
Tenses are inarguably one of the core pillars of English grammar. The future tense in grammar is used to describe an act that has not yet happened but is expected to take place in future. This applies to whether one’s talking about their goals, planning something, making predictions, and more.
Mastering the future tense is essential for effective communication in both spoken and written English. Much like the other tenses in English grammar, the future tense is a key tool in making a sentence cohesive and grammatically correct. Read the following article by Shiksha.com to learn about the definition, types, examples, common errors, and practice questions for future tense in English.
What is the future tense and examples?
In English grammar, the future tense is a verb form that is used to denote actions take will take place after the present time. It offers clarity on what is planned, assumed, or predicted to occur in the future.
Examples of future tense:
- He will go to the Church on Sunday.
- Shea will remove her makeup after she is done with the next act.
- I will eat ice cream for dessert.
What are the four future tenses?
In English grammar, there are mainly four types of future tense. Have a look at the types of future tenses:
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
What is the rule for future tense?
Future tense follows a simple rule: Subject + will/ shall + base form of the verb. For example, take a look at the following sentences:
- I will eat dinner at 11 PM.
- He will visit his grandma next week.
- What is Future Tense?
- Definition of Future Tense
- Types of Future Tense
- Key Rules for Using Future Tense in English
- Difference Between Will v/s Going to in Future Tense
