
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is an important chapter of English Grammar, especially Tenses. It is not just a crucial chapter of your English syllabus, but also plays an important role in your verbal and written communication. Present Perfect Continuous Tense is something which we use in our daily lives during conversation, be it formal or informal, as well as in written communication, or writing assignments, exams, email, etc.
The fundamental concept of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is to describe an action that began in the past and is still being continued, or has stopped recently and has a result at the present. This is a type of Present Tense which emphasises the action along with its duration and continuity. Some examples of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense are given below:
- I have been suffering from fever for the past two days.
- It has been raining since morning.
- I have been working in this company since its inception.
- I have been constantly calling Rohan, but he is not listening to me.
- What is Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Definition of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Types of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Grammar Rules of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Vs Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Vs Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Preparation Tips to Master Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Common Errors to Avoid in Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Best Books to Prepare for Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Engaging Practice Exercises for Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- FAQs Regarding Present Perfect Continuous Tense
What is Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense signifies an ongoing action and at times it also describes the result or impact. The structure or the formula of forming a sentence in this tense is given below:
Subject + have/has been + present participle (verb+ing) + sentence conclusion.
Also Read:
Definition of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
According to the Oxford Dictionary, the definition of Present Perfect Continuous Tense is, “the form of a Verb that expresses an action done in a time period up to the present, formed in English with the present tense of have and the past participle of the verb, as in I have eaten.”
As per the Collins Dictionary, Present Perfect Continuous Tense is defined as, “In grammar, the present perfect tenses of a verb are the ones used to talk about things which happened before the time you are speaking or writing but are relevant to the present situation, or things that began in the past and are still happening. The simple present perfect tense uses 'have' or 'has' and the past participle of the verb, as in 'They have decided what to do'.”
Also Read:
Past Perfect Tense: Definition and Types
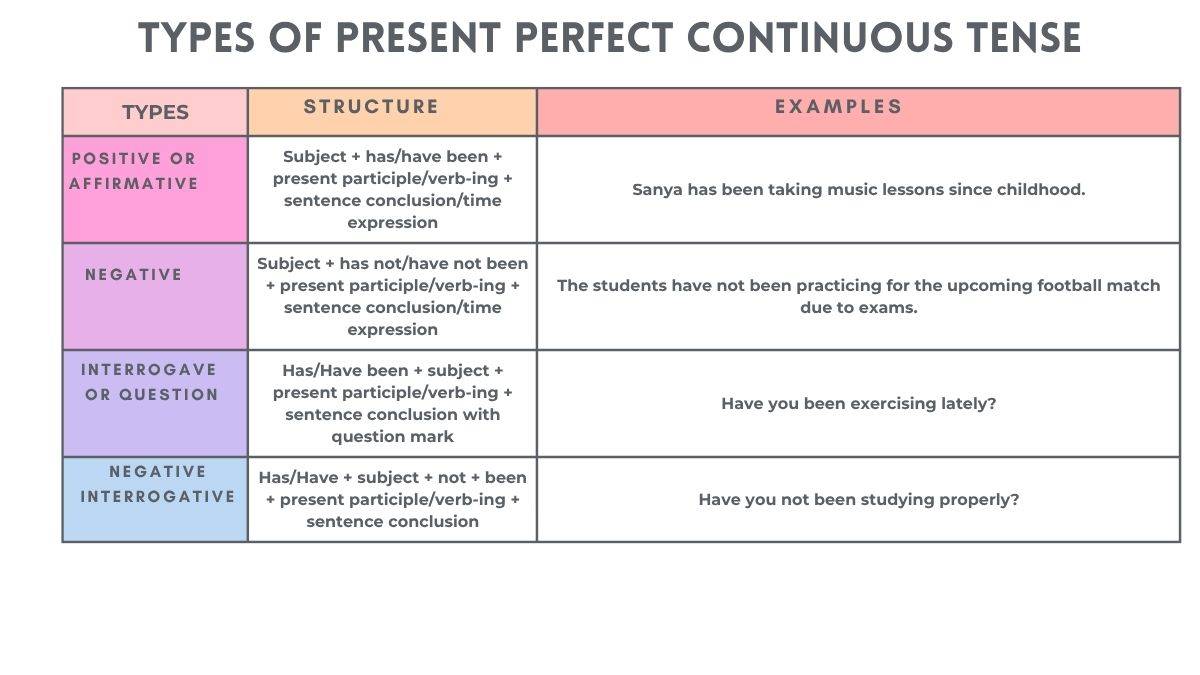
Types of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense can be segregated into three broad types: Positive or Affirmative, Negative and Questioning or Interrogative. The examples of each of these types is given below:
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Positive Sentence
The Affirmative or Positive Present Perfect Tense refers to those sentences which convey actions being done in an effective manner for a particular time period. The basic structure or formula which is used to frame a sentence in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in the affirmative or positive type is given below:
Subject + have/has + been + present participle/verb-ing + sentence conclusion.
Here are a few examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense in positive sentences.
- I have been into gardening since my childhood.
- I have been learning French for the last three months.
- I have been waiting for your call since yesterday.
- I have been cooking biryani for last couple of hours.
- Sana has been studying for hours.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Negative Sentence
In a negative context, the Present Perfect Continuous Tenses are used to refer to actions which are not being done for a considerable period of time. These sentences have negative connotations such as ‘Not’, ‘No’, ‘Never’, etc. The structure or formula of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is provided here:
Subject + have not/has not + been + present participle/verb-ing + sentence conclusion
Some examples of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in negative context are given below:
- Reema has not been doing her homework regularly.
- Tarun has not been an active member of his music band lately.
- My mother has not been visiting the temple for the past few weeks.
- Soniya has not been singing in the last few concerts.
- Grandpa has not been taking his medicines lately.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Questions or Interrogative Sentences
The interrogative type of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is that which asks a question regarding the action which is being done at present. The formula or structure to frame the sentence is given below:
Have/Has + Subject + been + present participle/verb-ing + sentence conclusion
Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used while asking a question as well. Here are a few examples.
- Have you been watching this web series?
- Where has he been going every evening?
- Are you reading this book lately?
- What have you been doing in the kitchen all this time?
- What has been taking you so long to finish this task?
Also Read:
Grammar Rules of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Some of the core principles or rules which are followed while forming a sentence in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense are as follows:
- There must be two helping verbs in the sentence, which are ‘have/has’, along with ‘been’. The words ‘has been’ or ‘have been’ are Auxiliary Verbs, also known as Helping Verbs. These will be followed by the present participle or the verb+ing. The common verbs used in Present Perfect Continuous Tense are Action Verbs such as ‘working’, ‘studying’, ‘singing’, ‘dancing’, ‘cooking’, ‘drawing’, etc. and not stative verbs like ‘know’, ‘believe’, ‘love’, ‘want’, etc.
- The Present Perfect Continuous Tense should be used to refer an ongoing action, and actions which have recently concluded but still have its impact.
- Usage of time expressions such as ‘for’ and ‘since’ or ‘off late’, ‘lately’ ‘recently’, ‘nowadays’, etc. to emphasise the duration of the action must be there in the sentence.
Also Read:
Rules and Exceptions of Present Tense
Rules and Examples of Uncountable Noun
Rules and Types of Transitive Verb
Structure of Different Types of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The following table shows the structure of the different types of Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Vs Present Perfect Tense
Students are often confused about Present Perfect Continuous Tense and Present Perfect Tense. While these two tenses are similar, there can be a thin line of difference. The following table brings the differences between the Present Perfect Continuous Tense and the Present Perfect Tense.
| Parameter |
Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Focus |
This tense focuses on the duration or continuation of action. For example, I have been working on this project all morning. |
This tense focuses on the completion or result of an action. For example, I have completed the project. |
| Structure or Formula |
Subject + have/has + present participle/verb-ing + sentence conclusion |
Subject + have/has + past participle/verb + sentence conclusion |
| Purpose of usage |
It is used to describe an ongoing or recently concluded action, which has started in the past and is continuing in the present. |
It is used to describe an action which was started and completed in the recent past with a result or impact in the present. |
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Vs Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The difference between the Present Perfect Continuous Tense and the Past Perfect Continuous Tense is in the timeline of a continuing event. While the former connects the past to the present, the latter connects the past timelines. The table below describes the differences between the two tenses.
