
Have you ever said things like, “I am talking to my friend right now,” or “Where are you going in the summer break”? If yes, then Voila! You are already using the Present Continuous Tense. It is a type of present tense that helps us describe what’s happening right now, what’s happening around this exact moment, or what’s planned for the near future. The present continuous tense is a part of English grammar that is also known as the Present Progressive Tense.
Imagine yourself standing in a market and you see people talking to each other, children laughing and eating snacks, parents shopping for their kids, and shopkeepers selling goods. All these actions that are happening right now in real time are what we call the Present Continuous Tense. It also describes temporary actions and actions-in-progress.
Understanding the Present Continuous Tense is essential for everyone, whether it be for normal day-to-day conversations, formal meetings, or competitive exams. This article of Shiksha aims at helping you achieve a strong hold on the definition of present continuous tense and its different forms. Learn the rules to use present continuous tense with examples. Also, find exercises of Present Continuous Tense with answers for practice.
Can I use present continuous tense for future?
Yes, we can use present continuous tense to talk about the planned or definite future events.
For example:
- We are meeting our Science teacher tomorrow.
- She is leaving for New York next week.
These two sentences shows that the plan is already made and will be fulfilled in the future. By writing or speaking a sentence about fixed future event using present continuous tense makes the plan more certain compared to using 'will' or 'shall'.
How to make negative sentences in present continuous?
To make a negative sentence in present continous, add 'not' after the helping verb is/am/are. The structure for Present Continuous Tense in Negative Form is:
Subject + is/am/are + not + verb + ing
For example:
- I am not playing football.
- He is not watching TV today.
- She is not cooking.
Negatives in present continuous tense are used when we want to deny that an action is happening right now.
- What is Present Continuous Tense?
- Present Continuous Tense Definition
- Present Continuous Tense Formula
- Present Continuous Tense Rules in English Grammar
- Forms of Present Continuous Tenses
- Present Simple vs Present Continuous Tense
- Present Continuous Tenses vs Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- English Present Continuous Tenses: Special Cases & Exceptions
- Present Continuous Tense in Spoken and Written English
- English Grammar Books for Present Continuous Tense
- Present Continuous Examples
- Present Continuous Tense Exercise with Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on Present Continuous Tense
What is Present Continuous Tense?
The present continuous tense is a type of present tense that describes an action happening right now or during a specific time period, or a planned future arrangement. There are a total of four forms of the present continuous tense: Affirmative, Negative, Interrogative, and Negative Interrogative. We will delve into the present continuous tense forms in the latter section of this article. Let’s first understand the meaning of present continuous tense with the help of some examples.
Present Continuous Tense Examples:
- It is raining heavily outside. (a temporary situation)
- We are playing football in the park. (current ongoing action)
- Are you attending the team meeting today? (Interrogative form of asking about future event)
- She is learning to drive. (action happening during specific time)
Commonly asked questions
How to make questions in present continuous tense?
To make a question in present continuous tense, place the helping verb is/am/are before the subject of the sentence, and then add the main verb in 'ing' form.
For example:
- Are you studying English Verbs?
- Is she dancing at the party?
Another way to make a question in present continuous tense is by using question words like What, Where, When, Who, etc., at the beginning of the sentence.
For example:
- What are you doing?
- Where are we going?
- Who is coming for the party?
What time expressions are used with present continuous tense?
To make a complete sentence, certain time expressions are used with present continuous tenses. These include: today, now, right now, at the moment, these days, currently, nowadays, this week, etc.
For example:
- He is working on a project right now.
- Currently, we are working from home.
- Today, I am going for an interview.
Present Continuous Tense Definition
Definition of Present Continuous Tense: Oxford Dictionary
According to Oxford Dictionary, the present continuous tense is ““A verb tense used to describe an action that is happening at the moment of speaking or a temporary situation.”
For Example,
- She is reading a book.
- Radhika is going to the museum.
Word Origin: Present comes from the Latin word praesens, meaning “existing now”; Continuous comes from the Latin word continuus, meaning “uninterrupted”; and Tense from the Latin word tempus, meaning “time.”
This means that Present Continuous Tense is the time form expressing an ongoing or uninterrupted action happening right now.
Pronunciation: UK: /ˌprez.ənt kənˈtɪn.ju.əs/ US: /ˌprez.ənt kənˈtɪn.ju.əs
Definition of Present Continuous Tense: Cambridge Dictionary
According to Cambridge University, the present continuous tense is “the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now.”