- Rules for Future Tense in Grammar
- Common Mistakes to Avoid while Using Future Tense
- Difference between Future Tense and Past Tense in English
- Why is Future Tense Important?
- Best Books for Future Tense in English
- Practice Exercises with Answers for Future Tense
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on Tenses
What is Future Tense?
In the simplest terms, the future tense is a form of verb that denotes the actions that will happen after the present time. It offers clarity on what is planned, assumed, or predicted to occur in the future.
Example:
- I will go to Paris next year.
- She is going to teach soon.
Definition of Future Tense
Cambridge dictionary defines future tense as “the form of a verb that you use when talking about something that will happen or exist”.
The Collins Dictionary defines future tense as “a tense of verbs used when the action or event described is to occur after the time of utterance.”
Word Origin: from Latin “fūtūrus about to be, from esse to be.
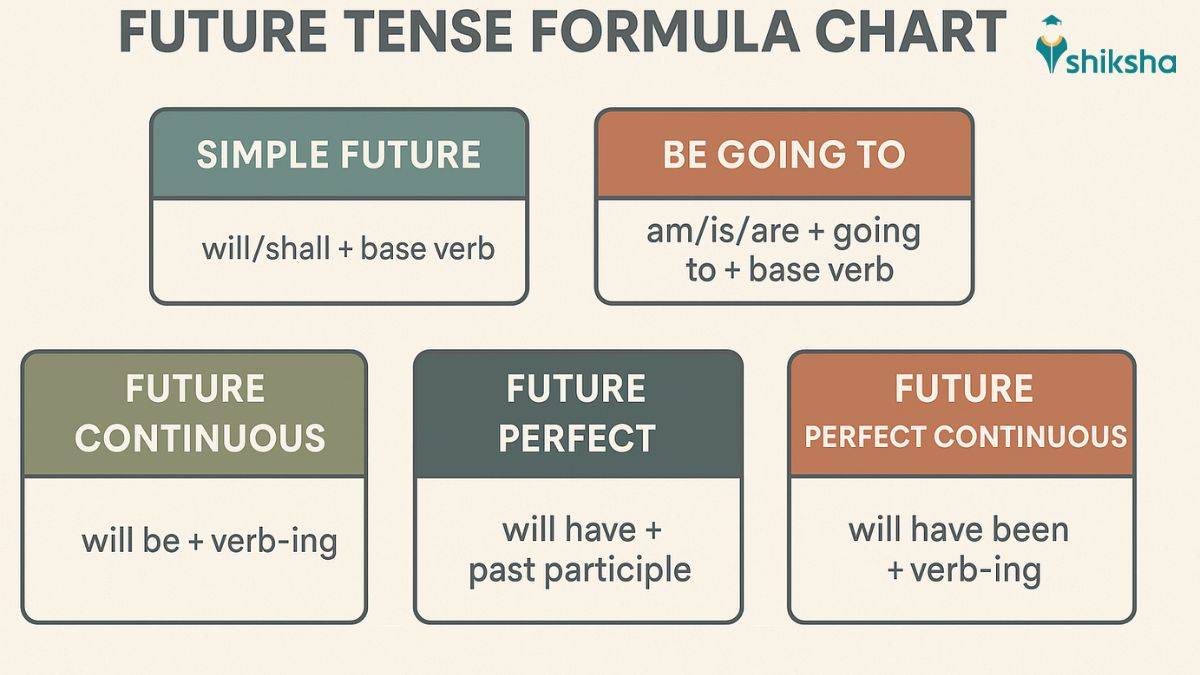
Types of Future Tense
In English grammar, there are four types of future tense. Each of these tenses is used to describe a different aspect of future actions. By understanding the types of future tenses, one can enhance their vocabulary, both verbal and written. Take a look at the types of future tenses in English listed below:
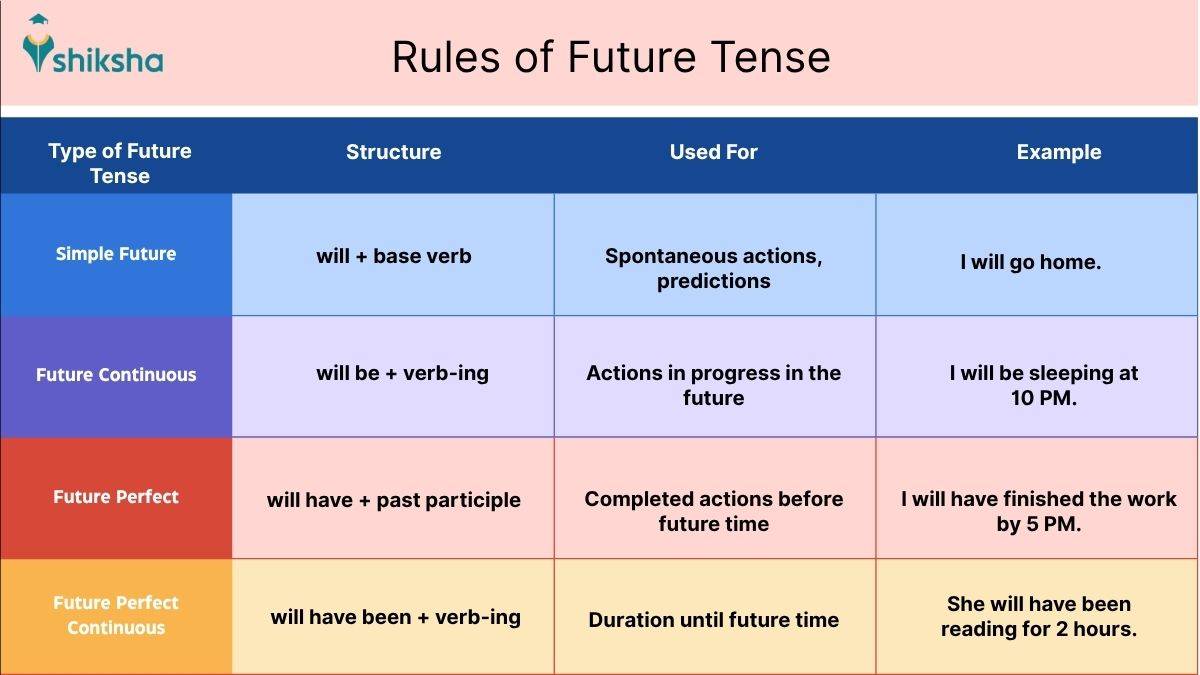
Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense is used to express spontaneous decisions, promises or predictions. These are often used with time expressions, such as tomorrow, next month, next year, soon, etc. It follows the following structure:
Subject + will/ shall + base verb
Example:
- Shane will drop you off tomorrow.