| Parameter |
Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Focus |
This tense denotes an action which started in the past and is being continued in the present. For example, I have been working in this company for years. |
This tense denotes an action which was ongoing in the past before another past action took place. For example, I had been working in this company for years before shifting to another city. |
| Structure or Formula |
Subject + have/has + present participle/verb-ing + sentence conclusion |
Subject + had been + present participle/verb-ing + sentence conclusion |
| Purpose of usage |
It is used to describe an ongoing or recently concluded action, which has started in the past and is continuing in the present. |
It is used to describe an action which was ongoing at the past before another major past event occurred. |
Preparation Tips to Master Present Perfect Continuous Tense
To prepare for the Present Perfect Continuous Tense, candidates should follow the points or strategies given below.
- Understand the concepts and structure: The first step to prepare for the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is to understand the concepts and the structure. At the same time, understanding and remembering the formula is key.
- Understand the difference with other tenses: The Present Perfect Continuous Tense can be confusing with other tenses. Hence, it is of utmost importance to understand the differences to avoid common mistakes or errors.
- Read and identify the tense: The next step is to read a lot and identify the Present Perfect Continuous Tense along with its usage. Reading it in textual format will make you habituated to the context and usage types, which will help you not only in scoring high in your English test but also improve your overall English communication skills.
- Listen to English conversation or speeches: Another effective way of Present Perfect Continuous Tense preparation is to listen to English conversation or speeches and note the usages. The best resources would be listening to English news bulletins, documentary shows, movies, etc.
- Practice: There is no alternative to practice. You must take multiple practice exercises and different types of questions to test your skills and learning of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense, such as identifying the tense, forming sentences, converting from other tenses, to name a few.
Also Read:
Preparation Tips and Best Books for Nouns
Preparation Strategy and Practice Questions for Prepositions
How to Identify Present Perfect Continuous Tense in a Sentence
Here are a few tricks to identify the Present Perfect Continuous Tense in a sentence:
- Identify the formula: The Present Perfect Continuous Tense will have the Auxiliary verb usage as ‘has been’ or ‘have been’ in the sentence.
- Identify the action type: The Present Perfect Continuous Tense in a sentence describes an ongoing action.
- Presence of ‘present participle’ in the sentence: The verb will have ‘ing’ at the end. For example, ‘reading’, ‘eating’, ‘sleeping’, etc.
- Note the time expression: In general, the time expressions used in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense are ‘for’ and ‘since’.
- Absence of Stative Verbs: In general, Stative Verbs such as ‘know’, ‘believe’, ‘understand’, etc., are not used in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Common Errors to Avoid in Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Best Books to Prepare for Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Engaging Practice Exercises for Present Perfect Continuous Tense
FAQs Regarding Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Commonly asked questions
What is Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense is one of the types of Present Tense, wherein a continuous action is described which was started before and is either still continuing, or has concluded recently. A Present Perfect Continuous Tense can be identified with the auxiliary verb of 'has/have been', followed by present participle or verb-ing, and a time expression.
What is the structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
The structure or the formula for the Present Perfect Continuous Tense is 'Subject + has/have been + present participle/verb-ing + time expression/sentence conclusion.'
What are the different types of Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
There are mainly three types of Present Perfect Continuous Tense, which are as follows:
· Positive or Affirmative
· Negative
· Interrogative or Question
The intettogative or question format of Present Perfect Continuous Tense can also be segregated into positive and negative contexts. In the latter type, the formula of the tense would be 'why/how/which/who/whom + have not been + present participle + sentence conclusion'.
What are the different types of Verbs used in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense uses two types of Verb, which are Auxiliary Verb and Action Verb or Dynamic Verb. While Dynamic Verbs may vary, Auxiliary Verb is a compulsory verb used in this tense. In general, Stative Verbs are generally not used in Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Can a concluded or repeated action used in Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
Yes, a recently concluded or a repeated action can be used in a Present Perfect Continuous Tense. But one must be careful not to use a past event or a universal truth such as sun has been rising in the east everyday, in a Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
English Tenses Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds


What is the structure of Present Perfect Tense and its rules?