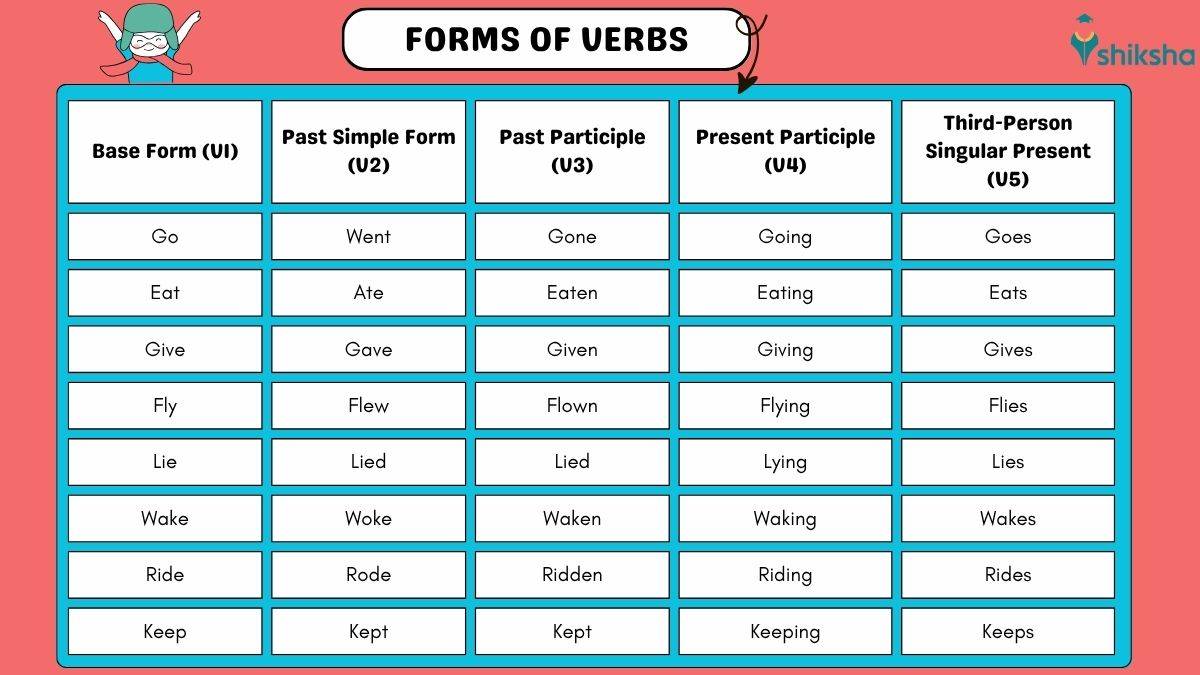
Do you know why we use the verbs ‘eat’ with today, ‘ate’ with yesterday, and ‘eaten’ in a sentence when the time of action changes? That’s because in English, verbs don’t stay the same and change their forms to show when an action happens. The different verb forms help write or speak correct sentences and express the accurate meaning.
Knowing which form of verb to use while speaking or writing is an essential part of English grammar. With this article, Shiksha aims to teach what verb forms are, the five forms of verbs, and how to use them in a sentence. Get a list of different types of verbs along with their forms and practice tips to learn them easily. Also, find practice worksheets on verb forms to test your knowledge.
- What are Verb Forms in English?
- Definition of Forms of Verb
- Five Forms of Verb in English
- What are the Root Verbs?
- Regular v/s Irregular Forms of Verbs
- List of Verb Forms
- Tips to Learn English Verb Forms
- English Grammar Books for Forms of Verbs
- Forms of Verb Examples
- Forms of Verb Exercise with Answers
- Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Forms of Verbs
What are Verb Forms in English?
In English Grammar, Verb Forms refer to the different ways in which a verb is used to show the time of action, the subject, and the grammatical condition of a sentence. Here, the time of action means that the different forms of verbs help us understand whether the action is happening in the present, has happened in the past, or will happen in the future.