- I will help you with the chores.
- I will call you once I get the gift.
Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense is used to describe an act that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future. This tense follows the following structure:
Subject + will be + present participle (verb + ing)
Example:
- They will be leaving for London next week.
- He will be eating mac & cheese for Thanksgiving next month.
- Wonyoung will be singing on the music show at that time.
Future Perfect Tense
In English grammar, future perfect tense is used to denote an action that will be completed before a certain time in the future. Future perfect tense structure is as follows:
Subject + will have + past participle
Example:
- By 2039, I will have travelled around the world.
- By next year, I will have moved to France for higher studies.
- Joon will have visited all the museums in India by then.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
When expressing the duration of an action that will continue to take place up to a specific point in the future. The future perfect continuous tense structure is as follows:
Subject + will have been + present participle
Example:
- By 2030, I will have been working at this organisation for six years.
- I will have been practising dancing for ten years by 2027.
- She will have been driving for twelve hours by midnight.
Key Rules for Using Future Tense in English
The future tense allows one to express what is going to happen in the future. The structure may seem simple, however, it is important that one uses it correctly in the right context. Check out the key rules for using the future tense in English grammar:
Rule #1: Using “Will” for spontaneous decisions & promises.
When a decision is made on the spot, one must use “will” + base form of the verb.
Examples:
- I will help you with your homework. (Spontaneous offer)
- I will protect you always. (Promise)
- We will discuss this in detail tomorrow. (Planned but sudden meeting)
Rule #2: Use “Going to” for planned actions
When referring to actions that you intend to proceed or talking about something pre-decided, use “am/ is/ are + going to + verb”.
Examples:
- I am going to start my business next month.
- Shean is going to play the piano at the party.
- They are going to visit Bali during their trip.
Rule 3: Use “Shall” when making offers or suggestions
Shall is a formal alternative used in place of “will”. It is typically used with “I” and “we” in British English.
Examples:
- Shall I close the door on my way?
- Shall we begin the meeting?
Rule #4: Use the right time expressions
To clearly mark a sentence as the future tense, use time indicators, such as tomorrow, next week/ month/ year/ decade/ soon/ later/ By (date/ time), etc.
Examples:
- We will finish this project by next week.
- He is going to meet his friends soon.
Difference Between Will v/s Going to in Future Tense
Future tense uses both “will” and “going to” when referring to the future. However, these are not always interchangeable. Both vary in intent, timing, certainty, and usage. Check out the table below to know about when to use “will” and when to use “going to” in English grammar:
| Particulars |
Will |
Going to |
|---|---|---|
| Decision timing |
On the spot |
Pre-decided/ pre-planned |
| Prediction Type |
Uncertain/ Opinionated |
Based on current signs |
| Function |
Promise, offer, future fact, sudden intent |
Plan, intention, prediction with evidence |
| Example |
Rehan will call you. |
Rehan is going to call her later. |
Rules for Future Tense in Grammar
Let’s take a look at the table below to learn about the rules, structures, and examples for each of the four future tenses. As a bonus, the table also mentions when to use will and going to, time expressions, and their usage.
Quick Grammar Reminder for Future Tense:
- Use base verb after “will”
Correct: She will go to the salon tomorrow.
Incorrect: She will goes to the salon tomorrow.
- Use “going to” for pre-decided plans
Example: I was going to visit grandpa next week.
- Use the future perfect when an action ends before a specific point in future.
Example: By next June, I will have finished my degree.
- Use future perfect continuous for duration up to a future time
Example: By next month, I will have been going to the gym for six months straight.