Present Continuous Tense Formula
The basic formula or structure of the present continuous tense is as follows:
| Subject + is/am/are + verb + ‘-ing’ + Object |
Key Point to Remember:
While framing a sentence with present continuous tense, a form of the verb ‘Be’ (is/am/are) is used, followed by the main verb + ing. The form of ‘be’ to be used depends on the subject of the sentence.
Rule for ‘Be’ Verb in Present Continuous Tense
Take a look at the table below to know the rule for using the verb ‘to be’ in present continuous tense:
| Subject |
Form of ‘Be’ |
Example |
|---|---|---|
| I |
am |
I am running for the position of Class President. |
| He/She/It |
is |
She is learning classical dance. |
| Singular Noun |
Is |
Gloria is shopping for Lily’s birthday party. |
| We/You/They |
are |
We are getting late for the French class. |
| Plural Noun |
are |
Jake and Amy are hunting down the thief. |
Quick Tip:
- Use ‘am’ only with ‘I’
- Use ‘is’ with one person/thing
- Use ‘are’ with more than one person/thing
Also Read:
| English Adverbs: Examples, Definition, Types | Gerunds in English Grammar | Subject-Verb Agreement: Grammar Rules, Examples & Exercises |
Present Continuous Tense Rules in English Grammar
The present continuous tense is used to describe ongoing actions, temporary situations, planned events, and repeated behaviours. Check out the space below to understand how to use the present continuous tense in English.
1. Action Happening Now
The present continuous tense is used to explain things/actions happening at the time of speaking.
Example:
- I am chopping vegetables.
- We are going to the mall.
2. Actions Happening During a Specific Period
It is used when an action is not happening at the same moment, but around the current time. These are typically of longer duration than immediate actions.
Example:
- They are working on a assignment together.
- I am making an itenary for the Girl's trip.
It is not necessary that such actions are occurring right now. But, they are ongoing during that time frame.
3. Future Plans
The present continuous tense is also used to talk about the future events. These events are planned in advance. This means that the time and place of the action has been already decided.
Example:
- We are meeting at Central Perk at 8 pm.
- They are going to Udaipur next week.
4. Temporary Actions
It is used for temporary or short-term events. These situations are expected to change soon. It helps to show that something is only for a limited time.
Example:
- I am working night shifts this month.
- We are staying in a guest house this week.
5. Repeated Actions
Present countinuous tenses are also used with adverbs. It is used to show repetition, irritation, or annoyance. The verb form is usually used with ‘Always, Constantly, Forever’.
Example:
- Joey is always eating my food.
- Sheldon is constantly ringing Penny's doorbell.
The tone of the sentence often shows frustration or criticism. These repeated actions are expressed with emotional emphasis.
Present Continuous Tense Example
Let’s take an example from one of the most popular Hollywood sitcoms, F.R.I.E.N.D.S. With a seris of actions, let's understand how to use the present continuous tense in different situations.
It’s pure chaos in Monica’s apartment this morning. Monica is checking her voicemail repeatedly. Rachel is staying with Monica and Chandler temporarily after the fire in her apartment. Meanwhile, everyone is going to London soon for Ross’s wedding, and Joey keeps practicing his British accent. In the living room, Joey is building an entertainment center, which has been going on for days. Chandler is always leaving his socks on the floor.
| Sentence |
Use of Present Continuous Tense |
|---|---|
| Monica is checking her voicemail repeatedly. |
Action happening right now |
| Rachel is staying with Monica and Chandler. |
Temporary situation |
| Everyone is going to London soon for Ross’s wedding. |
Future Planned Arrangement/Event |
| Joey is building an entertainment center. |
Ongoing action during a specific time |
| Chandler is always leaving his socks on the floor. |
Repeated annoying action |
In the same way, you can also identify the type of tenses used in a conversation while watching your favourite movies, sitcoms, or documentaries.