There are five verb forms in English, Base Form (Root Verb), Past Simple Form, Past Participle, Present Participle (‘-ing’ form), and Third-Person Singular Present Simple Form.
For example:
- I always go for a walk after dinner. (Base Form)
- We went to the mall yesterday. (Past Simple Form)
- He was gone when I reached his home. (Past Participle)
- They are going on vacation in August. (Present Participle)
- She goes for a run early in the morning. (Third-Person Singular Present Simple Form)
Commonly asked questions
Verbs are divided into different types based on how they function in a sentence. Here are the 11 important types of verbs you should know:
- Action Verbs
- Transitive Verbs
- Intransitive Verbs
- Linking Verbs
- Regular Verbs
- Irregular Verbs
- Finite Verbs
- Non-finite Verbs
- Stative Verbs
- Primary Helping Verbs
- Modal Helping Verbs
What are the V1, V2, V3 forms of verb?
V1, V2, and V3 are the three basic forms of a verb.
- V1 is the base form of a verb and is also known as a root verb. It is the original form of the verb that is used to create the different verb forms. For example: Write, Speak, Go, Listen
- V2 is the past simple form of a verb, which shows that an action was completed in the past. To frame V2 verb form suffixes like 'd', 'ed', or 'ied' are added to the regular verbs, while irregular verbs have no specific rule. For example: Wrote, Spoke, Went, Listened
- V3 is the past participle form of a verb that uses auxiliary verbs (has, have, had) to frame perfect tenses. For example: Written, Spoken, Gone, Listened
Definition of Forms of Verb
Verbs: The Three Basic Forms: Cambridge Dictionary
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, “Main verbs have three basic forms: the base form, the past form, and the –ed form (sometimes called the ‘ed participle’):
Base form: used as the infinitive form, with ‘to’ or without ‘to’ and for the present simple, except third person singular, which uses the –s form.
Past form: used for the past simple
-ed form: used after auxiliary ‘have’ and ‘be’
Verb Forms: Oxford Dictionary
According to the Oxford Dictionary, “Verb forms are the different inflected versions of a verb that express grammatical contrasts such as tense, aspect, mood, voice, person, and number. These include forms like the base form, third-person singular present, past tense, past participle, and present participle/gerund.”
Also Read:
Commonly asked questions
What is the base form of the verb?
The base form of a verb is the root verb, which remains unchanged. No suffixes are added to this verb form. When looking for the meaning of a verb, its base form is used. These include play, jump, smile, carry, etc.
Example:
- Please write your name and roll number on the answer sheet.
- Children play in the garden every evening.
- Sunflowers grow well in sunlight.
- I want to watch a documentary today.
Give 10 examples of verb forms.
Below are 10 examples of the different forms of a verb:
Base Form (V1) | Past Simple Form (V2) | Past Participle (V3) | Present Participle (V4) | Third-Person Singular Present (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Attract | Attracted | Attracted | Attracting | Attracts |
Boil | Boiled | Boiled | Boiling | Boils |
Crush | Crushed | Crushed | Crushing | Crushes |
Enjoy | Enjoyed | Enjoyed | Enjoying | Enjoys |
Guess | Guessed | Guessed | Guessing | Guesses |
Grow | Grew | Grown | Growing | Grows |
Mourn | Mourned | Mourned | Mourning | Mourns |
Tear | Torn | Torn | Tearing | Tears |
Spit | Spat | Spat | Spitting | Spits |
Five Forms of Verb in English
There are five forms of verbs: Base Form (V1), Past Simple Form (V2), Past Participle (V3), Present Participle (V4), and Third-Person Singular Present Simple Form (V5). Let us understand each of these verb forms in detail and how to use the forms of verbs in a sentence, along with examples.
1. Base Form (V1)
The Base Form or V1 is the first form of a verb. It is also known as the Root Verb. The base form is the original or starting point of the form of verbs and remains unchanged. These root verbs are used to form different forms of verbs.
Example:
- I dance every day.
- They watch movies on weekends only.
- Let me finish my homework before 8 pm.
2. Past Simple Form (V2)
The simple past form or V2 form of the verb tells us that the action has already happened in the past. It shows that a task was finished/completed in the past. In general, the past simple form of a verb is formed by adding ‘-ed’ or ‘d’ at the end of the root verb. However, there are irregular verbs where this rule is not applicable and the V2 form is completely different (like Drink → Drank, Think → Thought).
Example:
- He lied to his teachers about the test.
- The team cheated to win the match.
- I read the news yesterday.
3. Past Participle Form (V3)
The past participle form or V3 form of the verb is used to form perfect tenses like present perfect tense, past perfect tense, or future perfect tense, and passive voice sentences.
Just like the past simple form, the past participle verb forms are also formed by adding ‘ed’ or ‘d’ at the end of the root verb. In this case, too, some irregular verbs do not follow the general ‘ed’ and ‘d’ rule and need to be remembered. The past participle verb forms always have an auxiliary verb with them.
Example:
- If only I had solved the puzzle on time, I would have won the championship.
- She has read all the novels.
- He was gone when I reached his house.
4. Present Participle Form (V4)
The present participle form, or V4 form, or the ‘-ing’ form of the verb, helps describe the ongoing actions. These forms of verbs are used in continuous tenses like present continuous tense, past continuous tense, and future continuous tense, and come with auxiliary verbs.
Example:
- Vedika is playing with her doll.
- They are going to college.
- He is decorating the Christmas Tree.
5. Third-Person Singular Present Simple Form (V5)
The third-person singular form, or V5 form of the verb, helps represent the simple present tense. These forms of verbs are used when the subject of the sentence is he, she, it, or a singular noun. To form the V5 verb form, ‘s’ or ‘es’ is added at the end of the root verb (‘ies’ in certain cases).
Example:
- Suhana dances every day after school.
- She watches thriller movies only.
- It takes time to complete a visual presentation.
Also Read:
Commonly asked questions
Here is the list of 10 commonly used regular verbs:
Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
help | helped | helped |
look | looked | looked |
wait | waited | waited |
start | started | started |
visit | visited | visited |
paint | painted | painted |
shout | shouted | shouted |
arrive | arrived | arrived |
repeat | repeated | repeated |
love | loved | loved |
What are the Root Verbs?
In English, the root verbs are the base or original form of a verb before any change. The root forms of a verb do not have any suffixes. They are used to create the other verb forms. For instance, choose, draw, drink, etc.
The root verbs are also known as the V1 form of the verb, as they are the foundation of all verb forms.
Examples:
- He must improve his English for the job.
- We eat lunch at the office cafeteria.
Root Verb Examples
Check out the table below for a list of root verbs. Also find their different forms of verbs:
| Root Verb |
Past Simple Form |
Past Participle |
Present Participle |
Third-Person Singular Present |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read |
Read |
Read |
Reading |
Reads |
| Throw |
Threw |
Thrown |
Throwing |
Throws |
| Pay |
Paid |
Paid |
Paying |
Pays |
| Forgive |
Forgave |
Forgiven |
Forgiving |
Forgives |
| Upset |
Upset |
Upset |
Upsetting |
Upsets |
| Grow |
Grew |
Grown |
Growing |
Grows |
| Ride |
Rode |
Ridden |
Riding |
Rides |
| Make |
Made |
Made |
Making |
Makes |
Regular v/s Irregular Forms of Verbs
Regular and Irregular verbs are two types of verbs that change form to show the tense of an action. Let’s understand how these two verbs are different from each other.
| Basis |
Regular Verbs |
Irregular Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning |
Verbs that follow the basic rule of adding a suffix to the root verb. |
Verbs that do not follow the basic rules. |
| Rule for Past Simple & Past Participle Form |
Add ‘ed’, ‘d’, ‘ied’ |
No specific rule. |
| Spelling Change |
No change in root spelling in the past form |
Partial, complete, or no change in root spelling in different forms |
| Example |
Explain → Explained → Explained
|
Go → Went → Gone Run → Ran → Run Do → Did → Done |
Examples:
- They spoke to the teacher about the assignment. (Irregular Verb)
- The dog jumped over the fence. (Regular Verb)
- She baked a delicious cake for my birthday. (Regular Verb)
- He came to the party with a date. (Irregular Verb)
Also Read:
List of Verb Forms
Below are the lists of the V1, V2, V3, V4, V5 verbs forms in different categories
No Change in the Verb Forms (V1, V2, V3)
Below is the list of verbs whose V1, V2, & V3 forms remain the same.
| Base Form (V1) |
Past Simple Form (V2) |
Past Participle (V3) |
Present Participle (V4) |
Third-Person Singular Present (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost |
Cost |
Cost |
Costing |
Costs |
| Put |
Put |
Put |
Putting |
Puts |
| Hit |
Hit |
Hit |
Hitting |
Hits |
| Set |
Set |
Set |
Setting |
Sets |
| Shut |
Shut |
Shut |
Shutting |
Shuts |
| Bid |
Bid |
Bid |
Bidding |
Bids |
| Quit |
Quit |
Quit |
Quitting |
Quits |
| Thrust |
Thrust |
Thrust |
Thrusting |
Thrusts |
| Cast |
Cast |
Cast |
Casting |
Casts |
| Read |
Read |
Read |
Reading |
Reads |
Regular Verbs
The table below includes regular verbs and their five forms of verbs.
| Base Form (V1) |
Past Simple Form (V2) |
Past Participle (V3) |
Present Participle (V4) |
Third-Person Singular Present (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Die |
Died |
Died |
Dying |
Dies |
| Earn |
Earned |
Earned |
Earning |
Earns |
| Face |
Faced |
Faced |
Facing |
Faces |
| Decorate |
Decorated |
Decorated |
Decorating |
Decorates |
| Clap |
Clapped |
Clapped |
Clapping |
Claps |
| Ask |
Asked |
Asked |
Asking |
Asks |
| Flee |
Fled |
Fled |
Fleeing |
Flees |
| Improve |
Improved |
Improved |
Improving |
Improves |
| Lie |
Lied |
Lied |
Lying |
Lies |
| Shred |
Shredded |
Shredded |
Shredding |
Shreds |
Irregular Verbs
Below listed are the irregular verbs with their V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5 verb forms.
| Base Form (V1) |
Past Simple Form (V2) |
Past Participle (V3) |
Present Participle (V4) |
Third-Person Singular Present (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Take |
Took |
Taken |
Taking |
Takes |
| Begin |
Began |
Begun |
Beginning |
Begins |
| Break |
Broke |
Broken |
Breaking |
Breaks |
| Come |
Came |
Come |
Coming |
Comes |
| Fly |
Flew |
Flown |
Flying |
Flies |
| Fall |
Fell |
Fallen |
Falling |
Falls |
| Sing |
Sang |
Sung |
Singing |
Sings |
| Steal |
Stole |
Stolen |
Stealing |
Steals |
| Swim |
Swam |
Swum |
Swimming |
Swims |
| Smell |
Smelt/Smelled |
Smelt/Smelled |
Smelling |
Smells |
Also Read:
| List of Synonyms | List of Common Idioms | List of One Word Substitution |
Tips to Learn English Verb Forms
Follow the simple and effective tips below to learn the forms of verbs.
1. There are different forms of verbs. Start with regular verbs. For these verbs, you have to simply add suffixes like ‘d’, ‘ed’, or ‘ied’ to form the past simple and past participle verb forms. Prepare a list of common regular verbs and understand the suffix required for different types of regular verbs.
- ‘ed’: Most of the regular verbs require ‘ed’.
- ‘d’: Regular verbs ending with the letter ‘e’, need the suffix ‘d’.
- ‘ied’: Regular verbs ending with a consonant and ‘y’ require ‘ied’. In these cases, ‘y’ is replaced with ‘ied’.
2. Now learn about the rule for the third-person singular present verb form. For these verbs, you have to add ‘s’, ‘es’, or ‘ies’ at the end of the root verb.
- ‘s’: Most verbs require ‘s’
- ‘es’: Verbs ending in ‘o’, ‘sh’, ‘ch’, ‘ss’, ‘x’, etc.
- ‘ies’: Verbs ending with ‘y’ required ‘ies’. ‘y’ is replaced with ‘ies’.
However, there are certain exceptions to the third rule. Verbs like pay, play, etc., are converted into V5 verb form by adding ‘s’ at the end, and ‘y’ also stays in its place.
3. As learnt above, irregular verbs do not follow one single rule, so it can be difficult to learn their verb forms. However, many irregular verbs follow patterns. Prepare a list of different groups of irregular verbs using the same pattern and learn them accordingly. For example:
- All forms remain the same (Hit → Hit → Hit)
- V2 and V3 are same (Bring → Brought → Brought)
- All forms are different (Sing → Sang → Sung)
4. Prepare flashcards or a chart with a verb table showing the V1, V2, V3, and V4 verb forms. Revise from the table regularly.
5. Write, speak, and practice the different forms of verbs with sentences. Try to frame sentences with a single verb in different forms.
Example (Write):
- I write short stories in my free time.
- I wrote two short stories yesterday.
- I have written 20 short stories till now.
- I am writing a short story on ‘A Trip to a Hidden Island’.
- She writes short stories on motivational topics.
English Grammar Books for Forms of Verbs
Forms of Verb Examples
Forms of Verb Exercise with Answers
Related English Grammar Topics for Preparation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Forms of Verbs
Commonly asked questions
A verb is a word that shows an action or a state of being. It tells what the subject of a sentence is doing (like run, eat, write) or what is happening (like is, seems, feels). Verbs are one of the most important parts of a sentence because they give life to the subject.
Without verbs, we wouldn't know what is happening or what someone is doing in a sentence. They help us understand time, mood, and condition too.
What is a Verb Form?
Verb forms refer to the different ways in which a verb or root verb changes its form to show the time of an action (present, past, future). The different forms of the verb help to frame a grammatically correct sentence by matching the verb with the subject and using the proper tense.
Examples:
- Tear -> Tore-> Torn
- Strike-> Struck-> Struck
- Go-> Went-> Gone
- Sit-> Sat-> Sat
How many forms of verbs are there?
There are five forms of verbs in English grammar. These are:
- Base Form/Root Verb (V1): Hear, Lead, Freeze, Eat
- Past Simple Form (V2): Heard, Led, Froze, Ate
- Past Participle Form (V3): Heard, Led, Frozen, Eaten
- Present Participle Form (V4): Hearing, Leading, Freezing, Eating
- Third-Person Singular Present Simple Form (V5): Hears, Leads, Freezes, Eats
English Verbs Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
Other Class 10th English Chapters
- English Past Tense
- English Idioms
- English Punctuation
- English Analogy
- English Interjections
- English Prefixes
- English Adjectives
- English Future Continuous Tense
- English Letter Writing
- English Suffix
- English Grammar
- English One Word Substitution
- English Mood
- English Direct and Indirect Speech
- English Figures of Speech
- English Composition
- English Para Jumbles
- English Reading Comprehension
- English Sentences
- English Auxiliary and Modal Verbs
- English Formation of Words
- English Precis Writing
- English Nouns
- English Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- English Prepositions
- English Verbs
- English Paraphrasing
- English Articles
- English Subject and Predicate
- English Pronouns
- English Tenses
- English Active and Passive Voice
- English Vocabulary
- English Subject Verb Agreement
- English Phrases
- English Synonyms
- English Etymology and Roots
- English Spelling Rules
- English Parts of Speech
- English Gerunds