Check out the table below to understand this better:
Common Mistakes to Avoid while Using Future Tense
It is only natural to make errors while using the future tense in grammar. However, with some practice and tips, these mistakes can easily be avoided. Find below some common errors while using the future tense that the students make:
Using “will” instead of “going to” for planned actions
One of the most common errors made by students is using will everywhere when it comes to future tense, even for planned actions.
Incorrect: I will visit my grandpa tonight.
Correct: I’m going to visit my grandpa tonight.
Using the present tense for future actions
Some students often mix up the present simple to refer the non-scheduled future events.
Incorrect: She goes to college next year.
Correct: She will go to college next year.
Incorrect Structure of Future Perfect Tense
Another common error is to use the base form of the verb in place of the past participle after “will have”. Future perfect tense follows the structure “will have + past participle”.
Incorrect: Sia will have eats dinner by 9 PM.
Correct: Sia will have eaten dinner by 9 PM.
Using “will” after time expressions like “when”, “before”, “after”
An important note: do not use will after time expressions even if it’s about the future. Instead, use present simple tense after such words.
Incorrect: When she will arrive, they will leave for Phuket.
Correct: When she arrives, they will leave for Phuket.
Difference between Future Tense and Past Tense in English
Why is Future Tense Important?
Best Books for Future Tense in English
Practice Exercises with Answers for Future Tense
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs) on Tenses
Commonly asked questions
Future tense in English grammar is used to describe an act that has not yet happened but is expected to take place in future. This applies to whether one's talking about their goals, planning something, making predictions, and more. Some common future tense examples are as follows:
- I will eat out tomorrow.
- She will go to the mart next friday.
- Rayn is going to Dubai next month.
There are four types of future tenses in grammar. These are; Simple Future, Future Continuous, Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous tense. Find below examples for each of the four future tenses:
- Simple Future: I will text you later. (Subject + will/ shall + base verb)
- Future Continuous: He will be partying until the sunrise. (Subject + will be + verb + ing)
- Future Perfect: By next Wednesday, I will have turned this report in. (Subject + will have + past participle)
- Future Perfect Continuous: By 2032, I will have been learning guitar for a decade. (Subject + will have been + present participle)
Find below the list of ten examples for future tense:
- I will call you on coming Monday.
- She will take you to the cafe.
- Jane is going to attend the ball tomorrow.
- By next week, I will have finished working on this painting.
- Next month, they will have been living in Seoul for over a decade.
- At this time coming July, I will be travelling to Japan.
- Joon will dance after Jin.
- I am going to visit the art gallery this weekend.
- The guests will arrive at noon.
- Sarah is going to bake apple pie for dinner.
If you're looking to practice future tenses or examples and structure of future tenses, the following books are some of the popular options to purchase:
Book Name | Author/ Publication |
|---|---|
English Grammar in Use | Raymond Murphy |
Practical English Usage | Michael Swan |
Oxford Practice Grammar | George Yule |
English Verb Tenses: The Complete Guide | Ken Xiao |
How to identify tenses in an English sentence?
Knowing how to identify tenses is important to complete understand what are tenses. Focusing on the verb form and how it relates to the action's time (past, present or future) can help in identifying the tenses in a sentence. Auxiliary verbs such as have, be, will, etc. help in identifying the tense and its aspect -simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous.
How can I use tenses correctly?
Using the tenses correctly is important to make proper grammatically correct sentences. To know how to use tenses, understand the time they indicate when an action has happened or is about to happen.
In English, there are three main types of tenses, i.e. Present, Past and Future. Each of these tenses have different forms to indicate how is the action occuring or its relation with time.
The '-ing' form of a verb is called the present participle. It can act as:
- A gerund (noun)
- A participle (adjective)
- Part of a continuous tense
Examples:
Cooking is relaxing. (Gerund)
The boiling water is hot. (Present Participle)
She is cooking dinner now. (Continuous Verb)
English Tenses Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds



What is the structure of Present Perfect Tense and its rules?