Also Read:
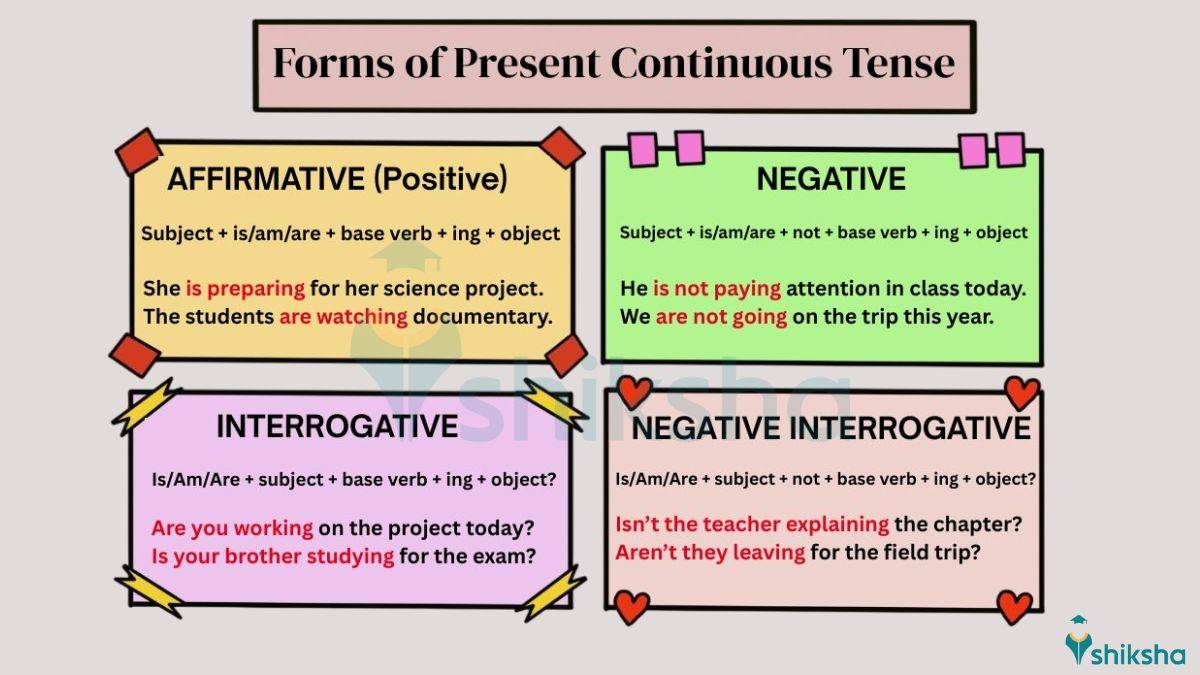
Forms of Present Continuous Tenses
In English Grammar, there are four forms of present continuous tense: Positive/Affirmative, Negative, Interrogative, and Negative Interrogative. Let us understand each form and structure of the present continuous tense with the help of examples.
1. Positive/Affirmative Form:
The affirmative form of present continuous tense is used to show what is happening right now.
Subject + is/am/are + base verb + ing + object
Examples of Present Continuous Tense in Positive Form:
- She is completing her homework.
- They are practicing for the upcoming match.
2. Negative Form:
As the word suggests, the negative form of present continuous tense is used to explain what is NOT happening right now.
Subject + is/am/are + not + base verb + ing + object
Examples of Present Continuous Tense in Negative Form:
- She is not going to the party.
- We are not watching TV today.
3. Interrogative Form:
The interrogative form of present continuous tense is used to ask questions about what is happening right now.
Is/Am/Are + subject + base verb + ing + object?
Examples of Present Continuous Tense in Interrogative Form:
- Is she doing her homework?
- Are you coming to the party?
4. Negative Interrogative Form:
The negative interrogative form of present continuous tense is used to ask negative questions.
Is/Am/Are + subject + not + base verb + ing + object?
Examples of Present Continuous Tense in Negative Interrogative Form:
- Isn’t she going on a trip?
- Aren’t you learning German these days?
Present Simple vs Present Continuous Tense
Check out the table below for the difference between simple present tense and present continuous tense:
| Basis |
Simple Present Tense |
Present Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Usage |
Regular or Habitual Actions |
Actions happening right now or around the current time |
| Time Reference |
Always, Usually, Often, Every Day |
Right Now, Now, Currently, At the Moment |
| Structure |
Subject + base verb + s/es + Object |
Subject + is/am/are + verb + ‘-ing’ + Object |
| Nature of Action |
Permanent or Routine |
Temporary or In-Progress or Future Planned Event |
| Example |
She drinks juice every morning. |
She is drinking juice right now. |
Examples of Simple Present and Present Continuous Tense
Convert the following from Simple Present Tense to Present Continuous Tense:
- Simple Present: Phil teaches his kids life lessons in silly ways. (General Habit/Routine)
- Present Continuous: Phil is teaching his kids how to be polite at the dinner table. (Action happening right now)
- Simple Present: Cam and Mitchell attend parenting classes on weekends. (Regular Activity)
- Present Continuous: Cam and Mitchell are attending a parenting workshop this afternoon. (Planned event happening in the future)
Present Continuous Tenses vs Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Understand the difference between present continuous tense and present perfect continuous tense from the table below:
| Basis |
Present Continuous Tense |
Present Perfect Continuous |
|---|---|---|
| Usage |
Current or Temporary Actions |
Actions that started earlier and are still going on |
| Time Reference |
Now, Currently, At the Moment |
For, Since, Lately, Recently, All Day |
| Structure |
Subject + is/am/are + verb + ‘-ing’ + Object |
Subject + has/have been + verb + ‘-ing’ + Object |
| Example |
She is dancing right now. |
She has been dancing for an hour. |
Examples of Present Continuous Tense and Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Convert the above present continuous tense into present perfect continuous tense:
- Present Continuous: Phil is teaching his kids how to be polite at the dinner table. (Action happening right now)
- Present Perfect Continuous: Phil has been teaching his kids how to be polite at the dinner table since this morning. (Action started earlier and is still going on)
- Present Continuous: Cam and Mitchell are attending a parenting workshop this afternoon. (Planned event happening in the future)
- Present Perfect Continuous: Cam and Mitchell have been attending parenting workshops for the past three weeks. (Ongoing Action that started in the past)
Also Read: Articles Exercises with Answers, Types of Articles
English Present Continuous Tenses: Special Cases & Exceptions
Present Continuous Tense in Spoken and Written English
English Grammar Books for Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Examples
Present Continuous Tense Exercise with Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on Present Continuous Tense
Commonly asked questions
What is the rule for Present and Present Continuous Tense?
Simple Present Tense Rule:
Subject + base verb (s/es for he/she/it)
Example: She goes to college.
Shows habit, facts, and routines.
Present Continuous Tense Rule:
Subject + is/am/are + verb-ing
Example: She is going to college.
Shows actions happening now or temporary actions.
What is Present Continuous Tense and examples?
The present continuous tense is a verb tense describing actions happening in the present or to be continued in the future. The formula for Present Continuous Tense is Subject + is/am/are + present participle (verb + ing) + Object.
Examples:
- I am driving the car.
- They are going on a trip to Meghalaya.
What are the 3 uses of Present Continuous Tense?
The Present Continuous Tense is used in three cases:
Case 1: Actions happening right now
Examples:
- She is talking on the phone.
- We are ordering Pizza from Dominos for lunch.
Case 2: Temporary or ongoing actions
Examples:
- I am staying at my friend's house for a few days.
- She is going to Decathlon to buy a winter jacket.
Case 3: Future planned events (with a specific time frame)
Example:
- They are having a cricket match this Sunday.
- He is flying to London next week.
What is the rule for Present Continuous Tense?
The rule of Present Continuous Tense in English Grammar is:
Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing + Object
Examples:
- I am playing.
- He is writing a letter.
- They are watching TV.
How can I use tenses correctly?
Using the tenses correctly is important to make proper grammatically correct sentences. To know how to use tenses, understand the time they indicate when an action has happened or is about to happen.
In English, there are three main types of tenses, i.e. Present, Past and Future. Each of these tenses have different forms to indicate how is the action occuring or its relation with time.
The '-ing' form of a verb is called the present participle. It can act as:
- A gerund (noun)
- A participle (adjective)
- Part of a continuous tense
Examples:
Cooking is relaxing. (Gerund)
The boiling water is hot. (Present Participle)
She is cooking dinner now. (Continuous Verb)
How many tenses are there in the English language?
There are three main tenses, Present, Past and Future. These tenses are further divided into four sub categories each. Hence, making the total to 12 tenses. These are:
Present Tense:
- Simple Present
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Past Tense:
- Simple Past
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
Future Tense:
- Simple Future
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
How to identify Present Continuous Tense?
To identify the Present Continuous Tense in a sentence, follow these three steps:
- Check if there is 'is/am/are' in the sentence.
- Check for the –ing form of verb.
- Lastly, confirm that the sentence is describing an action happening right now, a temporary ongoing action, or a future action.
English Tenses Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds



What is the structure of Present Perfect Tense and its rules?