary verbs, also known as helping verbs, follow specific rules in English grammar.. For example, in continuous tenses, forms of ‘be’ are used with the present participle (She is running), while on perfect tenses, forms of ‘have’ are followed by past participle (He has eaten).
Also Read: Forms of Verbs
For forming negatives or questions, ‘do/does/did’ is used when there is no other auxiliary (Did you go?, I do not know). Modal auxiliaries like can, will, must, should are always followed by the base form of the main verb without ‘to’ (e.g. She can swim, not She can to swim).
Additionally, auxiliaries agree with the subject in number and tense (e.g. He is working, They are working). They do not take an –s or –ed ending themselves in the present or past simple forms.
Auxiliaries used in English - Special Cases and Exceptions
While auxiliary verbs generally follow standard rules, there are several special cases and exceptions. Let’s read about them below:
1. ‘Do’ as an auxiliary in affirmative sentences (for emphasis)
Using ‘do’ in affirmative sentences is a special case, as auxiliaries typically appear in questions or negatives. Here, ‘do/does/did’ add emphasis, like ‘She does work hard.’This is an exception to the usual rule, where auxiliaries aren’t needed in positive declarative sentences.
Example:
- I do like your idea!
- She did finish her work on time.
2. Omission of auxiliaries in informal speech
In informal speech, auxiliaries are sometime omitted, especially in casual questions like ‘You coming?’ instead of ‘Are you coming?’ This is a special case where grammar rules are relaxed. It is an exception to standard usage, acceptable only in conversational contexts.
For example:
Incorrect: You coming with us?
Correct: Are you coming with us?
Incorrect: She not here yet?
Correct: Is she not here yet?
3. Semi-modals acting like modals
Semi modals like ‘need’, ‘dare’, ‘used to’ and ‘ought to’ sometimes act like modals, taking no –s in third person and using the base verb. This is a special case because they mix features of main verbs and modals. It’s an exception when they behave fully like modals in formal or old-fashioned usage.
For example:
- You needn’t (modal-like use)
- You need to (main verb use)
- He dare not (formal)
- He dares to (less formal)
4. Double auxiliaries in complex tenses
In complex tenses, two auxiliaries can appear together, like in ‘She may have gone.’ This is a special case where one auxiliary shows tense or mood (may), or the other shows aspect or voice (have). It’s an exception to simple structures, but necessary for expressing layerd meanings.
For example:
- She must have been working all night.
- The documents should have been delivered by now.
Auxiliaries vs Verbs?
Verbs are words that show action, state or occurrence. They are a main part of a sentence and tell what the subject is doing or experiencing.
Auxiliary verbs, also called helping verbs, are used along with main verbs to form tenses, questions, negatives, voices and moods.
Difference Between Auxiliaries and Verbs
Students can understand the differences clearly from the table below:
| Feature |
Auxiliary verbs |
Main verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose |
Help express grammar (tense, mood, etc) |
Show main action or state |
| Standalone use |
Rarely used alone |
Can stand alone |
| Common forms |
Is, are, was, have, do, can, must, should |
Run, eat, write, sleep, dance |
| Used with another verb? |
Yes |
Often used alone |
| Forms questions/negatives? |
Yes (e.g Do you…?) |
Needs auxiliary for that |
Examples of Auxiliary and Verbs Compared
| Sentence |
Explanation |
|---|---|
| He runs every morning. |
‘runs’ is the main verb |
| He is running now. |
‘is’ is auxiliary, ‘running’ is main verb |
| They do not agree. |
‘do’ is auxiliary, ‘agree’ is main |
| They do yoga. |
‘do’ is the main verb (full meaning) |
Preparation Tips to Master Auxiliaries
To master auxiliaries in English, students must begin by understanding their basic types- primary and modal auxiliaries. They must learn how each type functions in performing tenses, questions, negatives, passives and modal expressions.
It is important to practice forming different tenses using auxiliary verbs with main verbs, and pay attention to subject-verb agreement. Reading and listening to English will help them observe how auxiliaries are naturally used in conversations and writing. They must also practice rewriting sentences in various tenses and voices to reinforce their understanding.
Students are also advised to practice error-correction exercises and take quizzes. Consistent practice and exposure will help build your confidence and accuracy with auxiliaries.
Also Read:
Auxiliaries - Common Errors to Avoid
Importance of Auxiliaries in Competitive Exams
Best Books for Auxiliaries in English
Examples of Auxiliaries
Auxiliaries - Practice Exercises with Answers
FAQs on Auxiliaries
English Grammar Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds