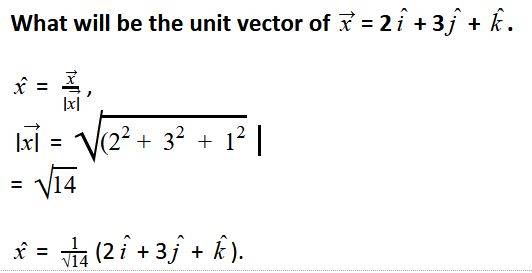In mathematics and physics, we have come across the terms velocity, forces, and displacement. These terms are described by a vector. We can describe a vector as a physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. It is denoted by an arrow.
A vector is categorised into various types based on its properties and uses. Knowing the different types of vectors will help to perform mathematical tasks and real-life problems, such as velocity, forces, and displacement. In this article, students can check the types of vectors, their application & properties. Moreover, the information available here will be useful in preparing for the exam.
Important Link:
| NCERT Class 12 notes | |
| Class 12 Maths notes |
- Define Vector Algebra
- Types of Vectors
- Operations in Vectors
- Application of Vectors
- Weightage of Topic
- Illustrative Examples on Types of Vectors
- NCERT Notes for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
Define Vector Algebra
In NCERT, a vector is defined as a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector is used to find the displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, momentum, weight, electric field intensity, etc. It is denoted by an arrow. The arrow indicates the magnitude, and the arrowhead the direction. For example: →AB.
Types of Vectors
Vectors are classified into various types based on their properties and relationships with other vectors. Different types of vectors help to perform various arithmetic calculations.
- Zero Vector: A vector that has zero (0) magnitude is called a zero vector.
- Unit Vectors: A vector is described as a unit vector if its magnitude is equal to 1. A unit vector is denoted as â = a / |a|. Examples: î, ĵ, k̂ on x, y, z axes.
- Coinitial Vectors: When two or more vectors have the same initial point then they are called coinitial vectors.
- Collinear Vectors: If two or more vectors are parallel to the same line, irrespective of their magnitude and direction they are called collinear vectors. It is also known as parallel vector.
- Equal Vector: When two vectors have the same magnitude and direction, whatever their initial position is, they are called equal vectors.
- Negative of a Vector: If two vectors have same magnitude but opposite in direction, then it is referred as negative vector.
Operations in Vectors
Vectors can perform various operations such as adding, subtracting, multiplying etc. Below are the operations of vectors.
- Addition of Vectors
- To perform addition in vector we use Triangle law of vector addition and parallelogram law of vector addition.
- Vector addition is commutative and associative.
- Subtraction of Vectors
- If you want to subtract two vectors, then add its negative.
- Multiplication of Vectors
- In vector multiplication is performed in two ways dot product and cross product.
- Dot product of two vector is scalar, and the cross product is vector.
Important Topics:
| NCERT Class 11 notes | |
| Class 11 Chemistry notes |
Application of Vectors
We know that vectors are not limited to mathematics and physics. It is also used in engineering and many real-life situations. Below are a few important applications of vectors.
- Physics
- In physics we use vectors to find force, acceleration and displacement. For example: If two or more forces are acting on a body, then what is the resultant force.
- Engineering and Mechanics
- Vectors are important in making machines, buildings and bridges because they help to identify the stresses, strain and forces acting on them.
- Navigation and GPS
- When travelling we use navigation and GPS system to determine the direction and distance. These systems use vectors for accurate data.
- Animations
- In video games the movement, 3D models and realistic animations are created using the vector.
- Electromagnetism
- In electromagnetism, vectors are used to represent the electric and magnetic field. This makes it easy to understand the flow of current and wave propagation.
Also Read: NCERT Solution for class 11 & 12
Weightage of Topic
Types of Vectors is present in class XII mathematics chapter Vector Algebra. The chapter's applications also have its importance in other subjects like physics. In class XII mathematics exams the weightage of vector algebra along with three-dimensional geometry ranges from 12 to 14 marks.
The chapter of Vector Algebra also includes topics such as:
- Operations of Vectors(Addition, Subtraction)
- A Scalar multiplication with a Vector
- 2 Vectors' Product
Illustrative Examples on Types of Vectors
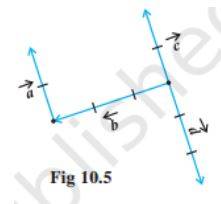
1. From the given figure, identify which vectors are Collinear, Coinitial, and Equal Vectors.
Solution.
2. If the given vectors are equal vectors then evaluate the values of a, b, and c.
Solution.
If the 2 given vectors are equal then
a = 2,
b = 2,
and c = 1.
3.
NCERT Notes for Class 12 Maths
| Chapter No. | Chapter Notes |
|---|---|
| 1 | Relations and Functions |
| 2 | Inverse Trigonometric Functions |
| 3 | Matrices |
| 4 | Determinants |
| 5 | Continuity and Differentiability |
| 6 | Application of Derivatives |
| 7 | Integrals |
| 8 | Application of Integrals |
| 9 | Differential Equations |
| 10 | Vector Algebra |
| 11 | Three-Dimensional Geometry |
| 12 | Linear Programming |
| 13 | Probability |
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
Commonly asked questions
If a vector's magnitude is zero, then what will be its direction?
A vector with zero magnitude is considered a zero vector. Since it has no magnitude, its direction is considered arbitrary. This means the zero vector has no specific direction.
What are the types of parallel vectors?
Two vectors which are parallel to each other, irrespective of direction, are called parallel vectors.
Types are given below
- Collinear vectors
- Parallel vectors
- Antiparallel vectors
Mention one real-life use of vectors?
You can use the position vector to find the real displacement of a point from a reference point.
Maths Vector Algebra Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 12th Maths Chapters
- Quantitative Aptitude Prep Tips for MBA
- Maths Integrals
- Maths Differential Equations
- Maths Vector Algebra
- Maths Matrices
- Maths Determinants
- Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Maths Differentiation
- NCERT Class 12 Maths
- Maths Continuity and Differentiability
- Maths Applications of Derivatives
- Maths Application of Integrals
- Maths Linear Programming
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test